From News to Forecast: Integrating Event Analysis in LLM-Based Time Series Forecasting with Reflection
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2409.17515
Abstract
Core Idea
- What? Text + TS reasoning 기반 forecasting
- How? LLM + Generative Agents를 활용
- Details: Language를 매개로 social events를 TS 변화와 align
Method
- LLM-based agents가 news를 반복적으로 필터링하여 irrelevant news 제거
- human-like reasoning으로 예측 결과를 평가하고 selection logic를 지속적으로 개선
- unexpected events, social behavior shifts 같은 복잡한 사건 처리 가능
Model Integration
- 선택된 news events + TS data를 결합
- Pre-trained LLM을 fine-tuning하여 digit sequence prediction 수행
1. Introduction
(1) Background
Motivation
- 기존 TSF은 distribution shift, sudden disruptions, external events에 취약
- Social events와 TS fluctuation 간의 연결을 체계적으로 다루지 못함
Role of News
- unexpected incidents, **policy changes, **public sentiment shifts를 반영
- Quantitative TS가 포착하지 못하는 non-linear, non-numeric influences 제공
- Real-time context + Qualitative signals로 예측 안정성과 정확도 향상
(2) LLM-based Forecasting Formulation
- Textual Prompt
- News + supplementary information을 textual prompts로 TS에 통합
- Next Token Prediction (NTP)
- TSF을 next-token prediction 문제로 변환
- Pre-trained LLM의 inductive reasoning과 multi-modal distribution modeling 활용
- Few-shot TS prediction 가능
(3) LLM Agents for News Filtering
- Dynamic news selection이 핵심 과제
- (단순 keyword 기반이 아닌) human-like reasoning 필요
- LLM agents가 few-shot learning으로 상황별 뉴스 중요도 판단
- 결과: Relevant news + TS를 결합한 context-aware dataset 구성
(4) Iterative Self-Reflection
- LLM agents가 forecast error ↔ news relevance를 비교하며 selection logic 개선
- CoT prompting으로 누락된 핵심 이벤트 식별
- External factors가 예측에 미치는 영향 구조적으로 분석
(5) Contributions
- Unstructured news + numerical TS 통합 forecasting framework 제안
- LLM agents 기반 news reasoning 및 filtering 도입
- Multidomain dataset 구축
2. Related Works
(1) TSF
-
외부 contextual / external factors는 여전히 충분히 반영 X
-
Text 활용 시도는 존재하나
- Keyword count, dummy variable 중심
- Sentiment, word frequency 기반 feature engineering 필요
- Long-text dependency와 deep contextual understanding 한계
-
LLM은 자동 feature extraction과 context-aware text understanding에 강점
$\rightarrow$ But, LLM의 text 이해 능력을 TSF에 완전히 활용한 연구는 부족
(2) LLM for TSF
- GPT, LLaMA는 general knowledge와 reasoning 능력을 학습
- LLM 기반 TS 접근
- TEMPO: GPT 기반 temporal representation
- TimeLLM: reprogramming + Prompt-as-Prefix
- FPT: frozen LLM 활용
- Lag-LLaMA: decoder-only probabilistic forecasting
- next-token prediction 관점의 TS modeling
- 한계점?
- 기존 연구는 주로 numerical regression mapping에 집중
- External textual input & Language reasoning은 활용되지 않음
(3) Reasoning with Language Models
- Chain-of-Thought (CoT): 단계적 reasoning 강화
- Tree-of-Thoughts (ToT): 탐색·검증 기반 multi-round reasoning
- LLM agents: feedback 반영, memory 활용, self-reflection
- LATM: tool 생성과 reasoning/action interleaving
- Multi-agent debate로 reasoning 품질 향상
- 기존 reasoning 연구는 TSF과의 결합은 미흡
3. Methodology
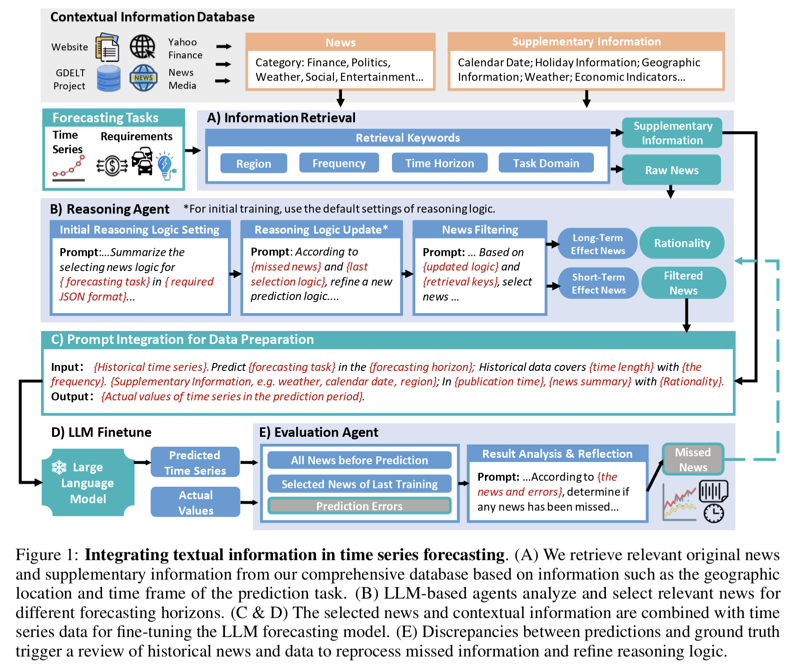
Overall Framework
- 목표: News insights + TS 통합 forecasting
- 핵심 과제
- a) Unstructured news 처리
- b) News–TS 간 relevance filtering
- c) Reasoning 오류에 대한 iterative refinement
- 구성 요소
- LLM-based forecasting module
- Reasoning agent
- for news filtering & inference
- Evaluation agent
- for self-reflection and refinement
(1) Rethinking TS Forecasting Problem and Elements.
a) TS as Conditional Generation
TS forecasting을 conditional sequence generation으로 재정의
- LLM은 TS를 digit token sequence로 처리
- Autoregressive modeling: $P(x_{t+1} \mid x_{0:t})$
Pre-trained LLM의 few-shot TS capability 활용
Textual prompt를 통한 TS conditioning 가능성 제시
b) News as Contextual Condition
News event E는 TS 변화의 causal context 제공
Event-conditioned forecasting: $P(x_t \mid x_{0:t}, E)$
- news를 text tokens로 표현하여 LLM 입력으로 통합
- multi-event context를 동시에 conditioning 가능
- prompt engineering으로 TS + news 결합
c) Supplementary Information
- weather, climate, finance 등 additional context
- supplementary info도 conditional variable로 취급
- 수치 정보를 natural language text로 변환하여 입력
d) Fine-Tuning LLMs for TS Forecasting
(Pre-trained LLM의) few-shot 예측의 한계?
- Long digit sequence 제어 어려움
- News–TS 관계 학습 부족
Supervised instruction tuning으로 conditional forecasting 학습
-
Input: TS + news + supplementary info
-
Loss: (Pre-training과 동일한) next-token prediction
-
LoRA 적용
(2) Analytical Agent for Aggregation and Reasoning of Contextual News Information
a) Motivation
(1) TS–news matching의 한계점?
-
noise가 많은 internet news 이슈!!
$\rightarrow$ Irrelevant news는성능을 저하시킴
(2) Agent의 필요성
-
Relevance + causality 판단이 필요함
-
이를 위해서는, societal knowledge + logical reasoning 필요
$\rightarrow$ But, 단일 LLM generation으로는 불충분
→ 해결책: Agent-based multi-step reasoning
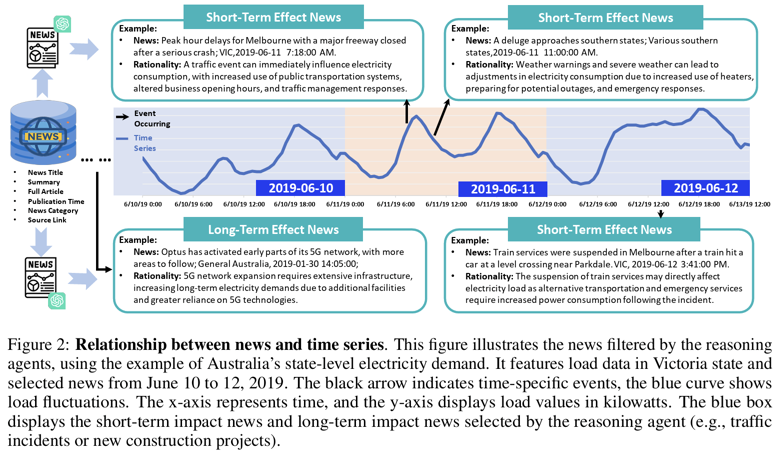
b) TS–News Pre-Pairing
- 기준: time frequency, forecasting horizon, geography
- 지역·기간 정렬을 통한 candidate news 1차 필터링
- crawler 기반으로 scalable한 rough selection 수행
c) Reasoning Agent for News Selection
- LLM-based reasoning agent 활용
- 역할 정의된 prompt로
- Screening
- Categorization
- Interpretation 수행
- Few-shot + Chain-of-Thought (CoT) 적용
- Multi-step reasoning으로 complex relevance 판단
d) Three-Phase Prompting Strategy
- a) Influencer Modeling
- TS 영향 요인 식별
- positive / negative, short-term / long-term 분류
- economic, policy, seasonal, technological factors 고려
- b) News Filtering & Categorization
- 자동 생성 or 사전 정의된 reasoning logic 사용
- relevance 및 impact type 분류 + rationale 생성
- c) Structured Output
- JSON 형식
- summary, region, time, rationale 포함
e) Automated vs Guided Reasoning
- Open-ended prompt로 agent가 자체 reasoning logic 생성 가능
- domain knowledge를 prompt에 주입하여 guided reasoning 가능
- 자동 logic과 user-provided logic 모두 지원
f) Evaluation Agent for Reasoning Update
- Reasoning agent 단독 사용의 한계 인식
- Forecasting 결과 기반 평가 수행
- 단순 metric이 아닌 human-like logical analysis
- prediction error 패턴을 통해 missing or overlooked news 식별
- news filtering logic를 feedback loop로 업데이트
g) Evaluation Prompt Phases
-
Task Understanding
- Forecasting task, horizon, background 입력
- Evaluation steps 생성
-
Error Analysis
- Loss(y_pred, y_gt_
- Selected + historical news 분석
-
Logic Refinement
- Error–event 관계 기반 logic 업데이트
- Validation 전체를 종합하여 final reasoning strategy 도출
