Rank consistent ordinal regression for neural networks with application to age estimation (2020)
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Proposed Method
- Preliminaries
- Ordinal Regression with Consistent Rank Logits Model
0. Abstract
명목형 class label에 relative ordering이 있는 경우
- ex) 학점 A>B>C>D>E or 상>중>하
\(\rightarrow\) 기존의 loss function으로는 잡기 어렵다!
대표적인 방법 :
- binary한 문제로 바꿔서 푼다!
- ex) 상/중/하 분류 = 상(1/0) + 중(1/0) + 하(1/0) , 총 3개의 binary classifier
\(\rightarrow\) 문제점 : INCONSISTENCIES ( 뒤에서 설명 )
이를 극복하기 위한 consistent한 방법인 CORAL (COnsistent RAnk Logits) framework를 제안한다
1. Introduction
Ordinal Regression ( = Ordinal Classification )
- target : \(\boldsymbol{y}=\left\{r_{1}<\ldots <r_{K}\right\}\)
Inconsistency Problem
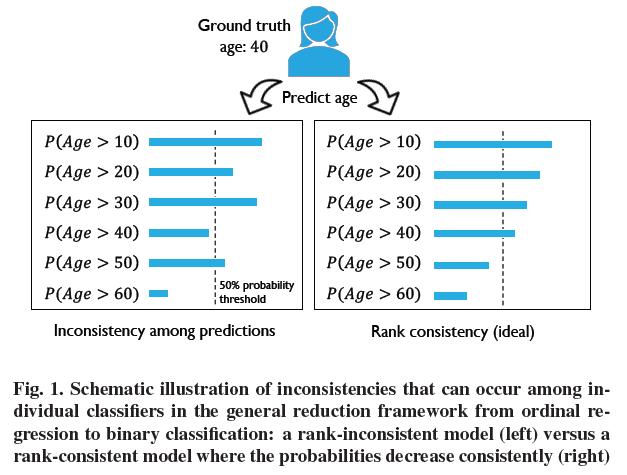
2. Proposed Method
(1) Preliminaries
rank
-
\(y_{i} \in \mathcal{Y}=\left\{r_{1}, r_{2}, \ldots r_{K}\right\}\).
where \(r_{K}>r_{K-1}>\ldots>r_{1}\).
cost matrix
-
\(C\) : \(K \times K\) cost matrix
-
요소 \(C_{y, r_{k}}\) : cost of predicting an example \((\mathbf{x}, y)\) as rank \(r_{k}\)
-
\(C_{y, y}=0\).
\(C_{y, r_{k}}>0\) for \(y \neq r_{k} .\)
-
-
바람직한 \(C\) matrix : \(V\)-shaped
-
\(C_{y, r_{k-1}} \geq C_{y, r_{k}}\)if \(r_{k} \leq y\)
\(C_{y, r_{k}} \leq C_{y, r_{k+1}}\) if \(r_{k} \geq y\)
-
(직관적 이해) “상을 하로 예측해서 틀리는 것”이 “중을 하로 예측해서 틀리는 것” 보다 BAD
-
일반적으로 사용하는 값 : \(C_{y, r_{k}}=\mid y-r_{k}\mid\)
-
(2) Ordinal Regression with Consistent Rank Logits Model
a) Label Extension & Rank Prediction
우선, rank \(y_{i}\) 를 binary label로 바꾸기!
-
\(y_{i}\) \(\rightarrow\) \(y_{i}^{(1)}, \ldots, y_{i}^{(K-1)}\),
where \(y_{i}^{(k)} \in\{0,1\}\) indicates whether \(y_{i}\) exceeds rank \(r_{k}\)
-
총 \(K-1\) 개의 binary classifier
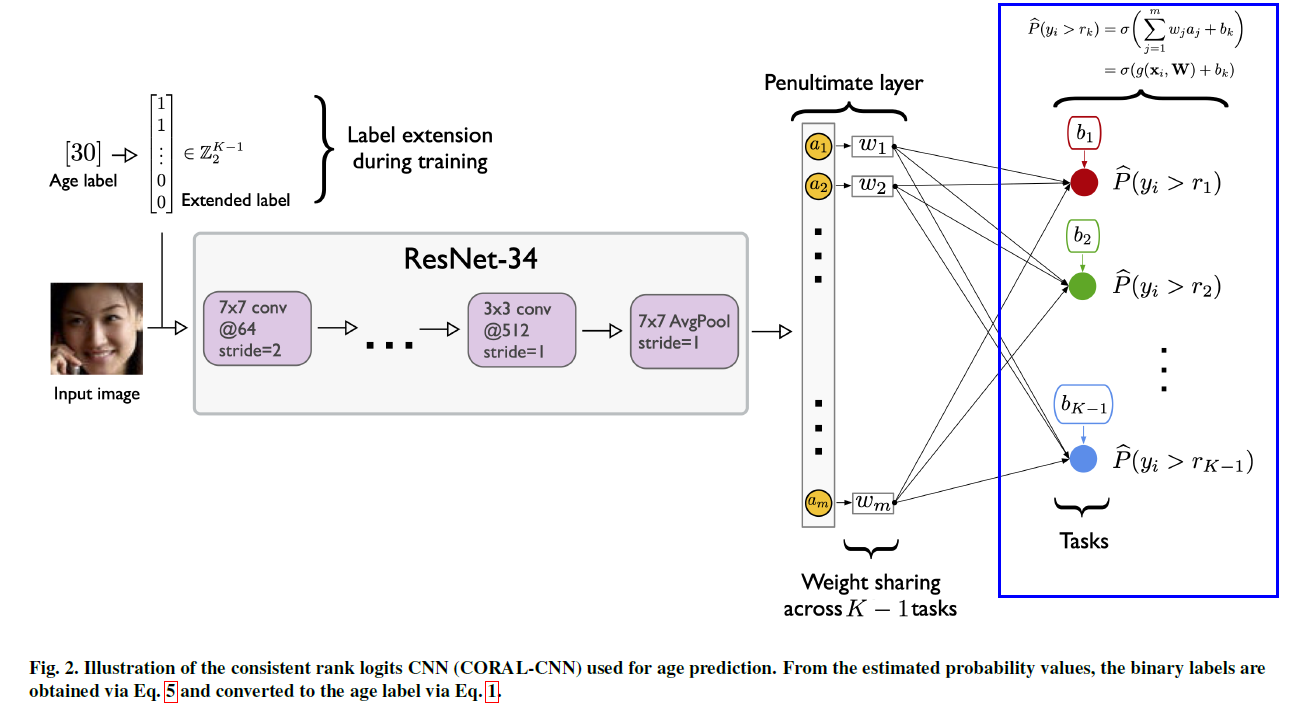
예측값 : \(h\left(\mathbf{x}_{i}\right)=r_{q}\)
-
\(q\) : rank index = \(1+\sum_{k=1}^{K-1} f_{k}\left(\mathbf{x}_{i}\right)\)
-
\(f_{k}\left(\mathbf{x}_{i}\right) \in\{0,1\}\) : prediction of the \(k\)-th binary classifier
-
\(f_{k}\) 가 rank-monotonic하게끔 만들고 싶다! ( for consistency )
( 즉, \(f_{1}\left(\mathbf{x}_{i}\right) \geq f_{2}\left(\mathbf{x}_{i}\right) \geq \ldots \geq f_{K-1}\left(\mathbf{x}_{i}\right)\) )
-
그러기 위해, \(K-1\)개의 binary tasks들은 weight는 공유하고, bias는 서로 다르게!
( Th1 증명을 통해 이렇게 하면 rank-monotonic됨을 증명함 )
-
b) Loss Function
\(W\) : (bias를 제외한) weight parameter
최종 Output값 (0~1) : \(\sigma(z)=1 /(1+\exp (-z))\)
- \(z=\left\{g\left(\mathbf{x}_{i}, \mathbf{W}\right)+b_{k}\right\}_{k=1}^{K-1}\).
predicted empirical probability for task \(k\) :
- \(\widehat{P}\left(y_{i}^{(k)}=1\right)=\sigma\left(g\left(\mathbf{x}_{i}, \mathbf{W}\right)+b_{k}\right)\).
Rank Prediction :
- \(f_{k}\left(\mathbf{x}_{i}\right)=\mathbb{1}\left\{\widehat{P}\left(y_{i}^{(k)}=1\right)>0.5\right\}\).
Loss Function :
\(\begin{aligned} L(\mathbf{W}, \mathbf{b})= &-\sum_{i=1}^{N} \sum_{k=1}^{K-1} \lambda^{(k)}\left[\log \left(\sigma\left(g\left(\mathbf{x}_{i}, \mathbf{W}\right)+b_{k}\right)\right) y_{i}^{(k)}\right.\\ &\left.+\log \left(1-\sigma\left(g\left(\mathbf{x}_{i}, \mathbf{W}\right)+b_{k}\right)\right)\left(1-y_{i}^{(k)}\right)\right] \end{aligned}\).
- weighted cross-entropy of \(K-1\) binary classifiers
