FinTSBridge: A New Evaluation Suite for Real-World Financial Prediction with Advanced Time Series Models
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2503.06928
Abstract
Problem:
- 기존 TSF 모델들이 많이 발전했음에도
- Financial asset pricing에 실제로 적용하는 데에는 여전히 큰 간극이 존재
Goal:
- 최신 TSF 모델과 Finance 예측 문제를 연결하는 체계적인 evaluation bridge를 구축
Proposal: FinTSBridge
-
Dataset: 3개의 real-world financial TS dataset
-
Models: 10개 이상의 TSF 모델
-
Metrics
-
(기존) MSE, MAE
-
(제안) msIC, msIR
- Finance 예측에서 중요한 time series correlation을 평가하기 위해
-
1. Introduction
(1) Problem Setting
-
최근 TSF 모델은 크게 발전했으나, 이를 financial asset pricing에 실제로 적용하는 데에는 여전히 큰 간극이 존재
-
Limitations of Existing Benchmarks
- 기존 TS benchmark는 stationarity, periodicity가 강한 데이터(electricity, traffic)에 편중
- (1) Dataset 한계점: 기존 financial dataset은
- Daily resolution → intraday dynamics 소실
- Limited variables → derivatives, multi-scale interaction 미반영
- (2) Metric 한계점: MSE, MAE 중심 평가는
- Point-wise accuracy만 측정
- temporal correlation 및 market trend alignment를 반영하지 못함
- 단순 last-value predictor도 MSE는 양호하나 → 실제 trading 관점에서는 무의미함
(2) Motivation
Financial TS에서는
-
(1) 예측 정확도
-
(2) time-series correlation
-
(3) economic utility
를 함께 평가하는 framework가 필요
(3) Proposed Framework: FinTSBridge
최신 TS 모델과 real-world financial prediction을 연결하는 종합 evaluation suite
Key Components
- Financial-specific preprocessing
- stationarity를 강화하면서
- 변수 간 관계(inter-relationships)는 유지
- Modeling stage
- 다양한 AI-based TS forecasting 모델 적용
- Task design
- Multi-perspective forecasting tasks 설계
- Evaluation
- 기존 metric(MSE, MAE)
- 신규 metric(msIC, msIR)
- financial metric 기반 strategy simulation
(4) Goal
단순 예측 성능을 넘어, investment decision support 관점에서 TS 모델의 실질적 활용 가능성과 robustness를 평가
2. Related Works
(1) Financial Task-Related Studies
기존 Financial TS 예측 연구
- 주로 single-step forecasting
- Next-step price prediction
- Price movement (up/down) prediction
최근 연구 흐름
- Multi-horizon / multi-step forecasting으로 전환
- sequence-to-sequence models 활용
- 미래 여러 시점의 trajectory를 한 번에 예측
- exchange time series의 장기 temporal dynamics 포착 목적
Cutting-edge TS models와 financial tasks 사이의 bridge 필요성 제기!
(2) The Predictability of Asset Prices
Quantitative hedge funds
- Historical data에서 predictive signals을 지속적으로 발굴
- Changing market environment에서도 excess return 달성
Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH)에 대한 재해석
- 일부 연구:
- 시장이 semi-strong 또는 strong-form efficiency를 항상 만족하지 않는다고 주장
- 실제 시장:
- weak-form과 semi-strong efficiency 사이에 위치하는 경우가 많음
- 경험적 근거
- Momentum effect
- 과거에 성과가 좋았던 자산이 미래에도 지속될 가능성
- Weak-form EMH에 대한 반례
- Multi-factor models
- asset pricing anomalies를 설명
- 시장 효율성이 제한적임을 간접적으로 시사
- Momentum effect
기술 발전의 영향
-
Data processing capability의 비약적 향상
-
과거에는 불가능했던
- Large-scale data
- Complex non-linear patterns
을 활용한 predictive models 등장
Summary
- Finance 시장은 완전 효율적이지 않으며
- 적절한 데이터, 모델, 평가 프레임워크 하에서는 asset price predictability가 실질적으로 존재!
3. Dataset Curation
기존 TS benchmark의 한계?
- Long-term TS forecasting 연구: Electricity, weather, traffic, exchange rate 중심의 8개 mainstream dataset에 집중
- Financial TS: Non-stationary, non-periodic 특성으로 인해 종종 제외되거나 ILI dataset으로 대체됨
그 결과: SOTA TS models는
- Controlled dataset에서는 성능이 높지만
- Real-world financial TS의 복잡성에 대한 robustness 부족
핵심 문제의식: 실제 Finance 문제를 반영하는
-
데이터 복잡성
-
비정상성
-
다양한 frequency
를 포함한 financial-specific dataset 필요!
(1) Data Sources
FinTSBridge는 3개의 Finance TS dataset을 구축
- 서로 다른 Finance sub-domain을 대표
a) GSMI
- Global stock market indices
- 20개 주요 지수
- daily frequency
- 기간: 2005–2024 (약 20년)
- 변수: price, trading volume
b) OPTION
- Chinese CSI 300ETF options
- call / put option의 risk-related variables
- derivative market 특성 반영
c) BTCF
- Bitcoin spot + perpetual futures
- hourly frequency
- spot–contract lag 분석
- long–short trading strategy 평가에 적합
Contribution
- Frequency, asset type, market structure가 다른 TS를 포괄
- 기존 benchmark 대비 현실 Finance 환경에 근접
(2) Data Preprocessing Methods
문제 배경: Finance TS는
- 변수 간 scale 차이가 큼
- 통일된 preprocessing 방식이 존재하지 않음
\(\rightarrow\) Task-specific preprocessing 필요
a) Log-return 기반 가격 변환 (GSMI, BTCF)
Notation
- Close price series 정의
- \(P^c_{0,t} = \{p^c_0, p^c_1, \dots, p^c_t\}\).
- Price change ratio
- \(R^c_i = \frac{p^c_i}{p^c_{i-1}}\).
- Log transformation
- \(\ln\left(\frac{P^c_{0,t}}{p^c_0}\right) = \{0, \ln(R^c_1), \dots, \ln(R^c_t)\}\).
의미
- Log price는 cumulative sum of log-returns
- 이전 시점 변화에만 의존 → additivity property
- Non-stationarity 완화
b) High price 변환 및 관계 유지
Notation
- High price series
- \(P^h_{0,t} = \{p^h_0, p^h_1, \dots, p^h_t\}\).
- Relative change to last close
- \(R^h_i = \frac{p^h_i}{p^c_{i-1}}\).
- Log transformation
- \(\ln\left(\frac{P^h_{0,t}}{p^c_0}\right) = \{0, \ln(R^h_1), \dots, \ln(R^h_t)\}\).
Close–high 관계
- \(\Delta(P^h, P^c) = \ln\left(\frac{P^h_{0,t}}{p^c_0}\right) - \ln\left(\frac{P^c_{0,t}}{p^c_0}\right) = \{\ln(\tfrac{R^h_i}{R^c_i})\}\).
장점
- OHLC 간 상대적 관계 보존
- 각 시점의 price structure 유지
c) Baseline anchoring
Notation
- 최종 가격 TS
- \(Z_{0,t} = \ln\left(\frac{P_{0,t}}{p^c_0}\right) + 100\).
- 목적
- Cumulative log 값의 음수 방지
- 모델 학습 안정성 향상
d) Trading volume
Notation
- Volume series
- \(V_{0,t} = \{v_0, v_1, \dots, v_t\}\).
- log transform
- \(Z^v_{0,t} = \ln(V_{0,t} + 1)\).
목적
- Zero volume로 인한 log 오류 방지
- scale 안정화
(3) Visualization of Preprocessing
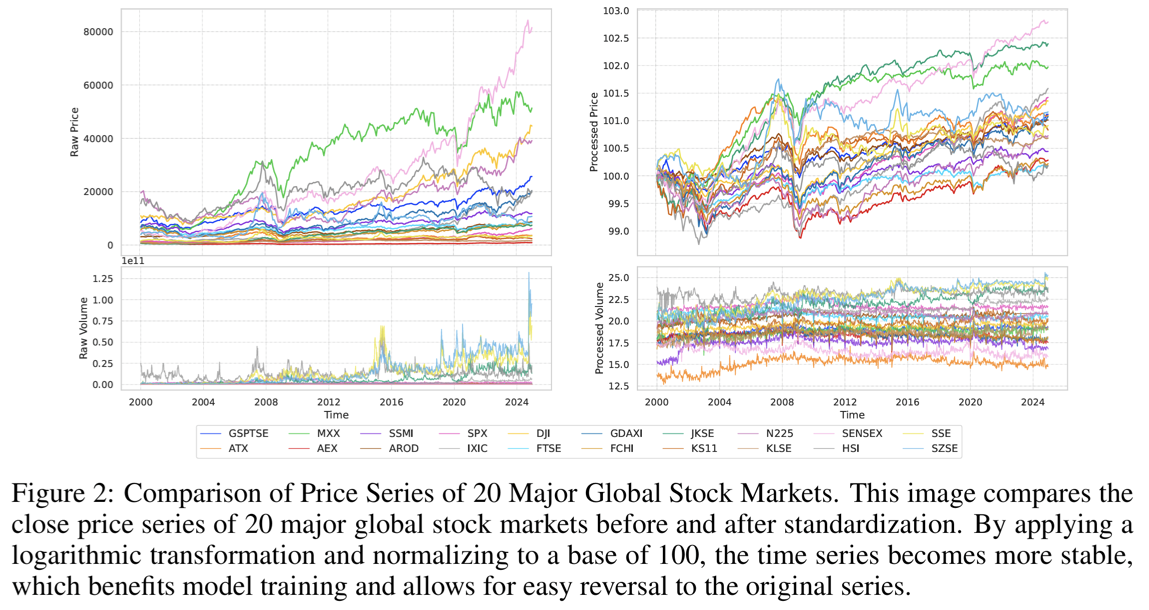
목적: 제안한 preprocessing이
-
(1) scale 정렬
-
(2) 변수 간 상대적 구조 보존
을 실제 데이터에서 어떻게 달성하는지 시각적으로 검증
**[LEFT] Preprocessing 이전**
- Closing price
- 지수별 변동 폭과 절대 크기가 크게 다름
- Cross-sectional 비교가 어려움
- Trading volume
- Temporal fluctuation이 매우 불안정
- 지수 간 volume 비교가 거의 불가능
[Right] Preprocessing 이후
- Price & volume 모두
- 동일한 magnitude range로 정렬
- Price series는 공통 초기 baseline에 anchor
효과
- Cumulative change 비교 가능
- 지수 간, 변수 간 일관된 비교 가능성 확보
4. New Evaluation Metrics
(1) 문제의식
기존 TS forecasting 평가
- 주로 MSE, MAE 같은 error-based metric에 의존
Finance TS
- 단순한 Naive model (last value prediction)도 낮은 MSE 달성 가능
- 실제 시장 trend, correlation을 거의 포착하지 못함
결론
- Finance TS에서는 prediction error + correlation metric이 함께 필요
(2) 기존 Correlation metric의 한계
Information Coefficient (IC), Information Ratio (IR)
- single-step
- univariate
\(\rightarrow\) Multi-step, multivariate forecasting 성능을 평가하기에는 부적합
(3) Proposal
두 개의 metric 제안
- msIC (multi-step IC)
- msIR (multi-step IR)
목적: multi-step, multivariate TS 예측에서, 아래의 두 가지를 동시에 평가
- Temporal correlation
- Stability
a) msIC (Multi-step Information Coefficient)
Notation
- Input: \(X \in \mathbb{R}^{B \times L \times C}\)
- \(B\): batch size
- \(L\): input length
- \(C\): number of variables
- Prediction: \(\hat{Y} = f(X; \theta), \quad Y, \hat{Y} \in \mathbb{R}^{B \times F \times C}\)
- \(F\): forecast horizon
msIC 정의
- (각 sample \(i\), 변수 \(j\)에 대해) Prediction horizon F에 대한 rank correlation
- \(\rho_{Y_{i,j}, \hat{Y}_{i,j}} = \frac{\text{Cov}(Y_{i,j}, \hat{Y}_{i,j})} {\sigma_{Y_{i,j}} \, \sigma_{\hat{Y}_{i,j}}} \tag{14}\).
- msIC 계산
- \(\text{msIC} = \frac{1}{B \times C} \sum_{i=1}^{B} \sum_{j=1}^{C} \rho_{Y_{i,j}, \hat{Y}_{i,j}} \tag{15}\).
의미
- Multi-step TS 전반에서 true TS와 predicted TS 간 temporal correlation을 직접 측정
- (Error-based metric에서는 못잡아내는) trend consistency를 평가
b) msIR (Multi-step Information Ratio)
문제
- msIC는 평균 correlation만 측정
- sample 간 correlation stability는 반영하지 못함
msIR 정의
-
Sample-level msIC
- \(\text{msIC}_i = \frac{1}{C} \sum_{j=1}^{C} \rho_{Y_{i,j}, \hat{Y}_{i,j}} \tag{16}\).
-
msIC sequence
- \(\{\text{msIC}_1, \dots, \text{msIC}_B\}\).
- chronological order 유지
-
msIR 정의
-
\(\text{msIR} = \frac{\text{msIC}} {\sqrt{ \frac{1}{B} \sum_{i=1}^{B} (\text{msIC}_i - \text{msIC})^2 }} \tag{18}\).
- numerator
- 평균적인 effective correlation
- denominator
- correlation의 temporal variability (noise)
-
의미
- 높은 msIR
- 높은 correlation
- sample 간 안정적 성능
- 낮은 msIR
- 일부 구간만 잘 맞고
- 전반적 신뢰도 낮음
(4) Summary
- msIC는 “얼마나 잘 맞추는가”를 correlation 관점에서,
- msIR는 “그 성능이 얼마나 안정적인가”를 함께 평가하는 Finance TS 특화 metric
def msIC(Y, Y_hat):
B, F, C = Y.shape
rhos = []
for i in range(B):
for j in range(C):
y = Y[i, :, j]
y_hat = Y_hat[i, :, j]
rho = np.corrcoef(y, y_hat)[0, 1]
rhos.append(rho)
return np.mean(rhos)
def msIR(Y, Y_hat):
B, F, C = Y.shape
msic_per_sample = []
for i in range(B):
rhos = []
for j in range(C):
y = Y[i, :, j]
y_hat = Y_hat[i, :, j]
rhos.append(np.corrcoef(y, y_hat)[0, 1])
msic_per_sample.append(np.mean(rhos))
msic_per_sample = np.array(msic_per_sample)
return msic_per_sample.mean() / msic_per_sample.std()
5. Experiments
(1) M2M Forecasting
Setup
- Financial TS의 non-stationarity와 low signal-to-noise ratio를 고려한 실험 설계
- 3개 dataset × 16개 TS model 평가
- Forecasting horizon
- \(H \in \{5, 21, 63, 126\}\).
- Evaluation metrics
- Error-based: MSE, MAE
- Correlation-based: msIC, msIR
Results
- 모든 dataset·metric에서 절대적으로 우수한 단일 모델은 존재하지 않음
- [1] PSformer, TimeMixer, TiDE, PatchTST
- 대부분 task에서 안정적인 성능
- PSformer가 12개 중 8개 setting에서 최고 성능
- [2] Transformer, FEDformer
- Error metric에서는 열세
- 일부 dataset에서 correlation metric(msIC/msIR) 기준 경쟁력 존재
- [3] Naive model
- Predictive correlation은 거의 없음
- 그럼에도 MSE/MAE는 매우 낮아, 일부 SOTA 모델보다 우수
- Financial TS의 non-stationary 특성에서 흔히 관찰되는 현상
(2) M2U Forecasting
Setup
- 다변량 입력을 활용한 single target forecasting
- 단순 예측 성능 평가뿐 아니라
- Timing trading
- Long-short trading
- 등 실제 Finance application 기반 investment strategy 성능 평가 포함
Results
- Error metrics (MSE, MAE)
- Naive model이 대부분 경우에서 가장 낮은 loss
- PSformer, PatchTST, DLinear도 안정적인 성능
- GSMI, BTCF에서는 Naive가 최저 error
- Price TS의 예측 난이도와 직결
Correlation metrics (msIC, msIR)
- PSformer, Stationary, DLinear가 상대적으로 우수
-
PSformer는 12개 지표 중 9개에서 1–2위
- Strategy evaluation
- Figure 7: GSMI 시장 타이밍 성능 시각화
- Table 2: 전략 수익률 및 통계 지표 비교
- 단순 예측 성능을 넘어 financial usability 관점에서 모델 차이를 명확히 보여줌
(3) M2P Forecasting
Setup
- 전체 변수 중 일부 변수만 예측하는 현실적 scenario
- GSMI dataset에서
- 20개 글로벌 index의 closing price만 target으로 설정
- 예측 결과를 활용한 portfolio selection strategy
- 동시에 보유하는 index 개수 변화에 따른 backtest 수행
Results
- Error metrics
- Naive, PatchTST가 상대적으로 우수
- Correlation metrics
- PSformer, Informer가 더 강한 성능
- Portfolio backtest
- 어떤 모델도 모든 holding size에서 일관된 최고 수익률은 아님
- 대부분 모델이
- 20개 index 평균 수익률보다 높은 cumulative return 달성
- 보유 index 수가 줄어들수록 이 경향이 더 뚜렷
(4) Summary
-
Financial TS에서는 error metric만으로는 모델을 평가할 수 없음
-
Correlation-based metric(msIC, msIR)과 strategy-level evaluation이 필수
-
PSformer는 전반적으로 가장 일관된 강자
-
Naive model의 강한 error 성능은
→ Finance TS 평가의 함정을 명확히 보여주는 사례
6. Conclusion
-
Advanced TSF models & Practical financial applications 간의 간극을 연결
-
Specialized financial datasets를 구축
- global indices, derivatives, cryptocurrency markets를 포괄
-
New metric 제안
- msIC와 msIR
- Multi-step forecasting에서의 temporal correlation을 정량화함
