Revisiting Feature Prediction for Learning Visual Representations from Video
Bardes, Adrien, et al. "Revisiting feature prediction for learning visual representations from video." arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.08471 (2024).
참고:
- https://aipapersacademy.com/v-jepa/
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.08471
Contents
- Recap
- Video Visual Representations
- JEPA
- I-JEPA
- V-JEPA
1. Recap
(1) Video Visual Representations
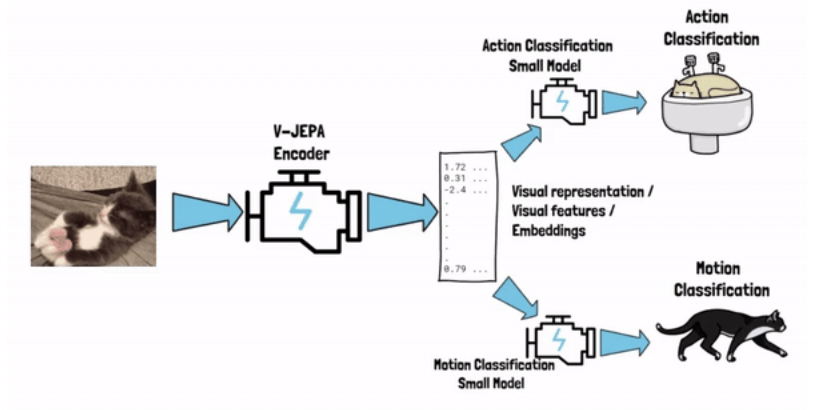
- How? Obtained via SSL (pretraining tasks)
- Captures semantic information about the input video
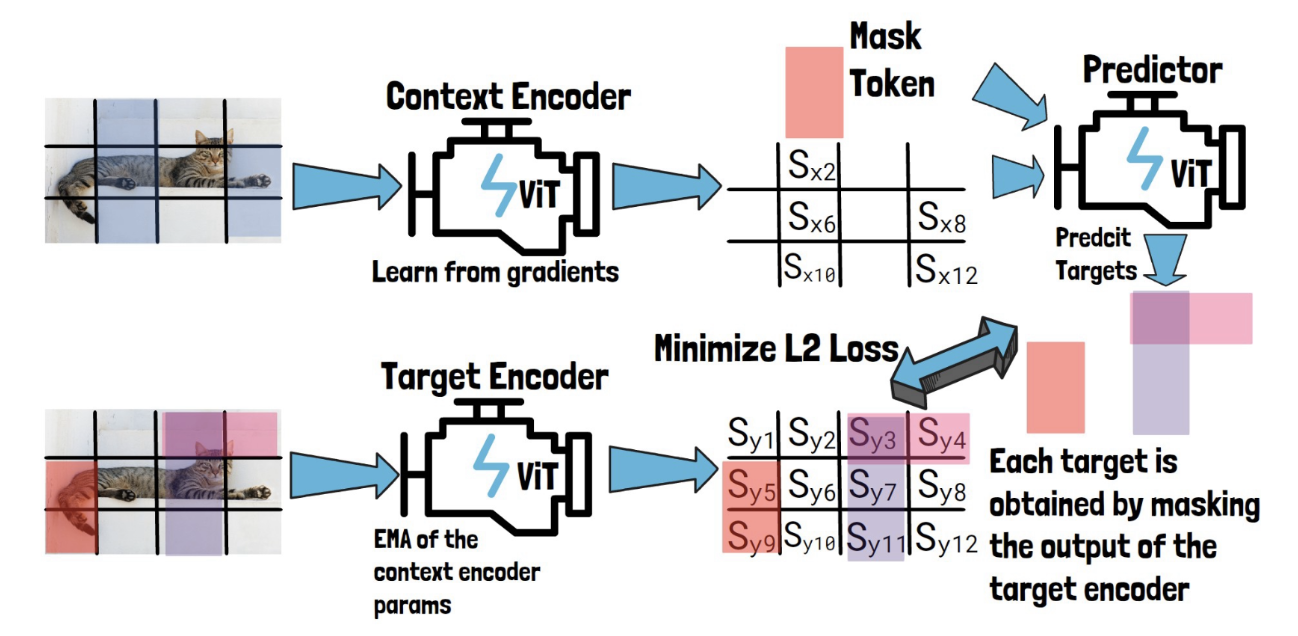
(2) JEPA
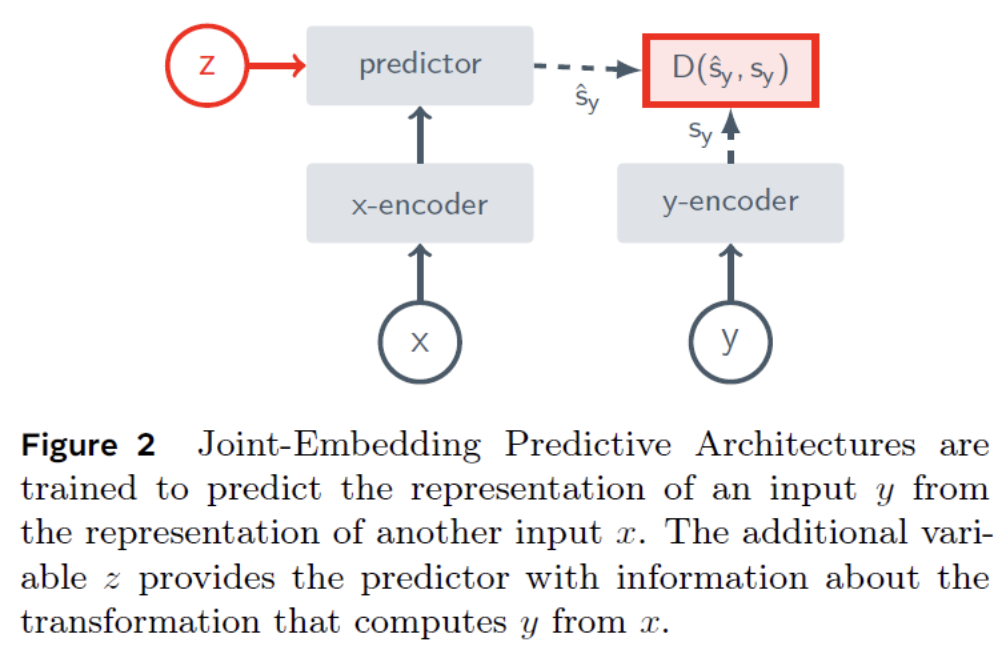
Feature Prediction
-
Predict missing info in representaiton space
( = Predict features, instead of pixels )
-
(For video) Same spatial blocks across all of the video frames
Framework
- Step 1) Predict the target representatinos based on context & target locations
- Step 2) Encode the target representations directly from the targets
- Step 3) Loss is based on the difference between them
- (\(y\)-encoder = EMA of \(x\)_encoder to avoid collapse)
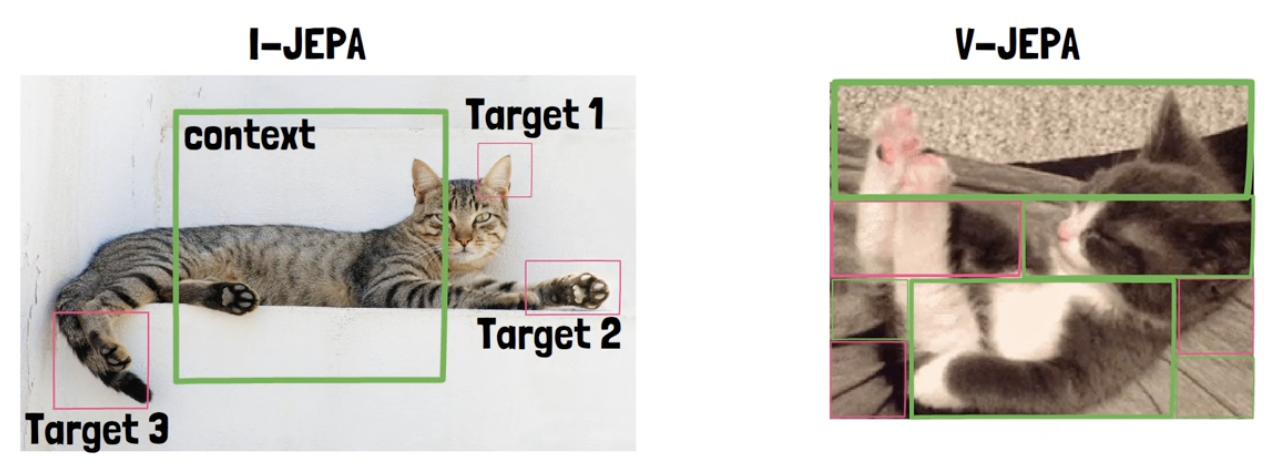
2. I-JEPA
3. V-JEPA
Video Joint-Embedding Predicting Architecture
- New collection of vision models by Meta AI
a) Flatten the input to patches
- Video is flattened to patches (for input to ViT)
- Patch = 16x16 pixels blocks spanning on two adjacent timeframes
b) Context & Target
Divide the video to context and targets
- Target blocks: have the same spatial area across the video frames ( =timeframes )
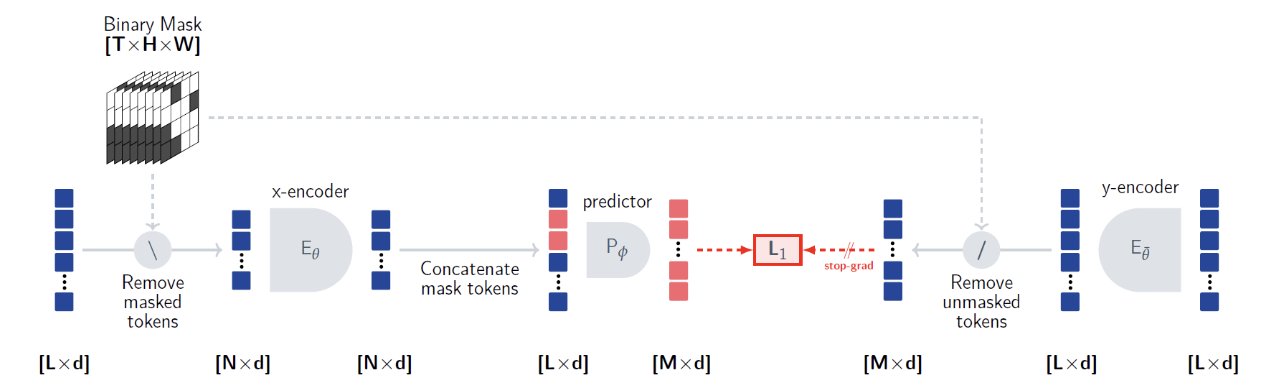
c) Prediction
- Step 1) Remove the masked tokens ( = targets ) from the input
- Step 2) \(x\)-encoder can process the context tokens
- Step 3) Add learnable mask tokens to the output of \(x\)-encoder output (with PE of target block)
- Step 4) Predictor predicts representations for the target blocks
( Use \(L_1\) loss (instead of \(L_2\) loss)
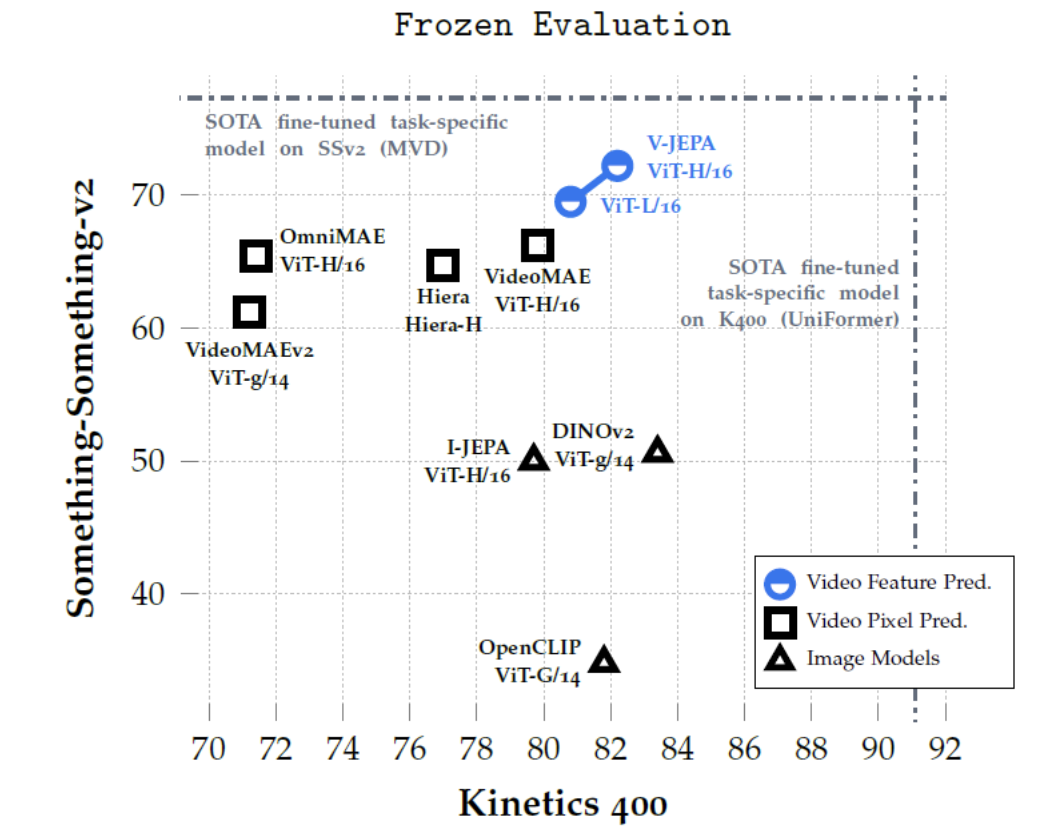
4. Experiments