Mitigating Embedding and Class Assignment Mismatch in Unsupervised Image Classification
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Model
- Stage 1 : Unsupervsied Deep Embedding
- Stage 2 : Unsupervised Class Assignment with Refining Pretraining Embeddings
0. Abstract
Unsupervised Image Classification
- latest approach : end-to-end
- unified losses from (1) embedding & (2) class assignment
- have different goals … thus jointly optimizing may lead to suboptimal solutions
Solution : propose a novel two-stage algorithm
- (1) embedding module for pretraining
- (2) refining module for embedding & class assignment
1. Introduction
Unsupervised Image Classification
- determine the membership of each data point, as one of the predefined class labels
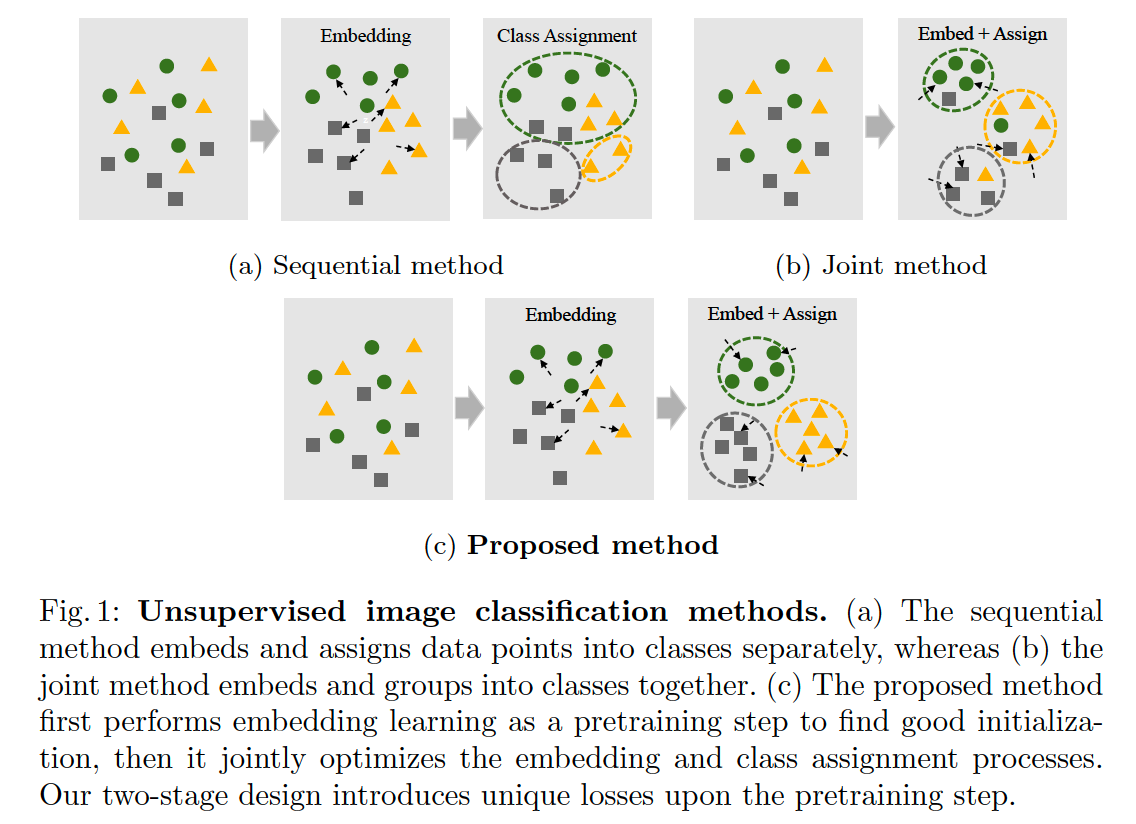
- 2 methods are used..
- (1) sequential method
- (2) joint method
This paper : two-stage approach
- stage 1) embedding learning
- gather similar data points
- stage 2) refine embedding & assign class
- minimize 2 kinds of loss
- (1) class assignment loss
- (2) embedding loss
- minimize 2 kinds of loss
2. Model
Notation
- # of underlying classes : \(n_c\)
- set of \(n\) images : \(\mathcal{I}=\left\{\mathbf{x}_1, \mathbf{x}_2, \ldots, \mathbf{x}_n\right\}\)
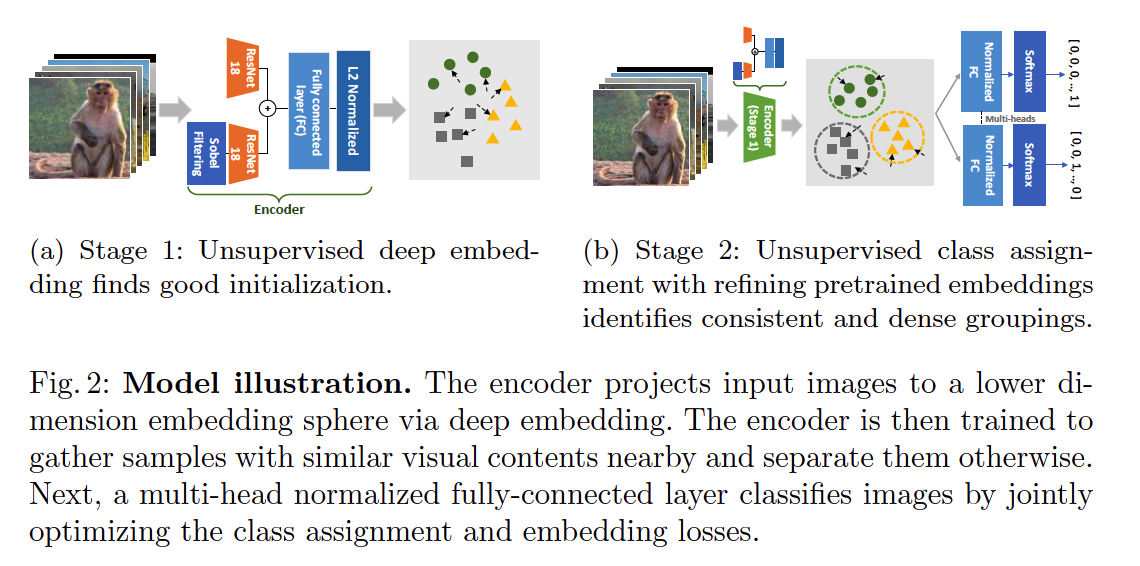
(1) Stage 1 : Unsupervised Deep Embedding
-
[GOAL] extract visually essential features
-
adopt Super-AND to initialize encoder
Super-AND
employs…
- (1) data augmentation
- (2) entropy-based loss
total of 3 losses
- (1) AND-loss ( \(L_{a n d}\) )
- (2) UE-loss ( \(L_{u e}\) ) ….. unification entropy loss
- (3) AUG-loss ( \(L_{a u g}\) ) ….. augmentation loss
Details
-
considers every data occurence as individual class
-
groups the data points into small clusters
( by discovering the nearest neighbors )
a) AND-loss
-
considers each neighborhood pair & remaining data as a single class to separate
-
\(L_{\text {and }}=-\sum_{i \in \mathcal{N}} \log \left(\sum_{j \in \tilde{\mathcal{N}}\left(\mathbf{x}_i\right) \cup\{i\}} \mathbf{p}_i^j\right)-\sum_{i \in \mathcal{N}^c} \log \mathbf{p}_i^i\).
-
\(\mathcal{N}\) : selected part of the neighborhood pair sets
- \(\mathcal{N}^c\) : complement of \(\mathcal{N}\)
- \(\tilde{\mathcal{N}}\left(\mathbf{x}_i\right)\) : neighbor of \(i\)-th image
- \(\mathbf{p}_i^j\) : probability of \(i\)-th image being identified as \(j\)-th class
-
b) UE-loss
- intensifies the concentration effect
- minimizing UE-loss = makes nearby data occurrence attract each other
- \(L_{u e}=-\sum_i \sum_{j \neq i} \tilde{\mathbf{p}}_i^j \log \tilde{\mathbf{p}}_i^j\).
Jointly optimizing a) & b)
\(\rightarrow\) enforce overall neighborhoods to be separated, while keeping similar neighbors close.
c) AUG-loss
-
defined to learn invariant image features
-
Regards augmented images as positive pairs
\(\rightarrow\) Reduce the discrepancey between original & augmented
-
\(L_{a u g}=-\sum_i \sum_{j \neq i} \log \left(1-\overline{\mathbf{p}}_i^j\right)-\sum_i \log \overline{\mathbf{p}}_i^i\).
Total Loss :
\(L_{\text {stage } 1}=L_{\text {and }}+w(t) \times L_{\text {ue }}+L_{\text {aug }}\).
- \(w(t)\) : initialized from 0 and increased gradually
(2) Stage 2 : Unsupervised Class Assignment with Refining Pretraining Embeddings
ideal class assignment : requires …
- (1) not only ideal embedding
- (2) but also dense grouping
\(\rightarrow\) use 2 kinds of loss in Stage 2
- (1) class assignment loss
- (2) consistency preserving loss
Mutual Information-based Class Assignment
Mutual Information (MI) :
\(\begin{aligned} I(x, y) &=D_{K L}(p(x, y) \mid \mid p(x) p(y)) \\ &=\sum_{x \in \mathcal{X}} \sum_{y \in \mathcal{Y}} p(x, y) \log \frac{p(x, y)}{p(x) p(y)} \\ &=H(x)-H(x \mid y) \end{aligned}\).
IIC (Invariant Information Clustering)
-
maximize MI between samples & augmented samples
-
trains the classifier with invariant features from DA
-
procedure
-
[input] image set \(\mathbf{x}\) & augmented image set \(g(\mathbf{x})\)
-
mapping : \(f_\theta\)
-
classifies images & generate probability vector
( \(y=f_\theta(\mathbf{x}), \hat{y}=f_\theta(g(\mathbf{x}))\) )
-
-
find optimal \(f_\theta\), that maximizes…
- \(\max _\theta I(y, \hat{y})=\max _\theta(H(y)-H(y \mid \hat{y}))\).
-
-
by maximizing MI, can prevent clustering degeneracy
Details of MI : \(I(x, y) =H(x)-H(x \mid y)\)
- (1) maximize \(H(y)\)
- when every data is EVENLY assigned to every cluster
- (2) minimize \(H(y \mid \hat{y})\)
- when consistent cluster
Loss Function :
-
joint pdf of \(y\) and \(\hat{y}\) : matrix \(\mathbf{P}\)
( \(\mathbf{P}=\frac{1}{n} \sum_{i \in \mathcal{B}} f_\theta\left(x_i\right) \cdot f_\theta\left(g\left(x_i\right)\right)^T\) )
-
\(L_{a s s i g n}=-\sum_c \sum_{c^{\prime}} \mathbf{P}_{c c^{\prime}} \cdot \log \frac{\mathbf{P}_{c c^{\prime}}}{\mathbf{P}_{c^{\prime}} \cdot \mathbf{P}_c}\).
Consistency Preserving on Embedding
add an extra loss term, \(L_{cp}\)
Notation
- image : \(\mathbf{x}_i\)
- embedding of \(\mathbf{x}_i\) : \(\mathbf{v}_i\)
- projected to normalized sphere
- \(\hat{\mathbf{p}}_i^j(i \neq j)\) : probability of given instance \(i\) classified as \(j\)-th instance
- \(\hat{\mathbf{p}}_i^i\) : probability of being classified as its own \(i\)-th augmented instance
Consistency preserving loss \(L_{cp}\) : minimizes any mis-classified cases over the batches
- \(\begin{array}{r} \hat{\mathbf{p}}_i^j=\frac{\exp \left(\mathbf{v}_j^{\top} \mathbf{v}_i / \tau\right)}{\sum_{k=1}^n \exp \left(\mathbf{v}_k^{\top} \mathbf{v}_i / \tau\right)}, \quad \hat{\mathbf{p}}_i^i=\frac{\exp \left(\mathbf{v}_i^{\top} \hat{\mathbf{v}}_i / \tau\right)}{\sum_{k=1}^n \exp \left(\mathbf{v}_k^{\top} \hat{\mathbf{v}}_i / \tau\right)} \\ L_{c p}=-\sum_i \sum_{j \neq i} \log \left(1-\hat{\mathbf{p}}_i^j\right)-\sum_i \log \hat{\mathbf{p}}_i^i \end{array}\).
Total Unsupervised Classification Loss :
- \(L_{\text {stage } 2}=L_{\text {assign }}+\lambda \cdot L_{c p}\).
Normalized FC classifier
Norm-FC classification heads :
- used for the second stage classifier
Predicted value :
- \(y_i^j=\frac{\exp \left(\frac{\mathbf{w}_j}{ \mid \mid \mathbf{w}_j \mid \mid } \cdot \mathbf{v}_i / \tau_c\right)}{\sum_k \exp \left(\frac{\mathbf{w}_k}{ \mid \mid \mathbf{w}_k \mid \mid } \cdot \mathbf{v}_i / \tau_c\right)}\).
