TinyGPT-V: Efficient Multimodal Large Language Model via Small Backbones
Yuan, Zhengqing, et al. "Tinygpt-v: Efficient multimodal large language model via small backbones." arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.16862 (2023).
참고:
- https://aipapersacademy.com/tinygpt-v/
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/2312.16862
Contents
- Introduction
- Model Architecture
- LLM Backbone
- Processing Images with Phi-2
- Trainable Params.
-
Training Process
- Experiments
1. Introduction
TinyGPT-V
- New multimodal LLM (MMLLM)
- with Small Backbones
Motivation
- Tremendous progress with LLMs
- e.g., GPT-4, LLaMA2, …
-
Vision-language models (VLMs)
-
LLM to undertstand images
-
e.g., GPT-4V, LLaVA, MiniGPT-4
-
\(\rightarrow\) Limitations: Require a substantial amount of resources to run
2. Model Architecture
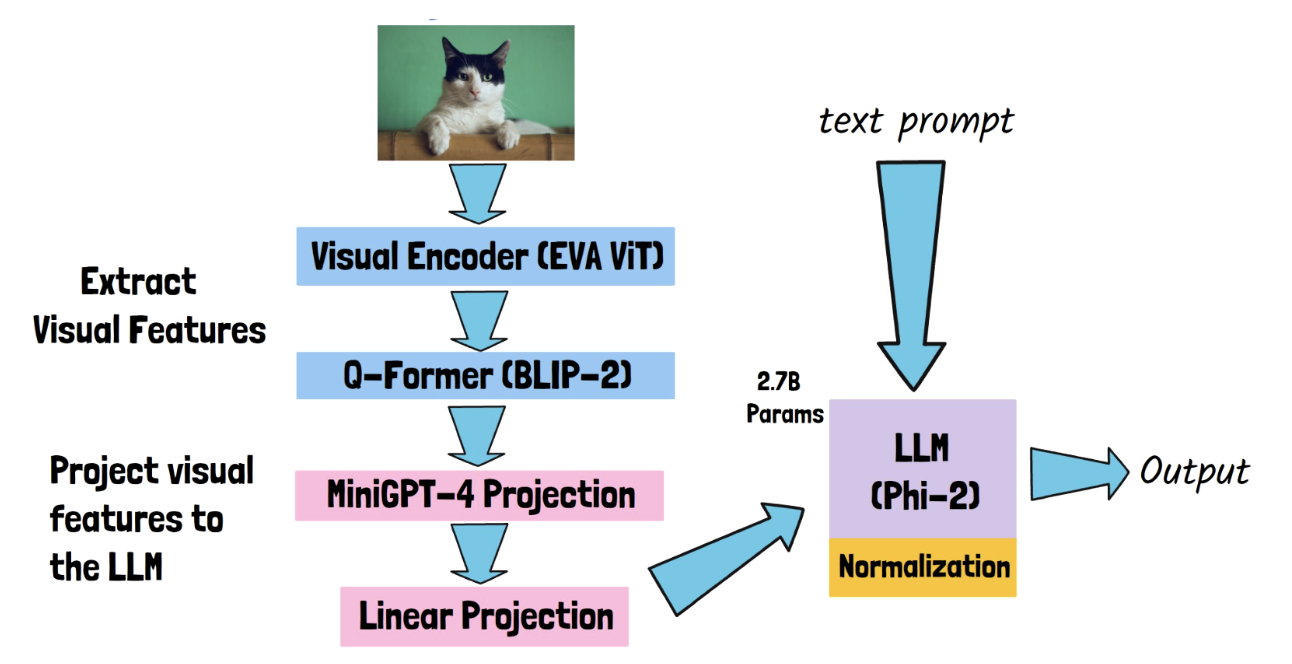
(1) LLM Backbone
LLM backbone = Phi-2 model
- 2.7B params ( still, beats much larger models )
- Phi-2 (2.7B): Contains most of the params of TinyGPT-V (2.8B)
- Of course, can hanle text inputs!
\(\rightarrow\) How to handle image inputs??
(2) Processing Images with Phi-2
2 stages required to handle image inputs
- Stage 1) Extract visual features
- 1-1) Pass through visual encoder (EVA ViT)
- 1-2) Pass through pre-trained Q-Former (from BLIP-2)
- Q-Former: A component that is trained to align the visual features from the ViT with the text instruction!
- Stage 2) Projection
- 2-1) MiniGPT-4 Projection
- 2-2) Linear Projection
- To converts the size from MiniGPT-4 to Phi-2
- 2-3) Feed the output results to Phi-2
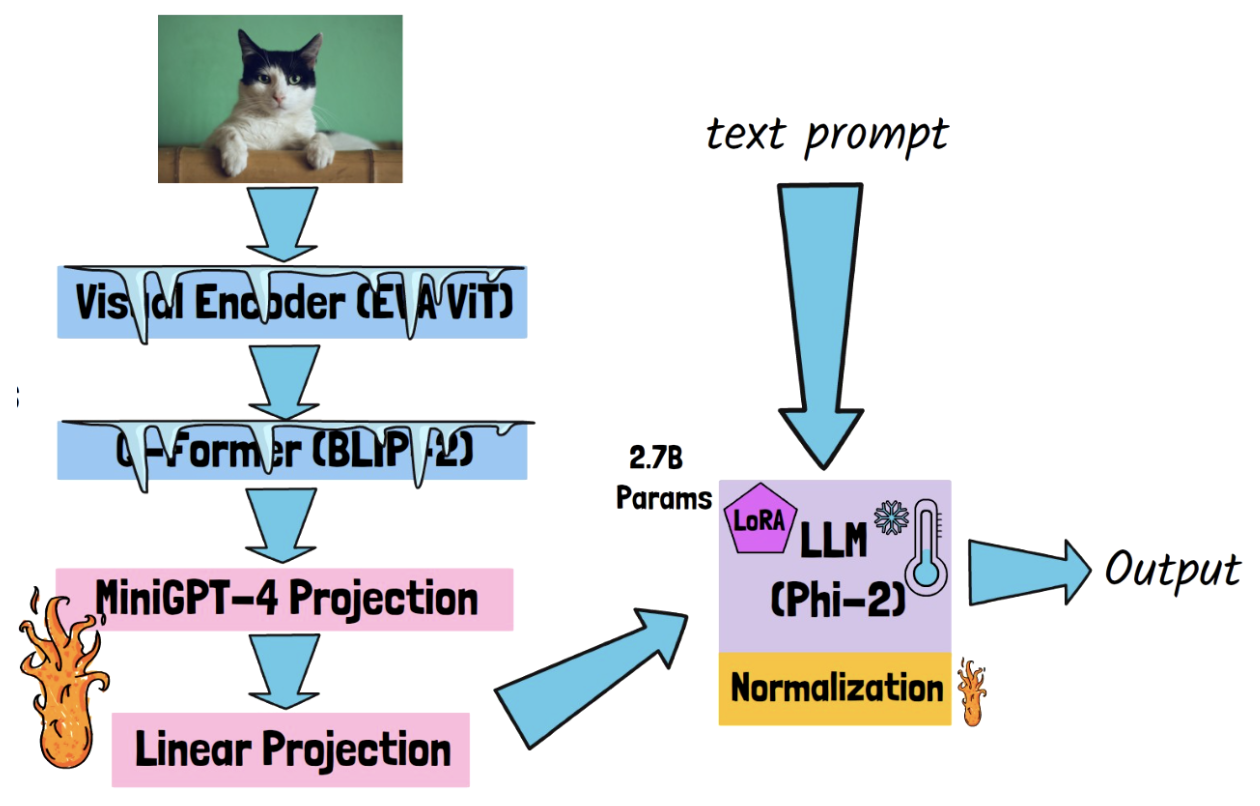
(3) Trainable Params.
3. Training Process
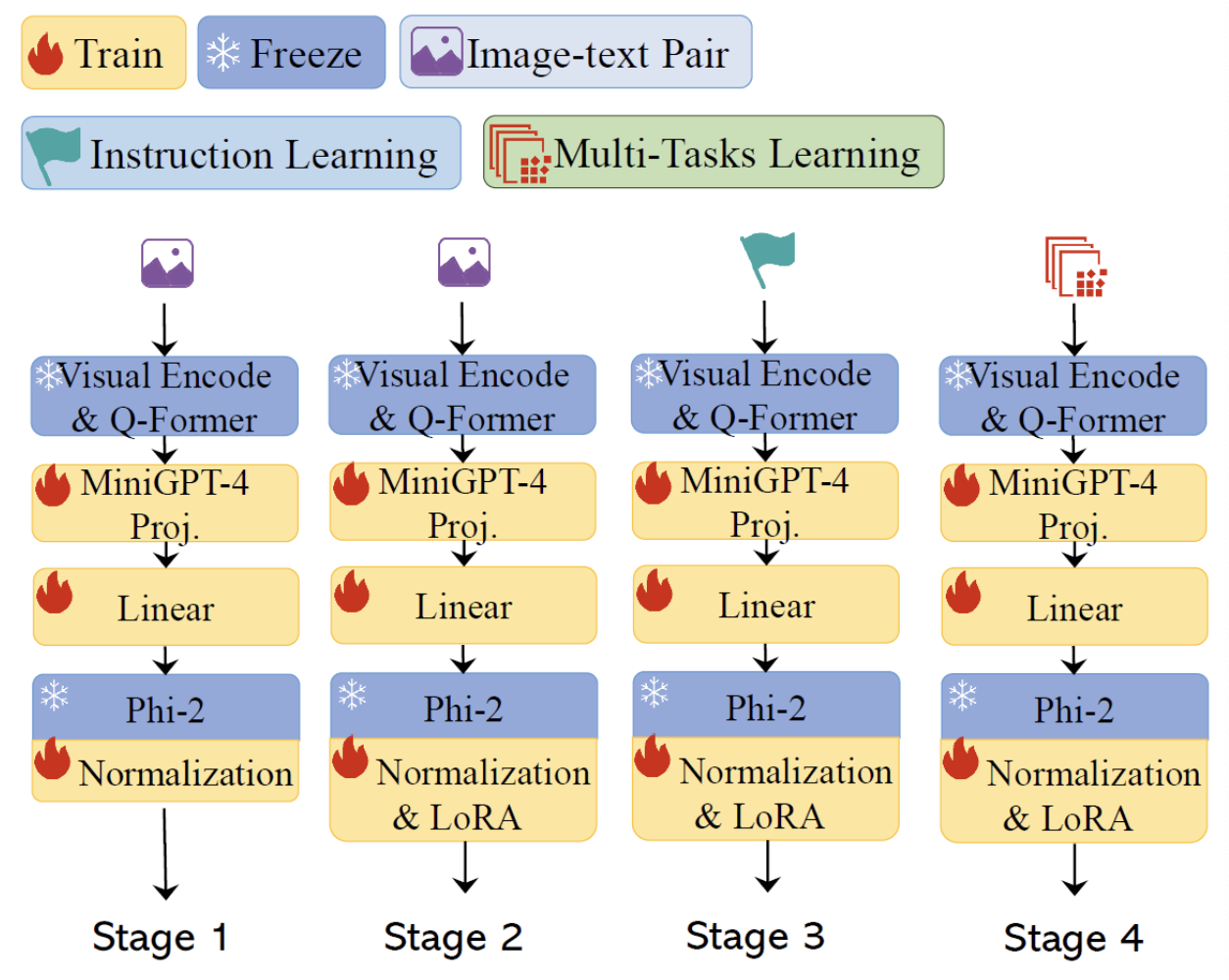
Step 1) Warm-up stage
- Data: image-text pairs
- Goal: Enable Phi-2 to process images
Step 2) Pre-training
- Data: Same as step
- Difference with step 1:
- LoRA weights are added ( & updated )
Step 3) Instruction Learning
- Dataset: Instructions
- Examples from MiniGPT-4 data
- Learnable params: same as step 2
Step 4) Multi-tasks Learning
- Trained on multiple datasets for various vision-language tasks
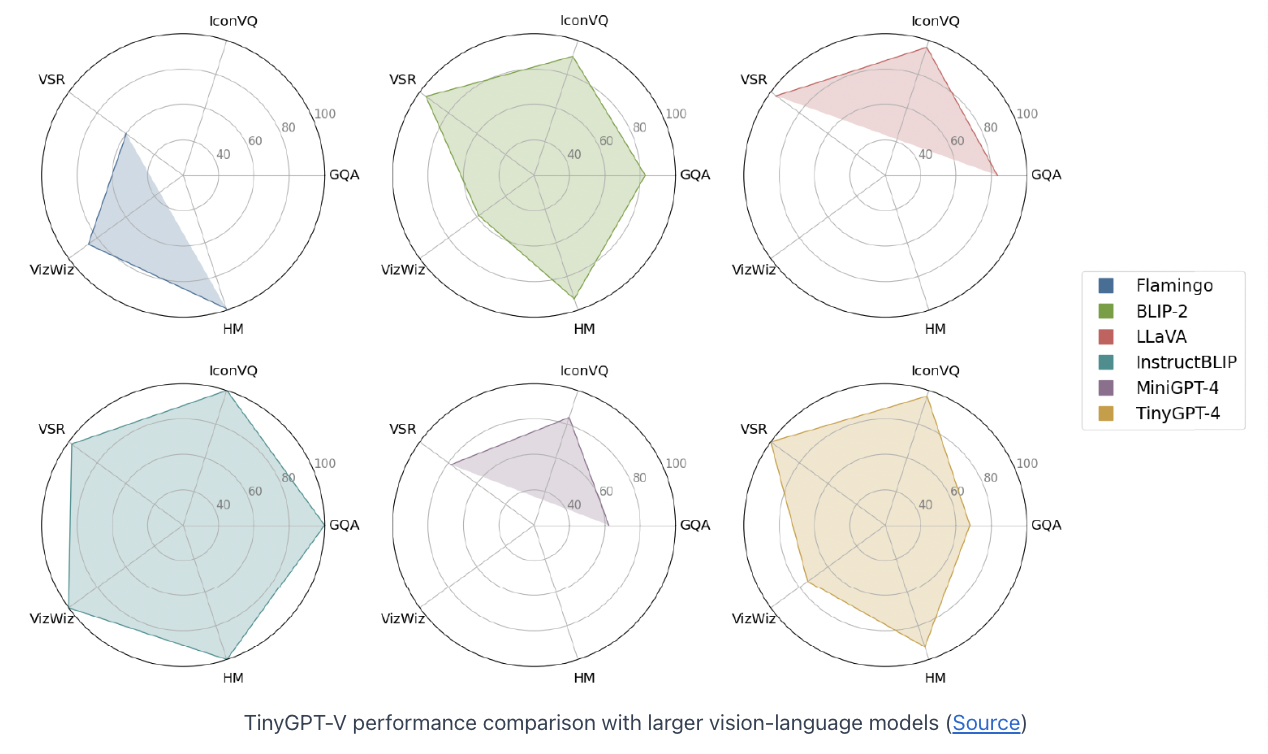
4. Experiments