( 참고 : 패스트 캠퍼스 , 한번에 끝내는 컴퓨터비전 초격차 패키지 )
Classical Computer Vision
1. Local Image Features
이미지 내에서 “핵심이 되는 부분” ( interesting part of an image )
Image Representation에 활용 가능
-
Ex) 인물 사진 : 눈/코/입/귀 등
\(\rightarrow\) Bag of (VISUAL) Words 구성 가능
좋은 Local Feature 란?
-
Saliency : 이미지 내에 “유의미한.흥미로운” 부분을 담고 있어야
- Locality : 이미지 내에서 “작은 크기/영역”을 차지해야
- ex) 한손에 꽃을 들고, 다른 손에 마이크를 든 가수의 경우
- 좋은 local feature : 꽃, 마이크, 가수 얼굴 등
- 나쁜 local feature : 위 가수의 전체 모습
- ex) 한손에 꽃을 들고, 다른 손에 마이크를 든 가수의 경우
- Repeatability : 다양한 변형 하에서도, 해당 local feature가 계속 발견되어야
Interest Point의 예시
- corner
- blobs
2. Convolution 연산
\(g=f * h, \quad \text { where } g(x, y)=\sum_{u, v} f(x-u, y-v) h(u, v)\).
특징
- Commutative: \(f * g=g * f\)
- Associative: \(f *(g * h)=(f * g) * h\)
- Distributive: \(f *(g+h)=f * g+f * h\)
- 선형 연산 (Linear Operation) 이다
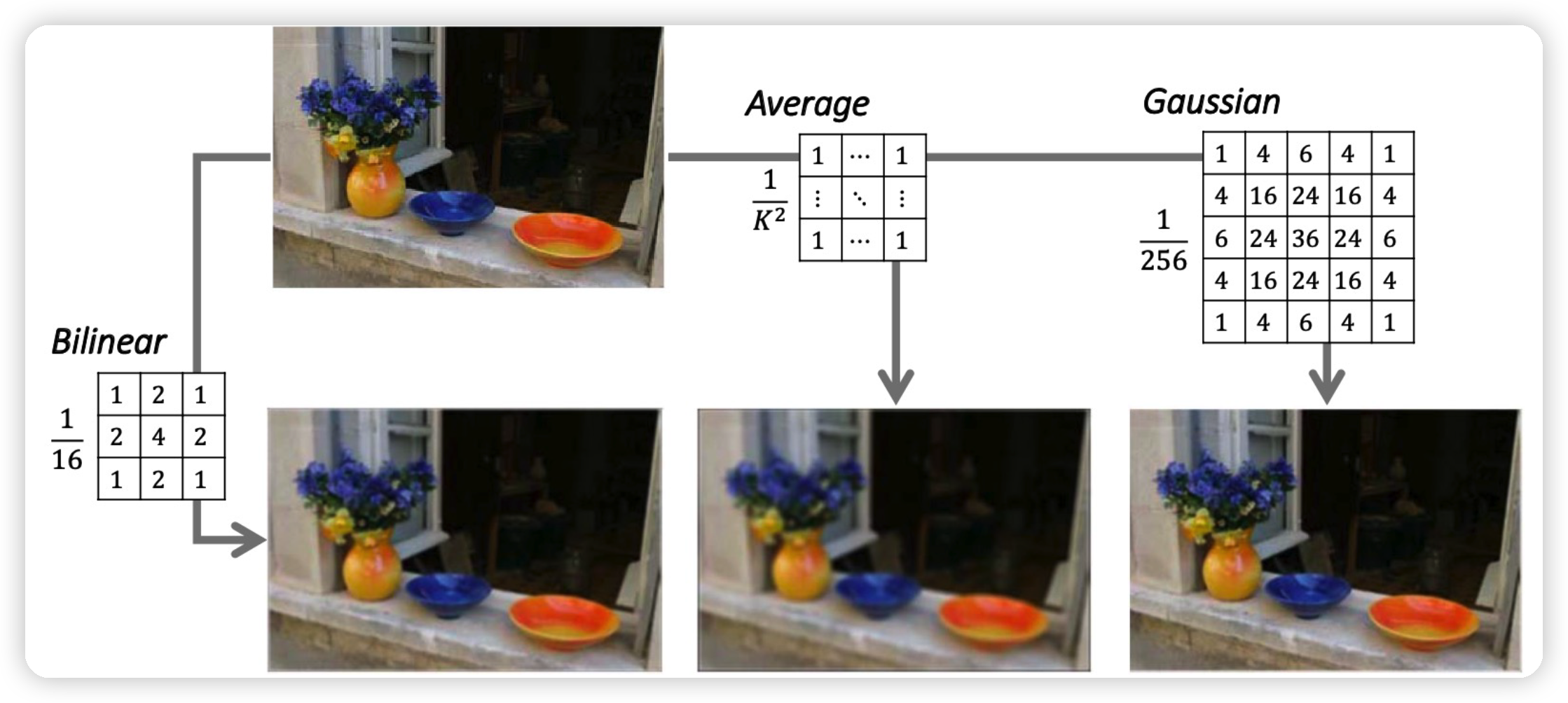
(1) 예시 1 : Smoothing
- with AVERAGE
- with BILINEAR INTERPOLATION
- with GAUSSIAN FILTER
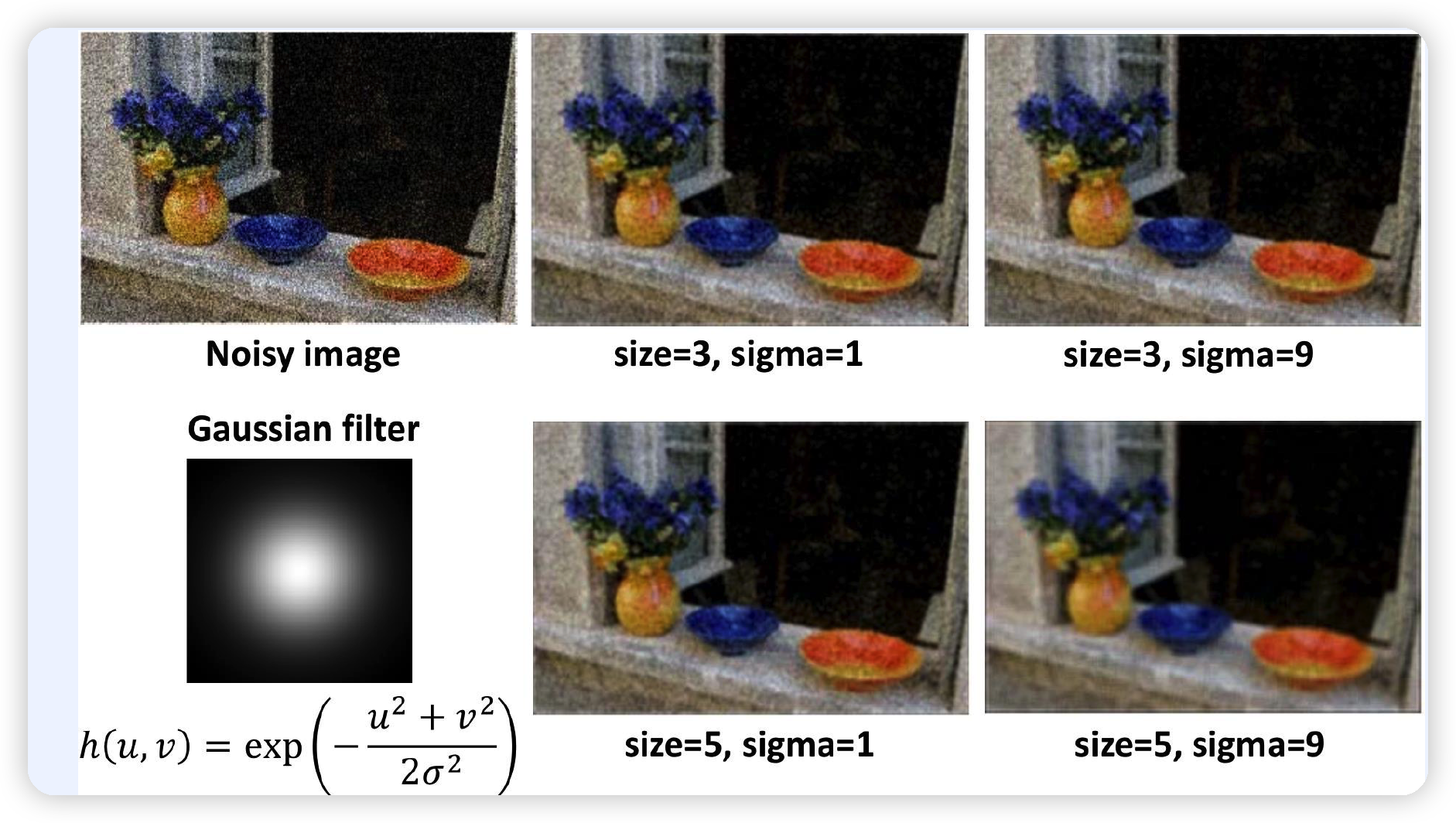
Gaussian Filter를 사용한 noise reduction
- filter size & sigma 변화에 따른 denoising 효과
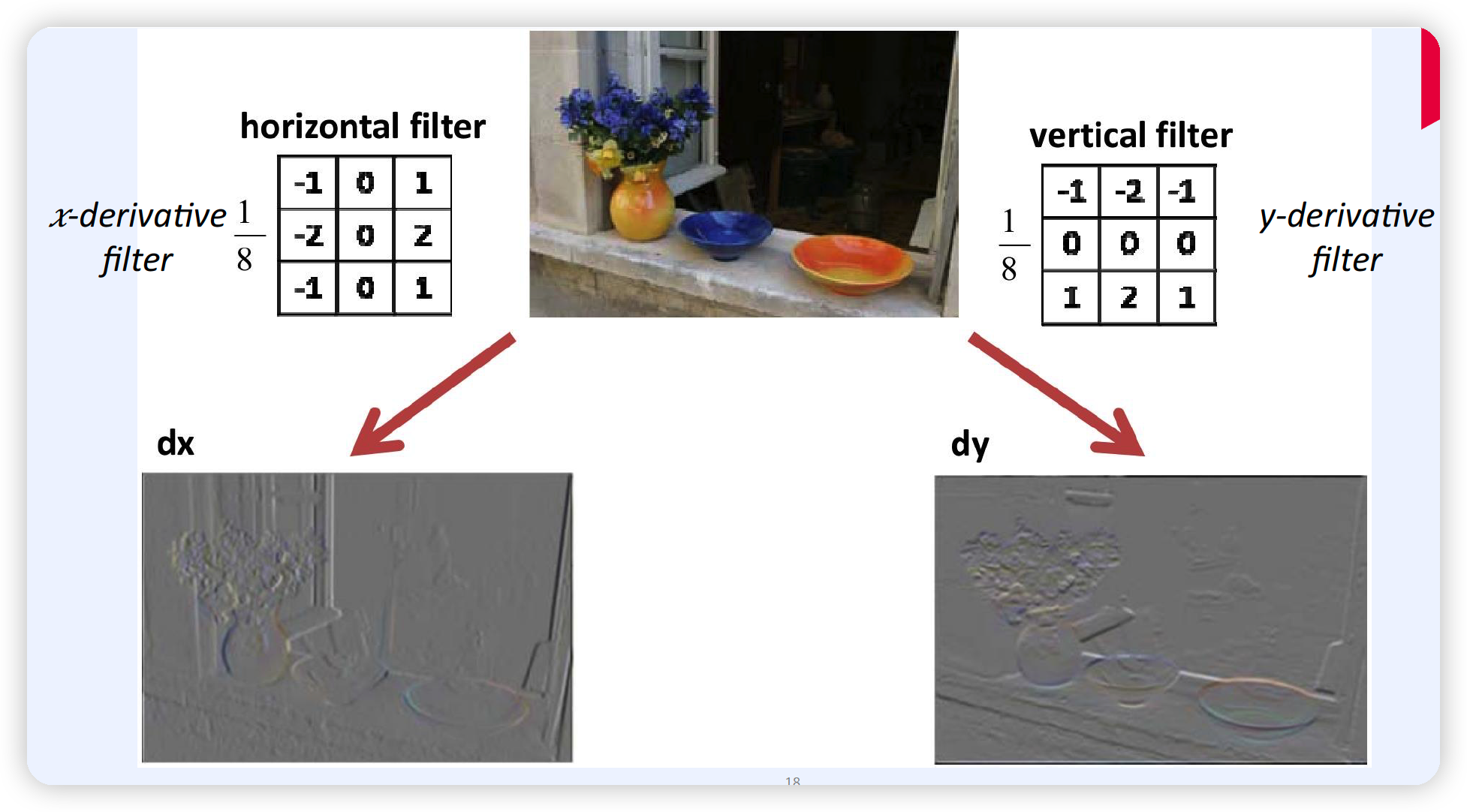
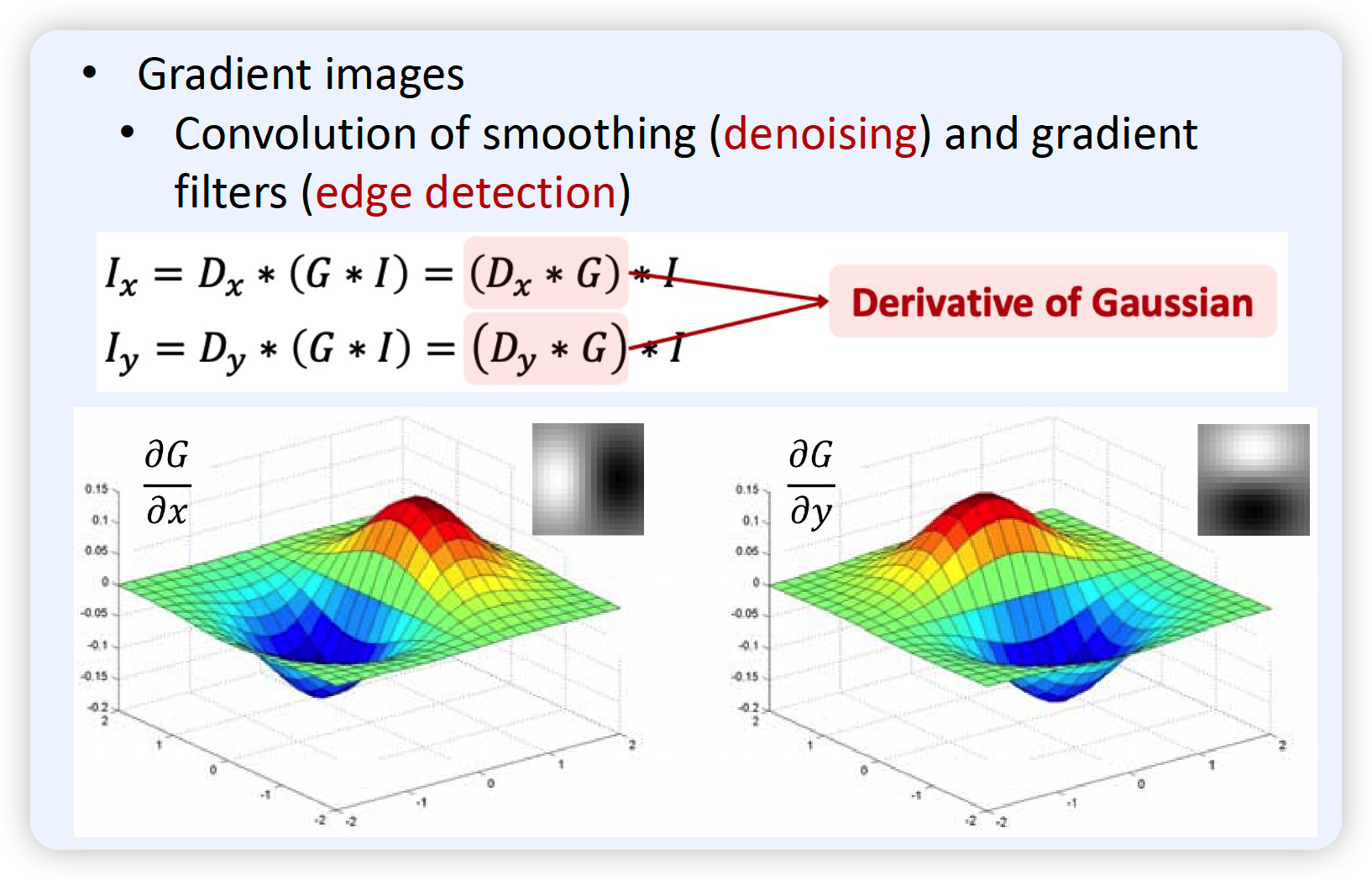
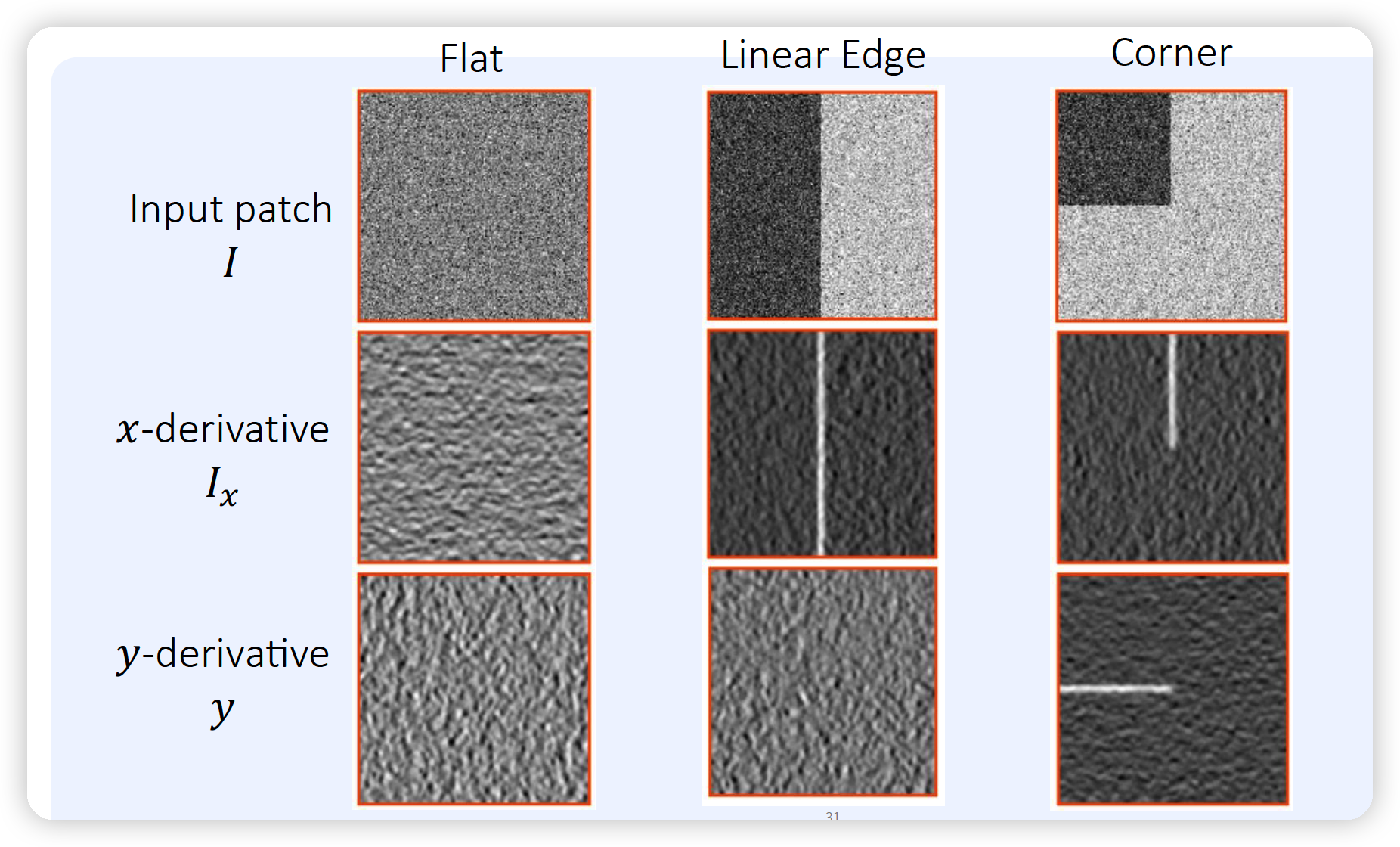
(2) 예시 2 : Gradient Filter
\(x\)축 / \(y\)축 방향의 모습을 캡쳐하고 싶을 때!
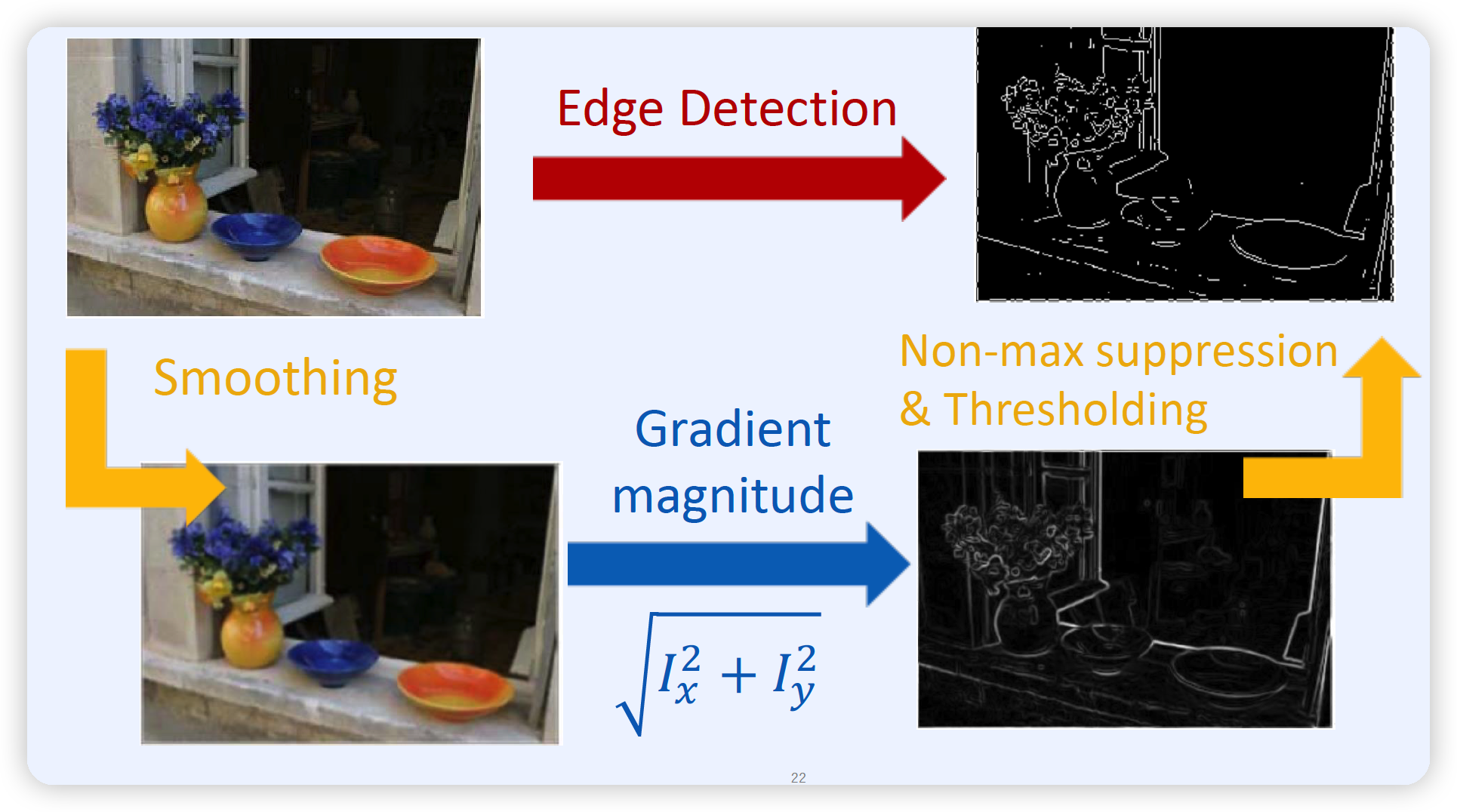
3. Edge
Edge = 두 region을 나누는 경계 ( 점들의 모임 )
일반적인 Edge Detection 과정
-
(1) smoothing
-
(2) gradient magnitude 계산
-
(3) NMS & thresholding
-
NMS = Non-Max Suppression
( 불필요한/사소한 부분을 큰 부분에 편입 or 죽이기 )
-
위 (2) 과정에서 \(I_x\) 와 \(I_y\)는?
4. Corners
edge direction이 뚜렷히 바뀌는 부분
대표적인 corner detection 알고리즘 : Harris Corner Detection
(1) Harris Corner Detection
용어 정리
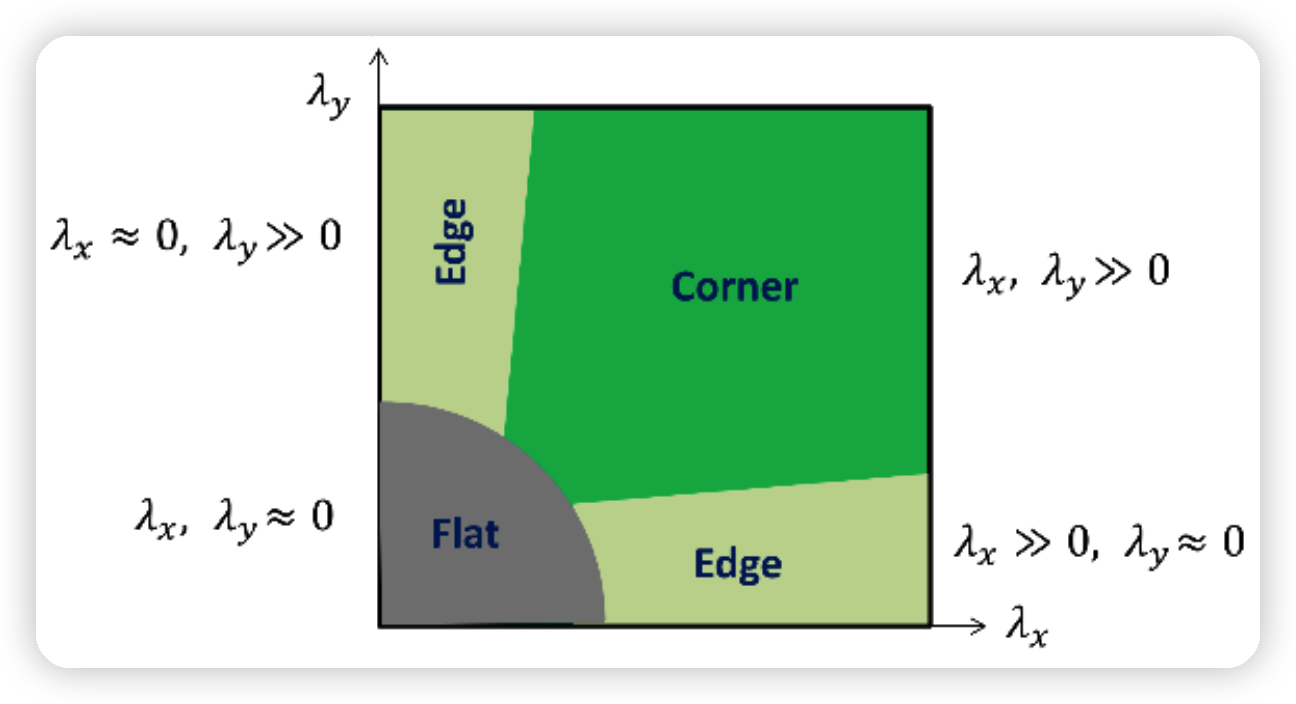
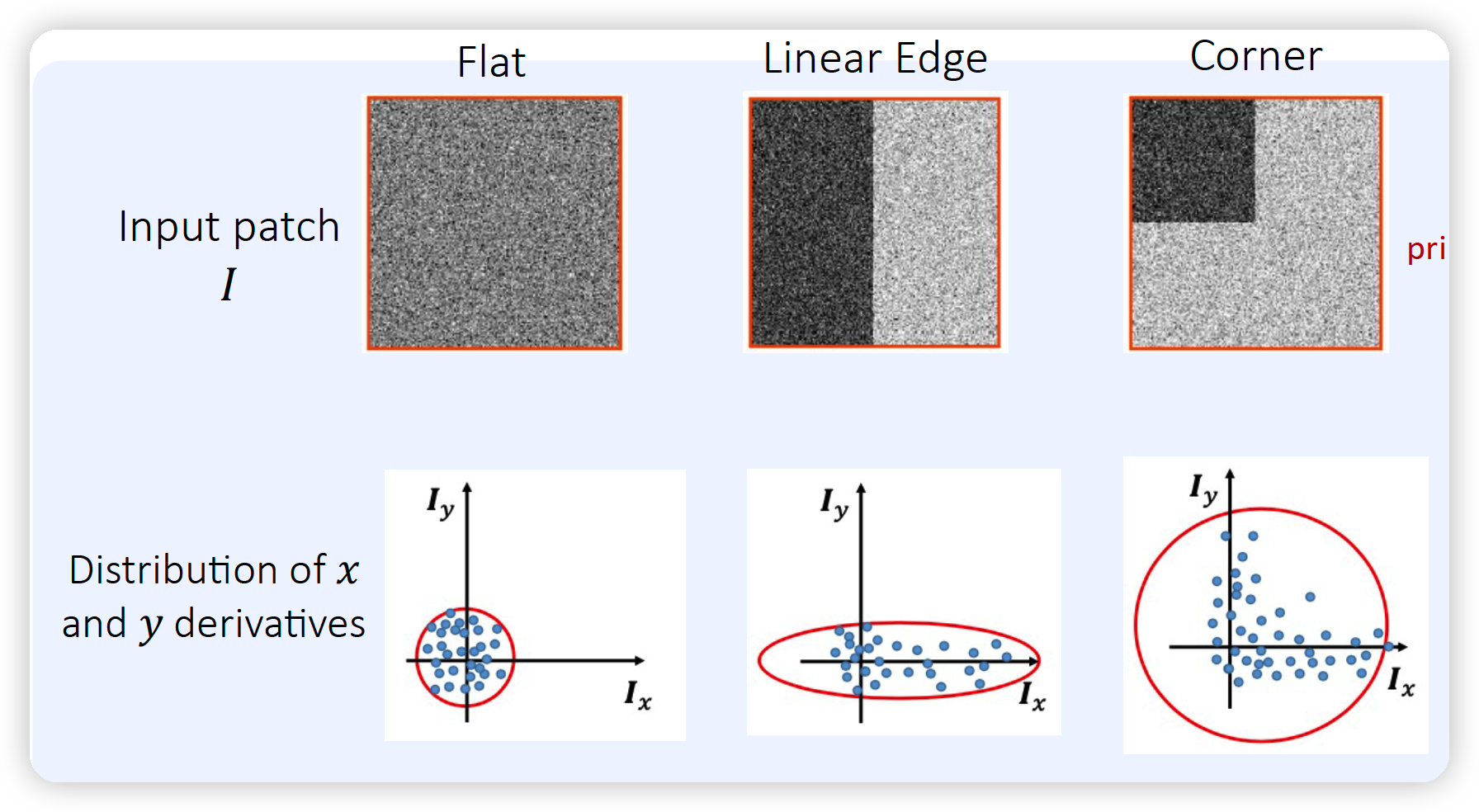
- corner : 모든 방향에서 direction이 급격히 변함
-
edge : edge direction에서의 변화 X
- flat region : 모든 direction에서의 변화 X
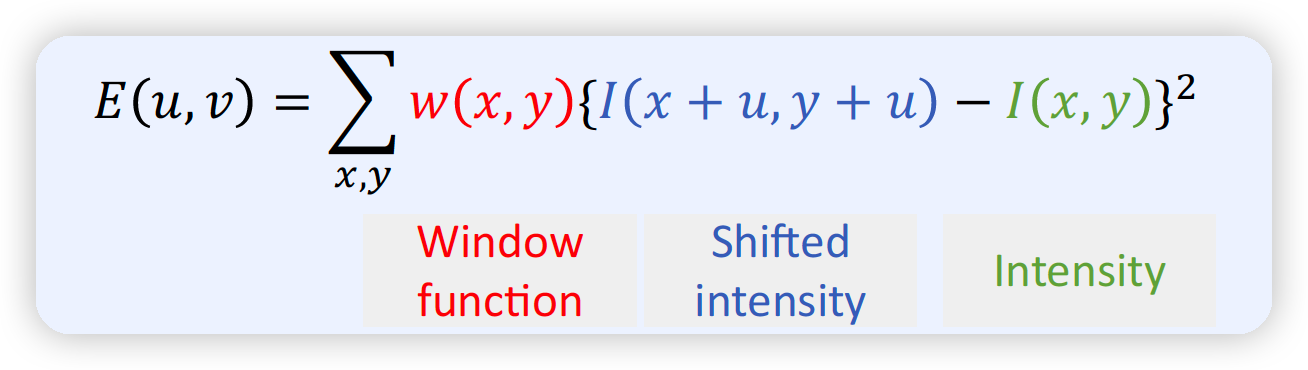
Detect하는 방법?
\(\rightarrow\) pixel을 이동했을 때, pixel intensity의 변화 파악!
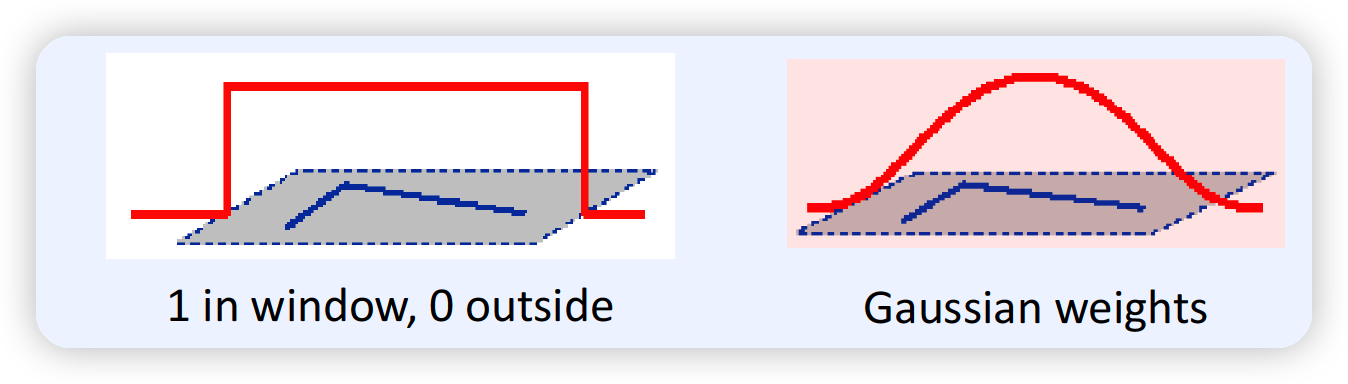
이때, 위에서 사용하는 Window Function에는…
- (1) window 내에서는 1, 밖에서는 0
- (2) Gaussian Weight
- noise에 보다 강함
Change of Pixel Intensity ( for shift [u,v] )
\(E(u, v) \approx\left[\begin{array}{l} u \\ v \end{array}\right]^{\top}\left(\sum_{x, y} w(x, y)\left[\begin{array}{cc} I_{x}^{2}(x, y) & I_{x}(x, y) I_{y}(x, y) \\ I_{x}(x, y) I_{y}(x, y) & I_{y}^{2}(x, y \end{array}\right]\right)\left[\begin{array}{l} u \\ v \end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{l} u \\ v \end{array}\right]^{\top} M\left[\begin{array}{l} u \\ v \end{array}\right]\),
where \(M=\sum_{x, y} w(x, y)\left[\begin{array}{cc} I_{x}^{2}(x, y) & I_{x}(x, y) I_{y}(x, y) \\ I_{x}(x, y) I_{y}(x, y) & I_{y}^{2}(x, y \end{array}\right]\). ( = from image derivatives )
위 식에서, \(u\) & \(v\) 를 unit vector라고 하자.
모든 unit vector는 아래와 같은 eigen vector들로써 나타낼 수 있다.
\(\rightarrow\) \([u \quad v]^{\top}=a_{1} x_{1}+a_{2} x_{2}\) where \(a_{1}^{2}+a_{2}^{2}=1\).
corner point가 되기 위해서는, 모든 unit vector에 대해서 \(E(u,v)\) 가 커야한다.
\(\rightarrow\) \(\min _{u, v} E(u, v)\) should be large!
\(\begin{gathered} \min _{u, v} E(u, v) \approx \min _{u, v}\left[\begin{array}{l} u \\ v \end{array}\right]^{\top} M\left[\begin{array}{l} u \\ v \end{array}\right]=\min _{a_{1} \cdot a_{2}}\left(a_{1} x_{1}+a_{2} x_{2}\right)^{\top} M\left(a_{1} x_{1}+a_{2} x_{2}\right) \\ =\min _{a_{1} \cdot a_{2}}\left(a_{1}^{2} x_{1}^{\top} M x_{1}+a_{2}^{2} x_{2}^{\top} M x_{2}\right)=\min _{a_{1} \cdot a_{2}}\left(a_{1}^{2} \lambda_{1}+a_{2}^{2} \lambda_{2}\right)=\lambda_{2} \end{gathered}\).
(2) Harris Corner Detection 예시
(3) Summary
결국, \(M\) 행렬을 eigen decomposition을 해서 알 수 있다.
\(M=\sum_{x, y} w(x, y)\left[\begin{array}{cc} I_{x}^{2}(x, y) & I_{x}(x, y) I_{y}(x, y) \\ I_{x}(x, y) I_{y}(x, y) & I_{y}^{2}(x, y \end{array}\right]=V\left[\begin{array}{cc} \lambda_{1} & 0 \\ 0 & \lambda_{2} \end{array}\right] V^{\top}\).
2개의 eigen value \(\lambda_1\) & \(\lambda_2\) 가 곧 shape & size를 결정한다.
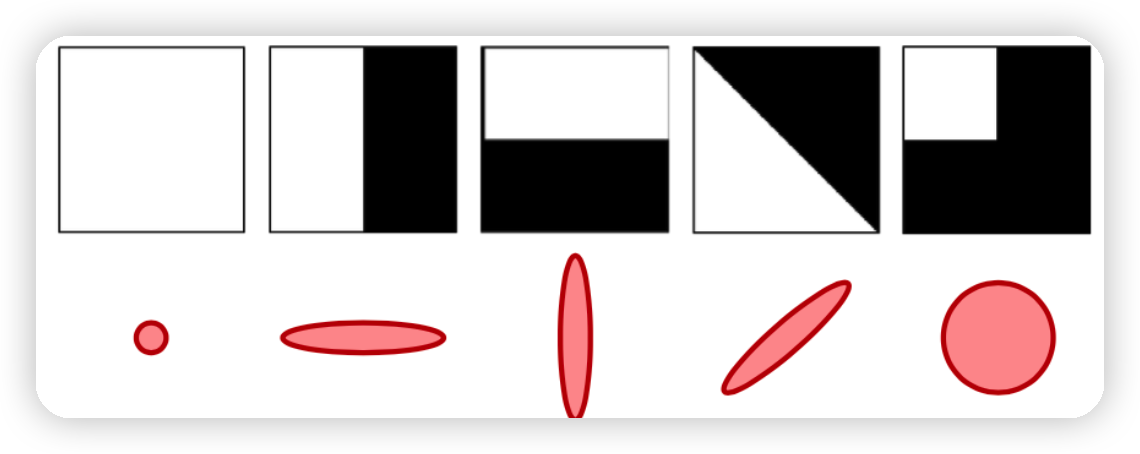
코너 / 엣지 / 플랫 구분하기
Corner response값 :
-
\(R=\operatorname{det}(M)-k \cdot \operatorname{tr}(M)^{2}=\lambda_{1} \lambda_{1}-k \cdot\left(\lambda_{1}+\lambda_{2}\right)^{2}\).
( \(k\)는 일반적으로 0.04 ~ 0.06으로 설정 )