ITI-C (Inference-Time Intervention – Contrastive) (NeurIPS 2023 Spotlight)
논문: Inference-Time Intervention: Eliciting Truthful Answers from a Language Model
1. ACTADD vs. CAA vs. ITI-C
-
ACTADD/CAA: 단순 평균 차이를 사용
-
ITI-C: 두 집합(toxic vs untoxic)을 더 정밀하게 구분하는 binary classifier를 학습
\(\rightarrow\) activation space에서 더 날카로운 분리 방향을 찾음
\(\rightarrow\) 이 분리 방향에 따라 shift vector를 정의 & inference 중 activation을 수정

2. Procedures
Step 1) 데이터 준비
- toxic sequence 집합
- non-toxic sequence 집합
Step 2) Activation 수집
- Model을 돌려서 특정 레이어의 hidden activation 벡터 모음 \(H_{toxic}, H_{untoxic}\) 확보
Step 3) Binary classifier 학습
- 이 두 집합을 구분하는 선형 classifier 학습 → hyperplane 획득
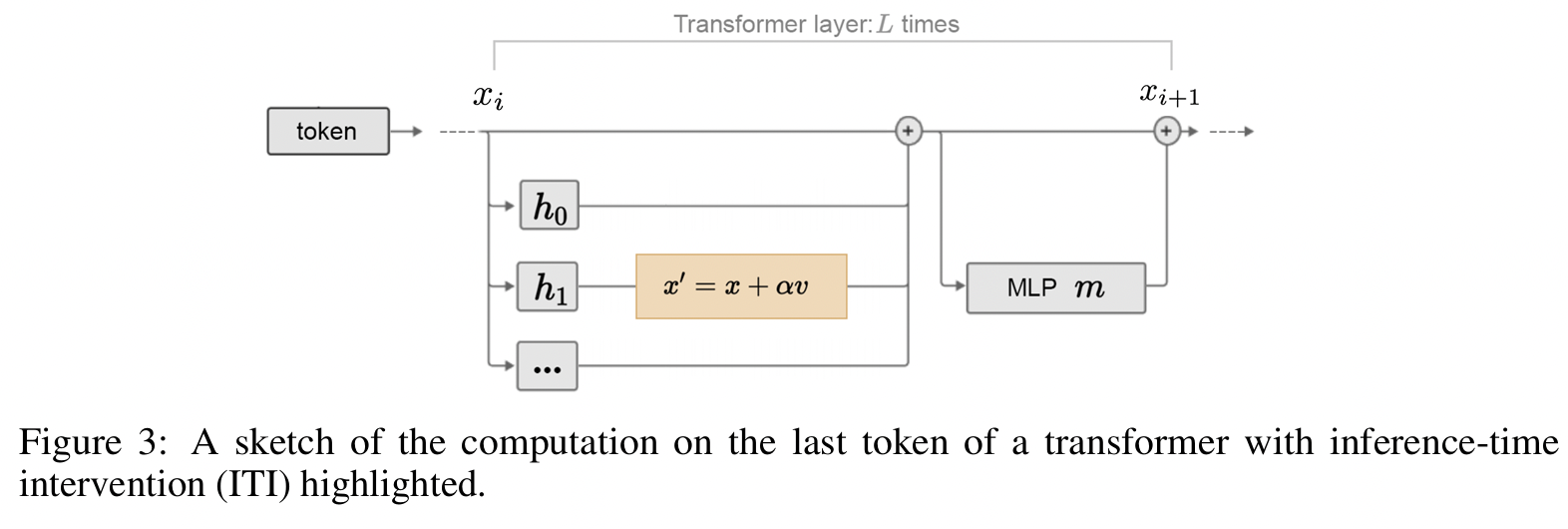
Step 4) Shift vector 정의
- hyperplane에 수직인 방향 벡터(normal vector)를 shift vector로 사용
- 즉, classifier가 toxic vs non-toxic을 구분하는 가장 핵심 축을 찾아냄
Step 5) Inference 시 intervention
- LM activation을 shift vector 방향으로 이동시켜, 원하는 쪽(untoxic)으로 steering
3. 장점
- 데이터 기반으로 학습한 hyperplane을 사용 → 보다 정확한 분리 가능
- 단일 프롬프트 차이(ACTADD)나 단순 평균(CAA)보다 더 세밀한 조정 가능
4. 한계
-
Binary classifier를 별도로 학습해야 함 (추가 학습 비용)
-
Task-specific: 학습한 classifier가 특정 속성(예: toxic vs non-toxic)에 최적화
\(\rightarrow\) 다른 속성으로 일반화 어려움
5. Details
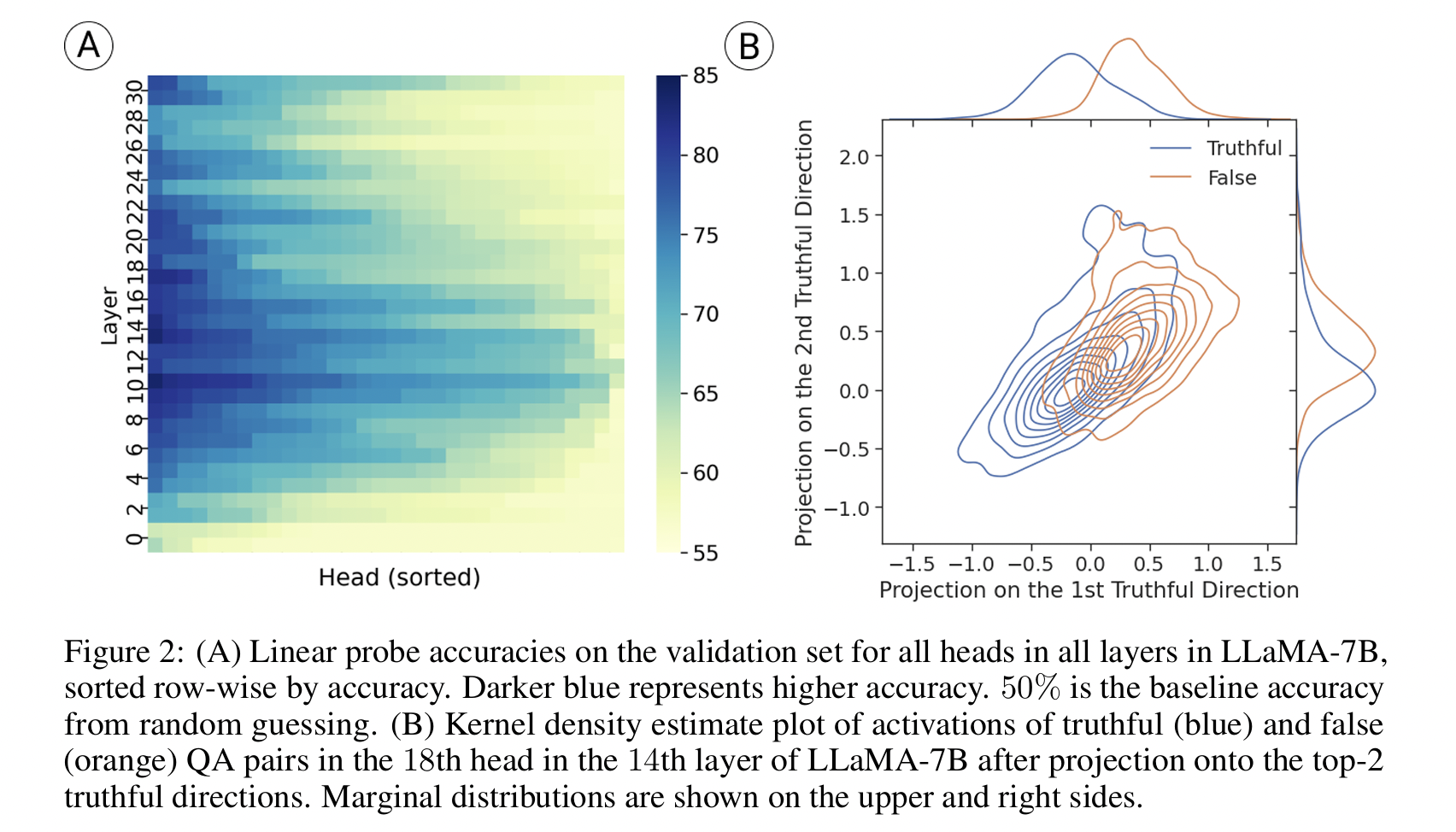
Figure 2(A) shows that the information is mostly processed in early to middle layers and that a small portion of heads stands out in each layer.