Co\(^2\)L: Contrastive Continual Learning (ICCV 2021)
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2106.14413
Cha, Hyuntak, Jaeho Lee, and Jinwoo Shin. "Co2l: Contrastive continual learning." Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International conference on computer vision. 2021.
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Methodology
- Asymmetric Supervised Contrastive Loss
- Instance-wise Relation Distillation (IRD)
- Experiments
- Experimental Setups
- Results
Abstract
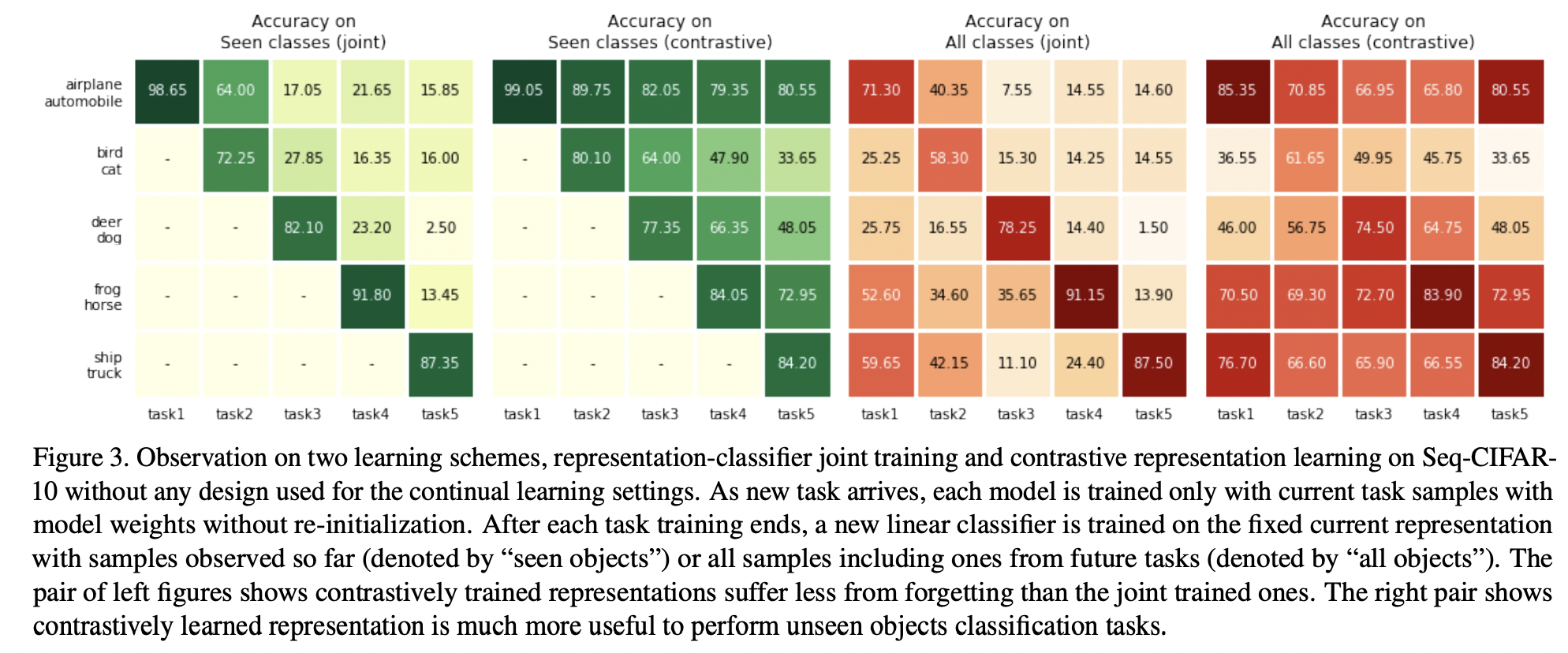
기존의 SSL 연구들의 finding
= Contrastive Learning (CL)이 cross-entropy (CE) 기반 방법보다 더 나은 transfer 성능을 보인다!
- CL: task-agnostic supervision
- CE: task-specific supervision
Findings: 이러한 특성이 continual learning 환경에서도 유사하게 나타남!
( 즉, CL으로 학습된 표현은 cross-entropy objective로 학습된 표현보다 catastrophic forgetting에 더 강인 )
Proposal: Co\(^2\)L
- Rehearsal 기반 continual learning 알고리즘
- Components
- CL objective
- Self-supervised distillation
1. Introduction
기존 방법론
- Rehearsal-based: 과거 sample의 일부를 저장하고 현재 작업 sample과 함께 rehersal
- Regularization-based: 현재 model이 과거 model과 충분히 가깝도록 강제
- Expansion-based: 각 작업에 대해 네트워크 할당
Main Contributions
- Assymetric한 Supervised contrastive loss 제안
- Instance-wise self-distillation을 사용
2. Methodology
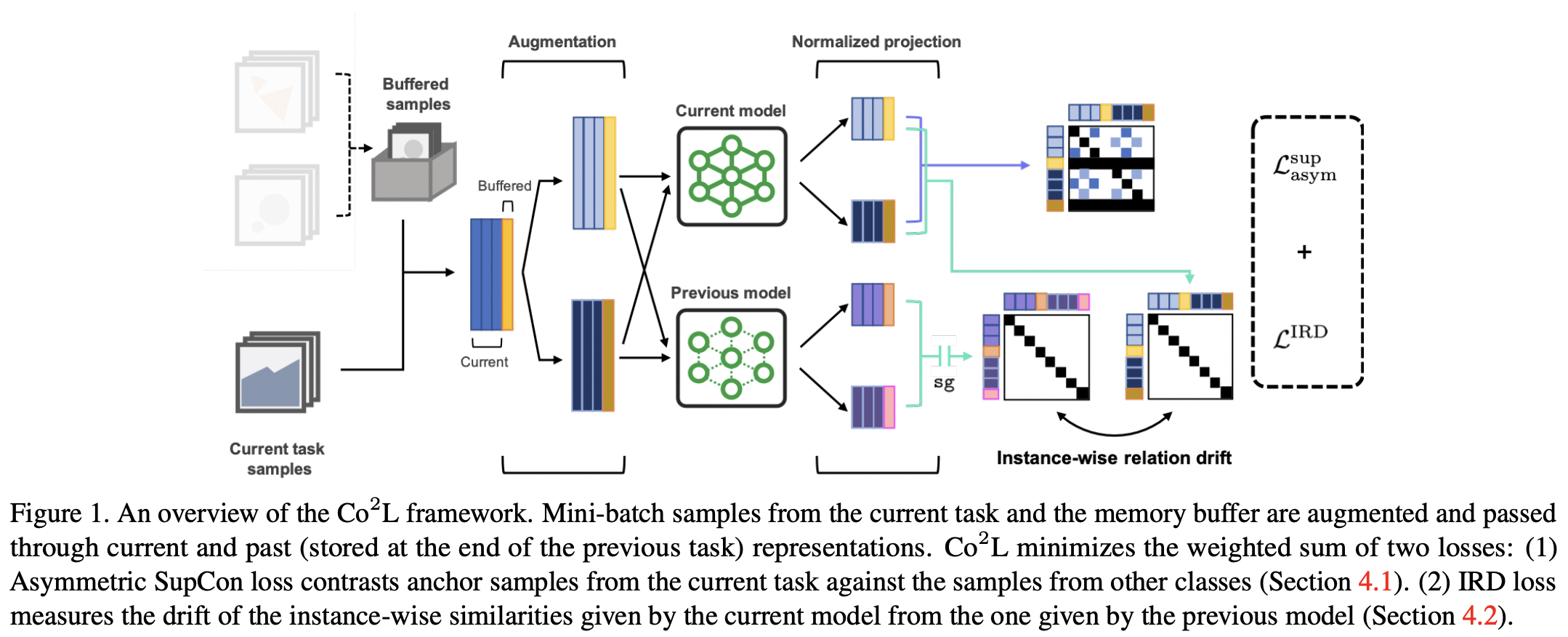
두 가지 Main conmponents
- Asymmetric Supervised Contrastive Loss
- 현재 작업의 sample을 anchor로 사용
- 다른 클래스의 sample을 negative로
- Instance-wise Relation Distillation (IRD) Loss
- 현재 model과 이전 model 간의 instance-wise 유사성의 변화를 측정
- 학습된 representation의 drift를 최소화
Loss function
\(\mathcal{L} = \mathcal{L}^\text{sup}_\text{asym} + \lambda \cdot \mathcal{L}^{\text{IRD}}\).
- \(\mathcal{L}^\text{sup}_\text{asym}\): Assymetric supervised contrastive loss
- \(\mathcal{L}^{\text{IRD}}\): Instance-wise relation distillation loss
(1) Asymmetric Supervised Contrastive Loss
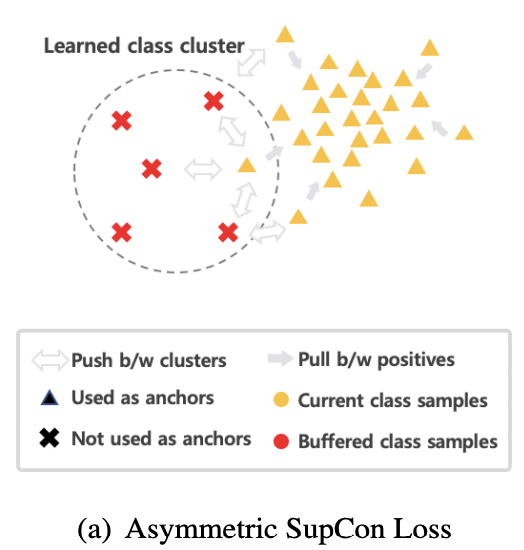
Setting
- 현재 task의 sample을 anchor로 사용
- 같은 클래스의 다른 sample과의 유사성을 높임
- 다른 클래스의 sample과의 유사성을 낮춤
- Assymetric: anchor로는 현재 task의 sample만을 사용
- ( i.e., 과거 작업의 sample은 negative로만 사용 )
Example
- 전체 class 수: 15개
- 과거 task들:
- Task 1: class 1~5
- Task 2: class 6~10
- 현재 task (Task 3): class 11~15
- 현재 anchor의 class: 13
| 용어 | 정의 |
|---|---|
| Anchor | 기준이 되는 sample (여기서는 class 13 sample) |
| Positive | 같은 클래스의 다른 sample들 (class 13 내) |
| Negative | 다른 클래스의 sample들 (class 112, 1415) |
(2) Instance-wise Relation Distillation (IRD)
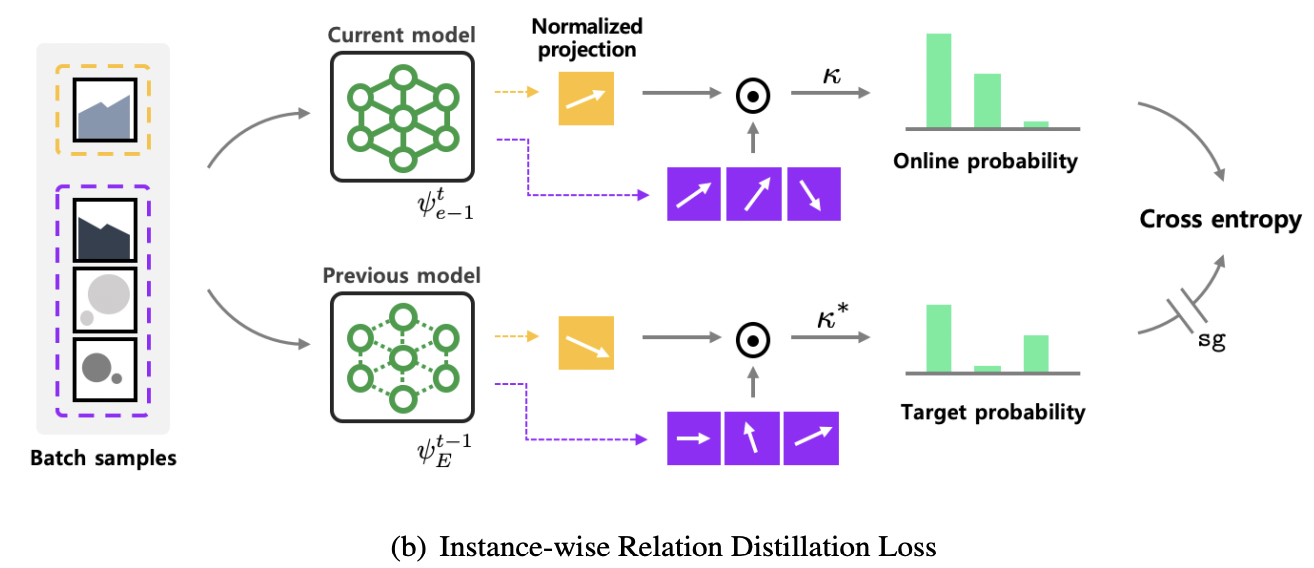
- 목적: 이전 model & 현재 model 간의 instance-wise 유사성 구조를 보존
- 방법:
- 이전 model의 encoder & projection head를 저장하고 fix
- 현재 model과 이전 model에서 각각의 sample에 대한 similarity 계산
- 두 similarity 벡터 간의 차이를 최소화하는 loss function
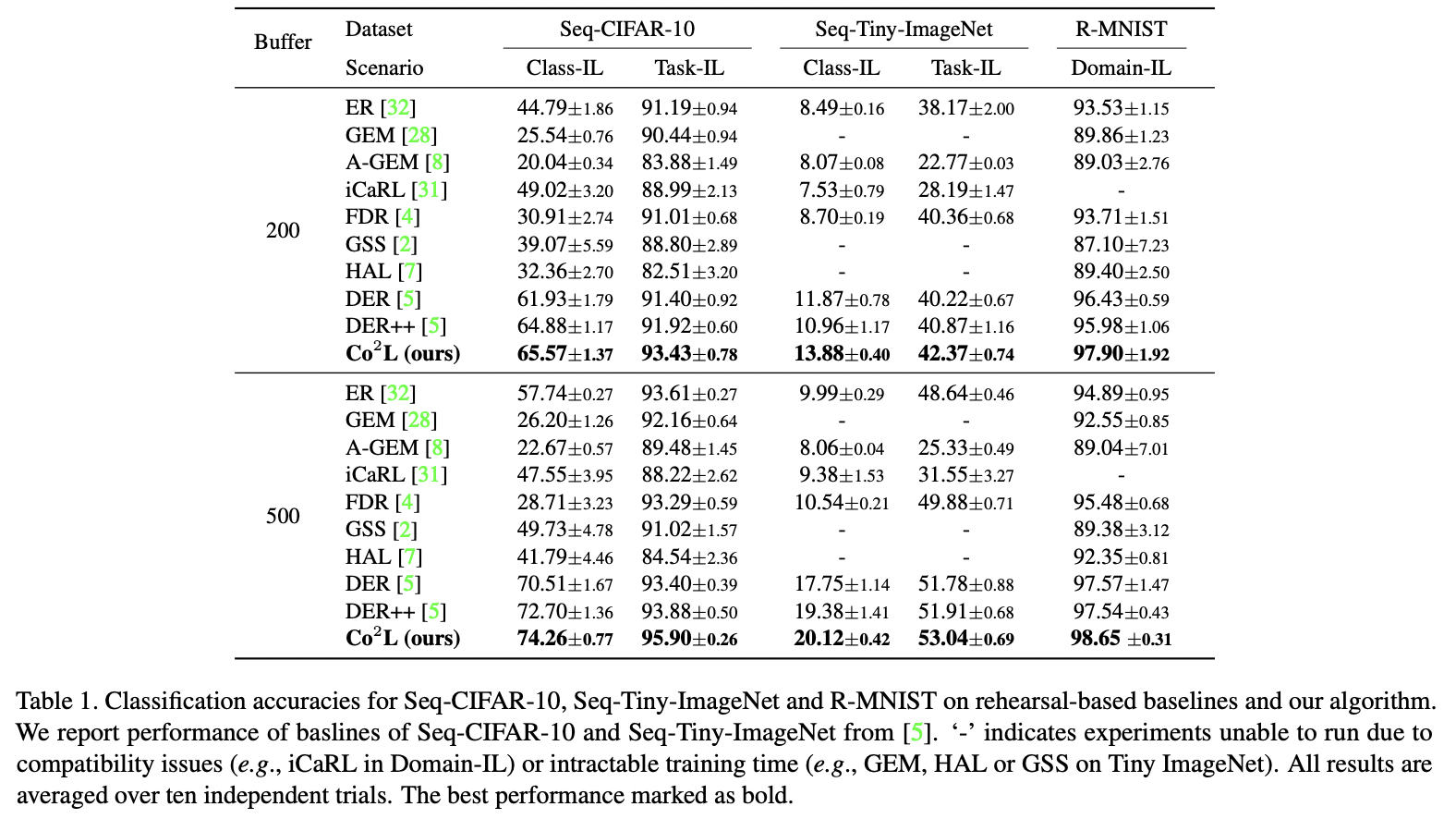
3. Experiments
(1) Experimental Setups
세 가지 continual learning 시나리오 (Task-IL, Class-IL, Domain-IL)
| 시나리오 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| Task-IL (Task Incremental Learning) | 모델이 “현재 task ID”를 알고 있음. 각 task는 독립적인 classifier를 가짐. |
| Class-IL (Class Incremental Learning) | task ID는 알 수 없고, 누적된 모든 클래스 중에서 하나를 예측해야 함. |
| Domain-IL (Domain Incremental Learning) | 클래스는 동일하지만 입력 분포(domain)가 바뀌며 task가 나뉨. |
a) Seq-CIFAR-10
CIFAR-10을 순차적(Sequential) task로 분할한 버전
- 원본: CIFAR-10 (10개 클래스, 32×32 컬러 이미지)
- 분할 방식: 5개 task로 분할
- 각 task는 2개의 클래스를 포함
- 예:
- Task 1: airplane, automobile
- Task 2: bird, cat
- … (총 5 task × 2 classes = 10 classes)
- 사용 시나리오: Task-IL, Class-IL
- 클래스 순서는 고정됨 (모든 run에서 동일)
b) Seq-TinyImageNet
TinyImageNet을 class 분할하여 만든 sequential task 구성
- 원본: Tiny-ImageNet (200개 클래스, 64×64 컬러 이미지)
- 분할 방식: 10개 task, 각 task는 20개 클래스
- 200 classes ÷ 20 = 10 task
- 사용 시나리오: Task-IL, Class-IL
- 클래스 순서 또한 고정됨
c) R-MNIST (Rotated MNIST)
입력 도메인 변화에 따른 continual task
- 원본: MNIST (손글씨 숫자 0~9, 흑백 28×28)
- 변형: 이미지를 회전(rotation)하여 각기 다른 domain 생성
- 구성:
- 총 20개 task
- 각 task는 MNIST 이미지를 서로 다른 각도로 회전 ([0, π) 범위 내 랜덤)
- 사용 시나리오: Domain-IL
- 중요 포인트:
- 같은 숫자 class라 하더라도 다른 도메인(task)이면 contrastive loss에서 다른 class로 간주
Summary
| Dataset | Task 수 | 클래스 분할 | 사용 시나리오 | 특이사항 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seq-CIFAR-10 | 5 | 2 classes/task | Task-IL, Class-IL | CIFAR-10 분할 |
| Seq-TinyImageNet | 10 | 20 classes/task | Task-IL, Class-IL | TinyImageNet 분할 |
| R-MNIST | 20 | 동일 class, 다른 도메인 | Domain-IL | 각도 회전, 같은 숫자도 다른 class로 간주 |
(2) Results