NExT-GPT: Any-to-Any Multimodal LLM
Wu, Shengqiong, et al. "Next-gpt: Any-to-any multimodal llm." arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.05519 (2023).
참고:
- https://aipapersacademy.com/next-gpt/
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.05519
Contents
- Introduction
- Framework
- Three Stages
- Multimodal Encoding Stage
- LLM Understanding and Reasoning Stage
- Multimodal Generation Stage
- Efficient Training
- Examples
- Training NExT-GPT
- Lightweight Multimodal Alignment Learning
- Modality-switching Instruction Tuning (MosIT)
- Experiments
1. Introduction
Multimodal large language model (MM-LLM)
2. Framework
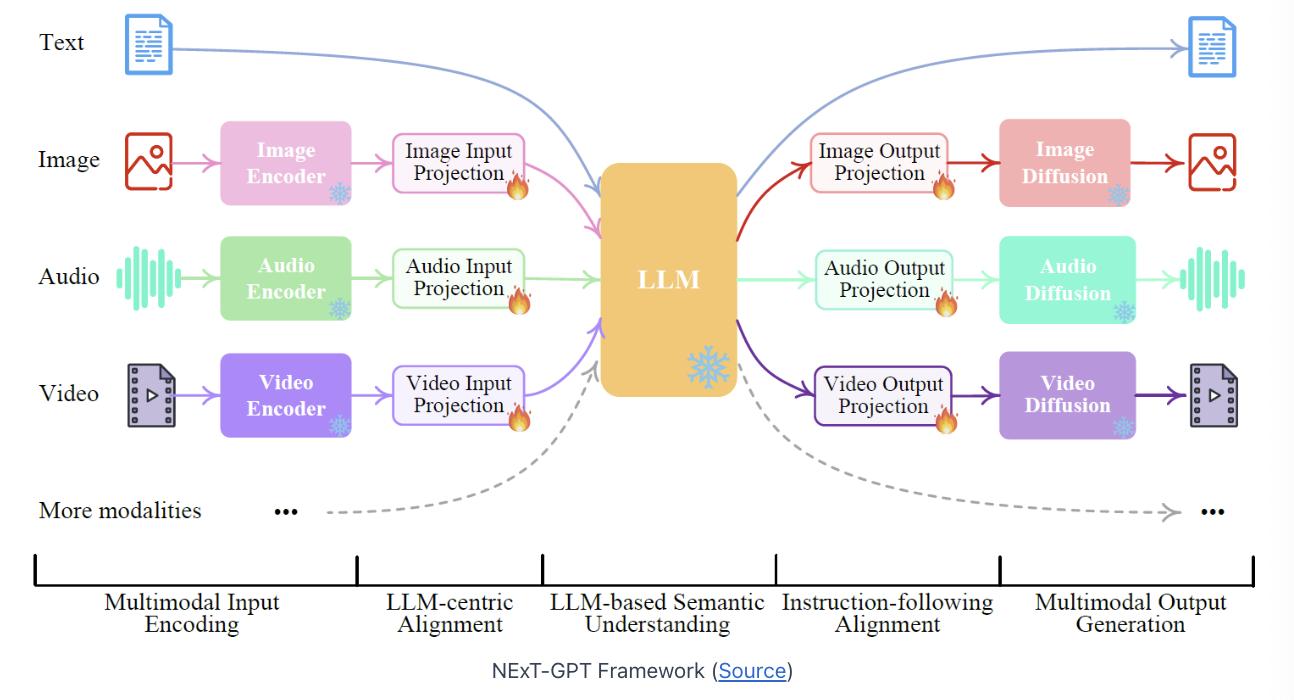
Framework
-
(1) Input: Possible input modalities: text, image, audio, video ….
-
(2) LLM ( = core of the framework )
-
Goal of LLM
- Process the input from “all modalities”
- Guide the generation of outputs for “all modalities”
-
But, current LLM can only understand and generate text.
\(\rightarrow\) How to solve?
3. Three Stages
3 main tiers
- (1) Multimodal Encoding Stage
- (2) LLM Understanding and Reasoning Stage
- (3) Multimodal Generation Stage
(1) Multimodal Encoding Stage
Goal: Convert (non-text) inputs \(\rightarrow\) text prompts
Two stage
-
Stage 1) Multimodal input encoding
- Each modality: through each encoder
-
Stage 2) LLM-centric alignment
-
Input projection to generate text from the embeddings
( for LLM to understand )
-
(2) LLM Understanding and Reasoning Stage
LLM yields ..
- a) Text response
- b) Instructions for the other modalities generation
\(\rightarrow\) LLM output can contain multiple parts!
....<IMG1>....<AUD1>....<VID1>....
(3) Multimodal Generation Stage
Goal: Generating the final output for all modalities (based on the LLM response)
Two stages
- Stage 1) Instruction-following alignment
- (For non-text modality output) Output is passed via small transformer-based models
- Why?
- To convert the LLM outputs
- into representations that can be processed by the modalities decoders
- Stage 2) Multimodal output generation
- Generate the output for each modality
- Model: Modality-specific diffusion decoder
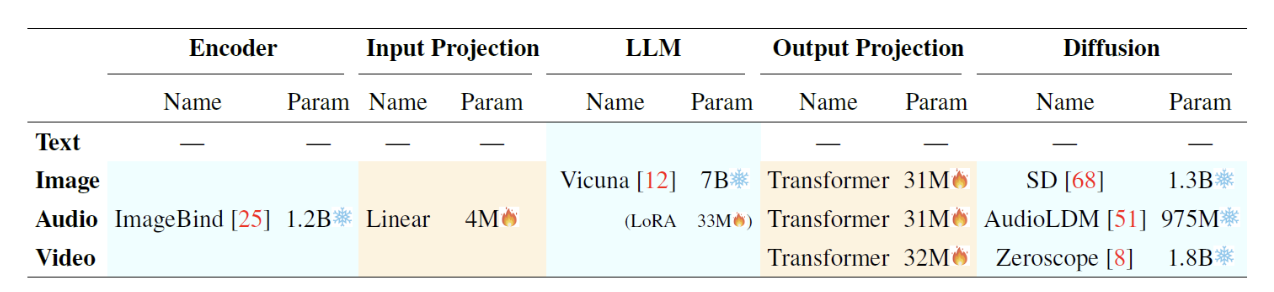
4. Efficient Training
Only need to train a very small portion of the weights.
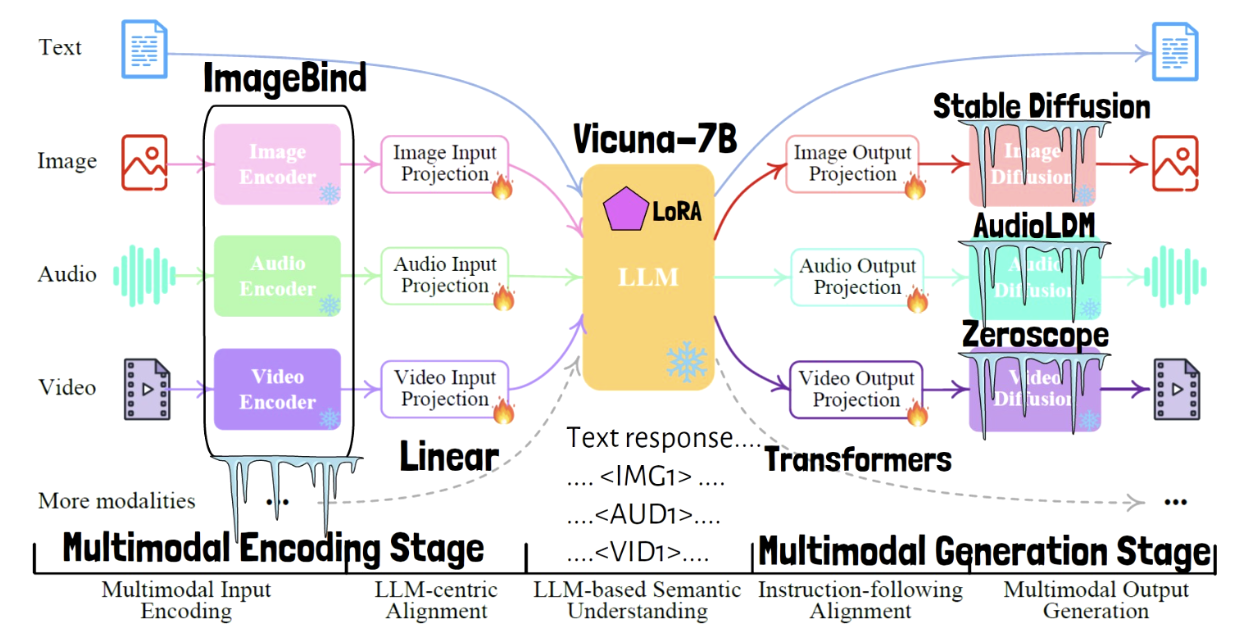
5. Examples
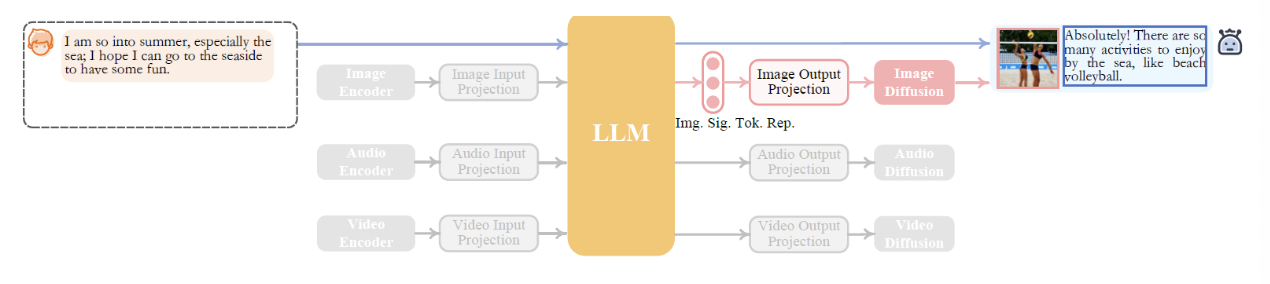
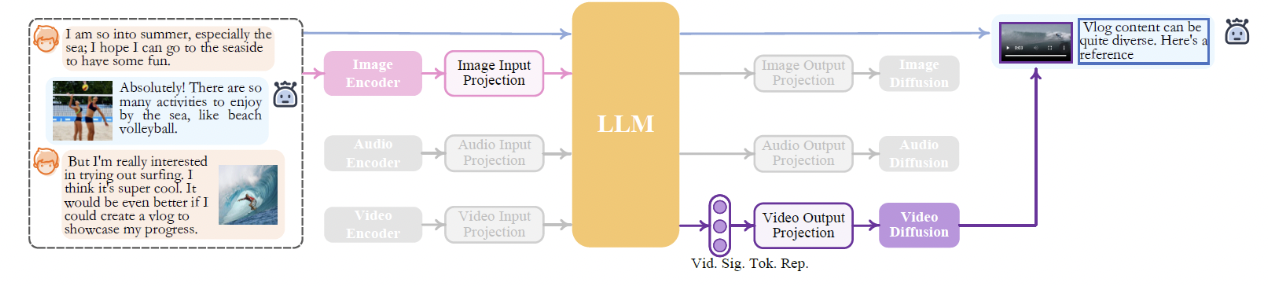
6. Training NExT-GPT
(1) Lightweight Multimodal Alignment Learning
How the input and output projection models are trained,?
- a) Input projection (= LLM-centric alignment)
- b) Output projection (= Instruction-following alignment)
a) Encoding-side LLM-centric Multimodal Alignment
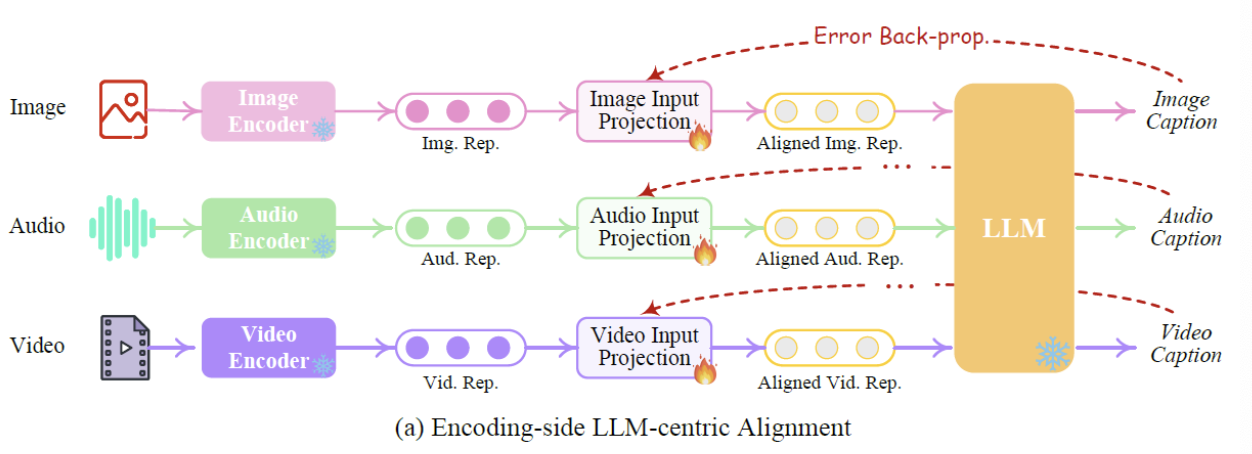
(1) Model: input projection
(2) Dataset:
- (image, text caption)
- (audio, text caption)
- (video, text caption)
(3) Procedure
- Step 1) Feed the non-text input to the encoder \(\rightarrow\) representations
- Step 2) Representation is fed to input projection model
- Yields an aligned representation for the LLM
- Step 3) Loss function: Comparison with the “text caption”
b) Decoding-side Instruction-following Alignment
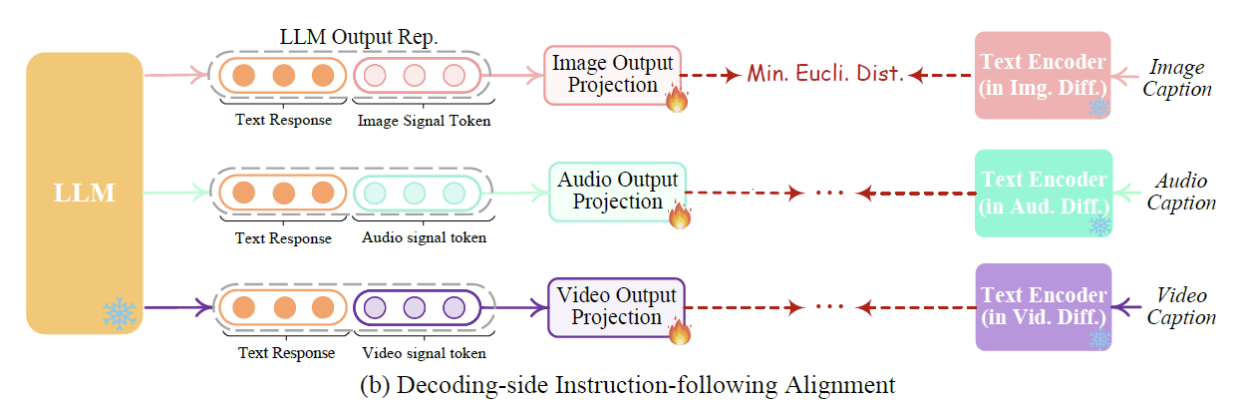
Next we review the decoding-side instruction-following alignment step, where we still use similar captioned inputs as before. We do not use any generation of image, audio and video here which is very interesting. The way it works is that the
Procedure
-
Step 1) LLM outputs a response with a signal token
-
Step 2) Output is passed via the output projection model
-
Step 3) Loss function: Comparison with the encoding obtained by feeding the caption to the text encoder (of the diffusion model)
\(\rightarrow\) Only need the text encoder from the diffusion model
( No need to run the diffusion process )
(2) Modality-switching Instruction Tuning (MosIT)
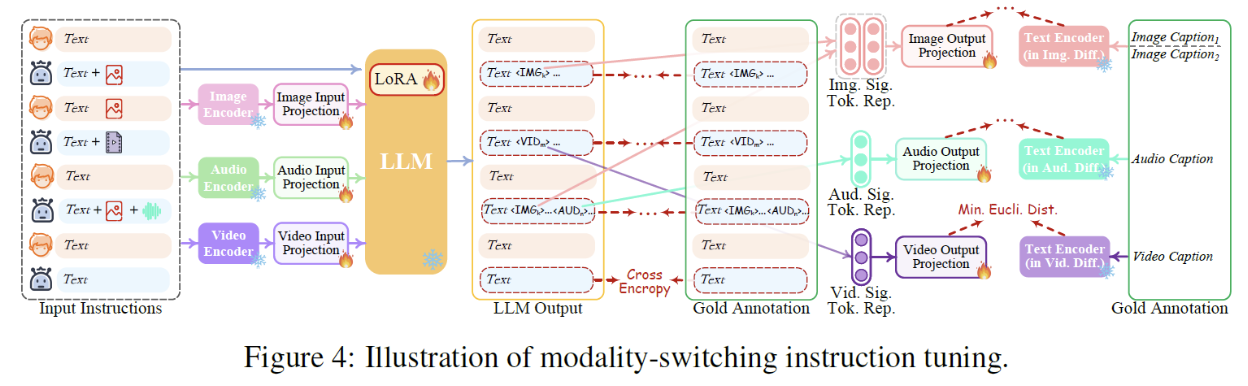
Goal: To follow instructions that include inputs from multiple modalities
Input: Ddialogue inputs with multiple modalities
How? Keep on training …
- (1) Trainable components mentioned before
- (2) LoRA weights
7. Experiments
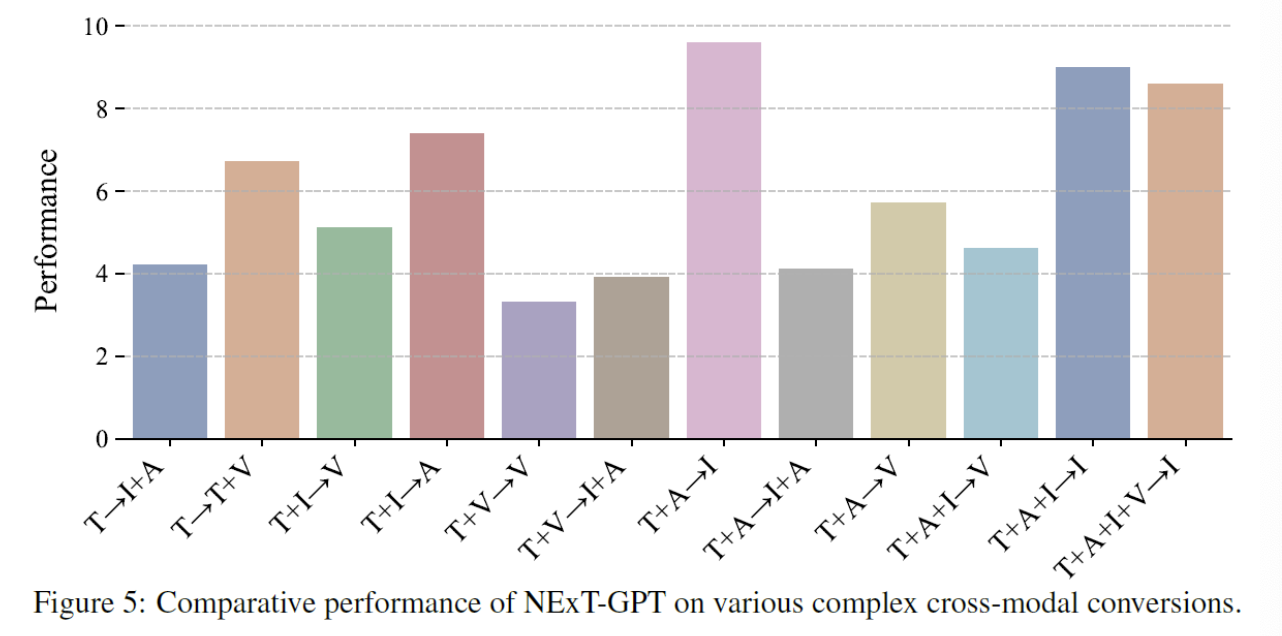
- Performance: Given by human evaluators ( Scale of 1 to 10 )
