3. Convex Functions
3-1. Basic Properties & Examples
a) Convex Function
\(f(\theta x+(1-\theta) y) \leq \theta f(x)+(1-\theta) f(y), \text { with } 0 \leq \theta \leq 1, \text { for all } x, y \in \text { dom } f\).
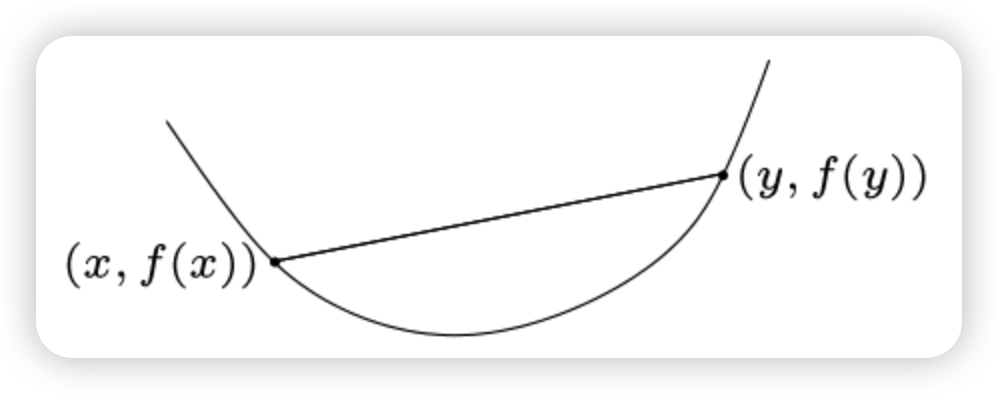
b) Stricty Convex
위 식에서 “등호가 제거”되는 경우
c) Strongly Convex
\(f-\frac{m}{2} \mid \mid x \mid \mid _{2}^{2} \text {, with } m>0\) 가 convex일 경우, \(f\) 는 strongly convex
strongly convex \(\rightarrow\) strictly convex \(\rightarrow\) convex
d) Concave Function
\(-f\) 가 convex function이면, \(f\) 는 CONCAVE function
[ 추가 ]
- affine 함수 ( \(f(x) = a^T x + b\) )는 convex 이면서 concave
e) EXAMPLES of Convex Functions
- Univariate Function
- Exponential Function : \(e^{ax}\)
- Power Function : \(x^a\) in \(\mathbb{R}_{+}\) , where \(a \geq 1\) or \(a \neq 0\)
- Affine Function : \(a^Tx +b\)
- Quadratic Function :
- \(f(x) = \frac{1}{2}x^tPx + q^T x +r\).
- \(\nabla f(x)=P x+q\).
- \(\nabla^{2} f(x)=P\).
- \(P\)가 posidive semi-definite일 경우, \(f\)는 convex
- Least Square Loss :
- \(f(x) = \mid \mid Ax-b \mid\mid_2 ^2\).
- \(A^TA\)는 항상 positive semi-definite이므로
- Norm
- Max Function
- max of convex \(\rightarrow\) also convex
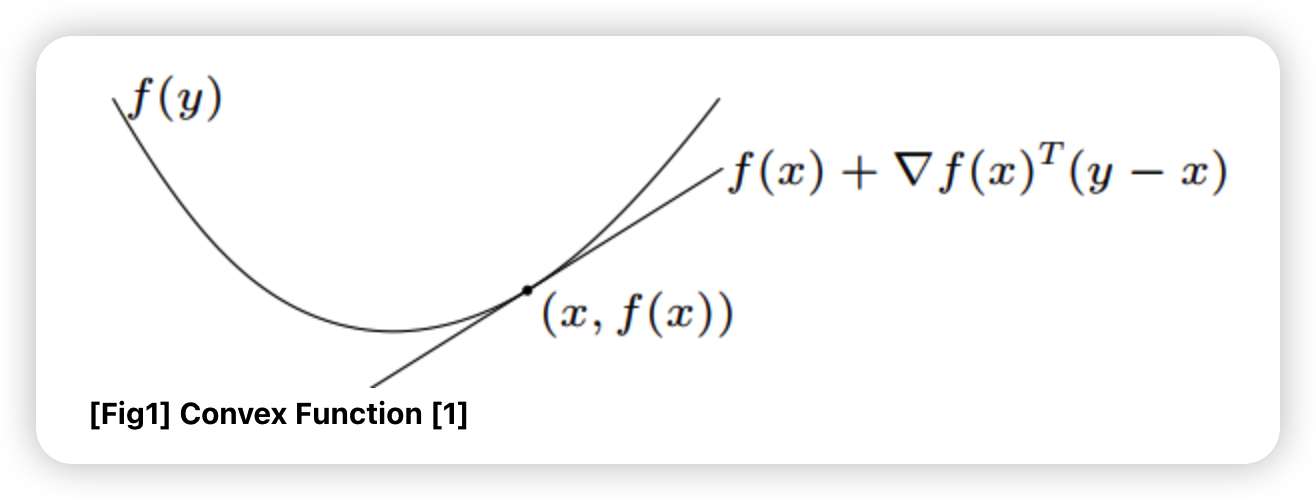
f) FIRST-order characterization
\(\text { f is convex } \Longleftrightarrow \text { dom } f \text { is convex, and } f(y) \geq f(x)+\nabla f(x)^{T}(y-x) \text { for all } x, y \in \text { dom } f\).
- 위 식의 우측 항 : 1차 Taylor Expansion
g) SECOND-order characterization
convex
- \(f\) is convex \(\Longleftrightarrow \nabla^{2} f(x) \succeq 0\) for all \(x \in \operatorname{dom} f, \operatorname{dom} f\) : convex
strictly convex
- if \(\nabla^{2} f(x) \succ 0\) for all \(x \in \operatorname{dom} f\), then \(f\) is strictly convex
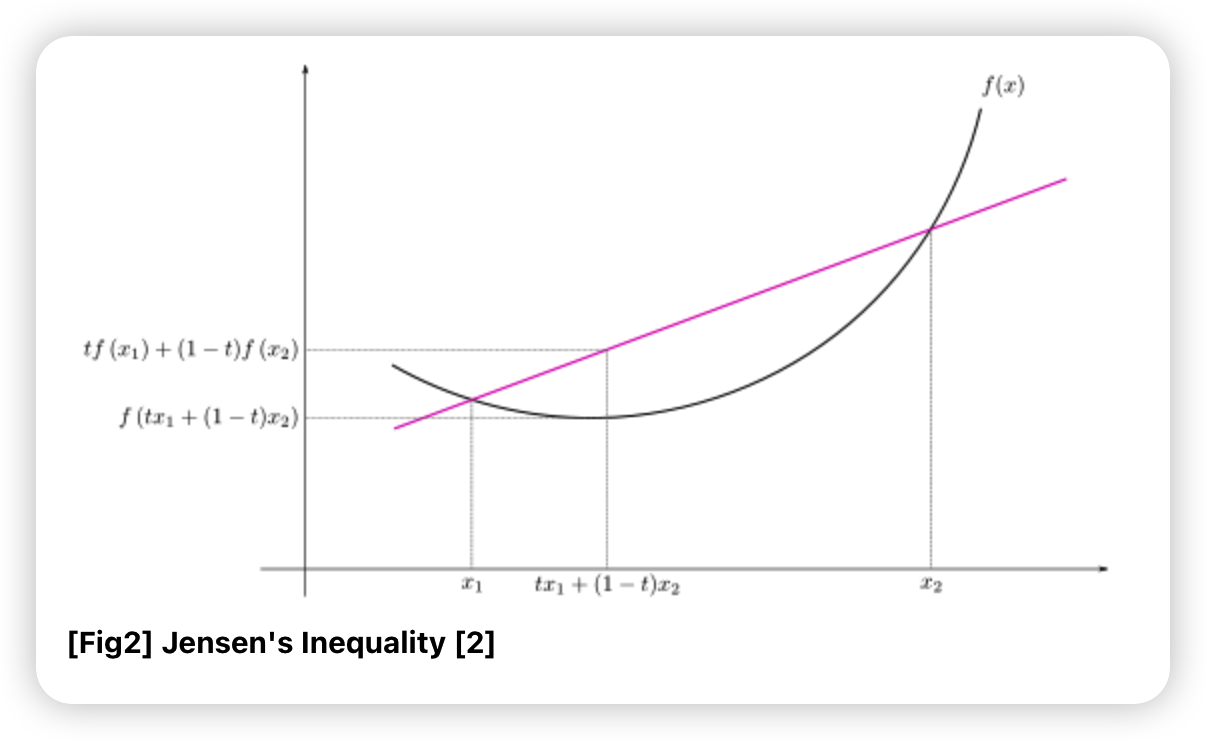
h) Jensen’s Inequality
\(f\)가 convex일 경우….
\(f\left(t x_{1}+(1-t) x_{2}\right) \leq t f\left(x_{1}\right)+(1-t) f\left(x_{2}\right), \text { for } 0 \leq t \leq 1\).
3-2. Operations that preserve convexity
- Nonnegative linear combination
- Composition (Affine/General/Vector)
- Pointwise maximum and supremum
- Minimization function
- Perspective function
a) Nonnegative linear combination
\(f_i\)가 convex면..다음도 convex다
- (1) \(\alpha f_i\) ( where \(\alpha \geq 0\) )
- (2) \(f_1 + f_2\)
- (3)\(\alpha_1 f_1 + \cdots \alpha_n f_n\) ( where \(\alpha_i \geq 0\) )
b) Composition (Affine/General/Vector)
(1) Affine Composition
- \(f_i\)가 convex면, \(f(Ax + b)\)도 convex
(2) General Composition
-
\(f(x) = h(g(x))\) 라고 하면,
- \(g\) : convex, \(h\):convex, \(h\)는 non-decreasing
- \(g\) : concave, \(h\) : convex, \(h\)는 non-increasing
일 경우, \(f\)는 convex
-
[proof] \(f^{\prime \prime}(x)=h^{\prime \prime}(g(x)) g^{\prime}(x)^{2}+h^{\prime}(g(x)) g^{\prime \prime}(x)\) 사용해서
(3) Vector Copmosition
- (setting) \(g : R^n \rightarrow R^k\), \(h : R^k \rightarrow R\)
- \(f(x) = h(g(x)) = h(g_1(x), … ,g_k(x))\).
- \(g\)가 convex, \(h\)가 convex & \(h\)가 각 인수에 대해 non-decerasing일 경우, convex
- \(g\)가 convex, \(h\)가 concave & \(h\)가 각 인수에 대해 non-increasing일 경우, concave
c) Pointwise maximum and supremum
(1) Pointwise Maximum
- \(f_{1}, f_{2} \text { are convex functions } \Rightarrow f(x)=\max \left\{f_{1}(x), f_{2}(x)\right\}, \operatorname{dom} f=\operatorname{dom} f_{1} \cap \text { dom } f_{2} \text { is convex }\).
(2) Pointwise Supremum
- \(f(x,y)\)가 \(y \in A\) 에 대하여 \(x\)에 볼록하다면, \(g(x) = \text{sup}_{y\in A} f(x,y)\) 는 convex 이다.
d) Minimization function
\(f\)가 \((x,y)\)에서 convex이면, \(g(x) = \text{inf}_{y \in C} f(x,y)\) 도 convex!
3-3. Conjugate Function
- pass
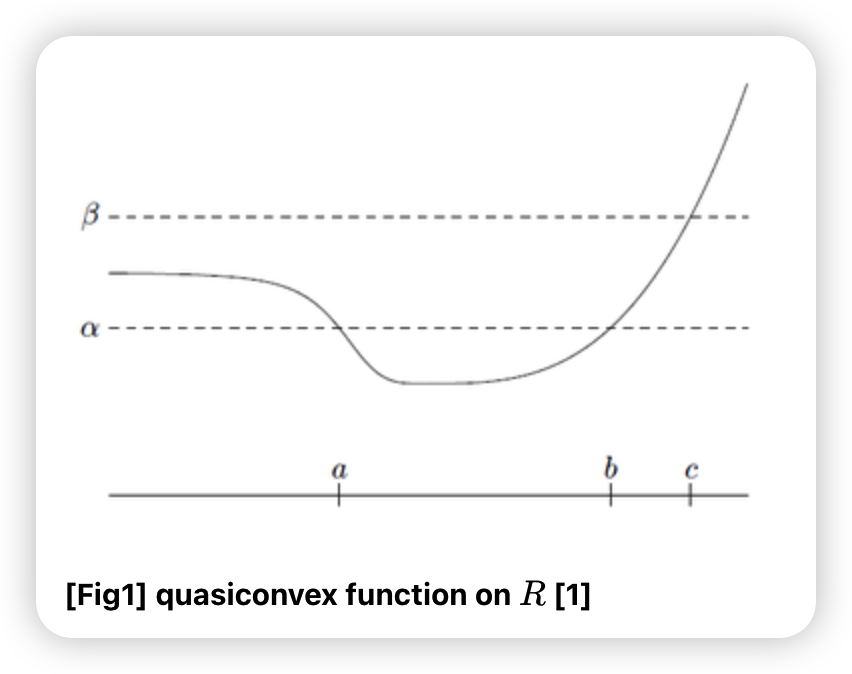
3-4. Quasiconvex Function
Quasiconvex ( = unimodal )
- \(f: R^{n} \rightarrow R \text { is quasiconvex if dom } f \text { and } S_{\alpha}=\{x \in \operatorname{dom} f \mid f(x) \leq \alpha\} \text { for } \alpha \in R \text { are convex. }\).
Quasiconcave
- \(f\)가 quasiconvex이면, \(-f\)는 quasiconcave
- \(f: R^{n} \rightarrow R \text { is quasiconcave if dom } f \text { and } S_{\alpha}=\{x \in \operatorname{dom} f \mid f(x) \geq \alpha\} \text { for } \alpha \in R\).
3-5. Log-concave & Log-convex Function
Log Concave
- (1) 모든 \(x \in \operatorname{dom} f\) 에 대해서 \(f(x)>0\) 이고,
- (2) \(\log f\) 가 concave라면
- \(f: R^{n} \rightarrow R\) 는 LOG CONCAVE하다
Alternative
- (1) \(f\) 는 log concave하다
- (2) \(f(\theta x+(1-\theta) y) \geq f(x)^{\theta} f(y)^{1-\theta}\) for \(0 \leq \theta \leq 1 .\)
Log Convex
- (1) 모든 \(x \in \operatorname{dom} f\) 에 대해서 \(f(x)>0\) 이고,
- (2) \(\log f\) 가 convex라면
- \(f: R^{n} \rightarrow R\) 는 LOG CONVEX하다
Alternative
- (1) \(f\) 는 log concave하다
- (2) \(\frac{1}{f}\) 는 log convex하다
Quasi convex/convcave
log함수는 “단조” 증가함수이기 때문에,
- log-concvex는 quasi convex하고,
- log-concave는 quasi concave하다
Examples
Log Concave
- [Affine Function]
- \(f(x)=a^{T} x+b\) on \(\left\{x \mid a^{T} x+b>0\right\}\)
- [Powers]
- \(f(x)=x^{a}\) 는 \(R_{++}\)에서, \(a \geq 0\) 일 때
- [Exponentials]
- \(f(x)=e^{a x}\).
- [CDF of Normal distn]
- \(\Phi(x)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi}} \int_{-\infty}^{x} e^{-u^{2} / 2} d u\).
Log Convex
- [Gamma function]
- \(\Gamma(x)=\int_{0}^{\infty} u^{x-1} e^{-u} d u\) , where \(x \geq 1\)
- [Determinant]
- \(\operatorname{det} X\) , in \(S_{++}^{n}\)
- [Exponentials]
- \(f(x)=e^{a x}\).
