( 참고 : 패스트 캠퍼스 , 한번에 끝내는 컴퓨터비전 초격차 패키지 )
Representation Learning (2)
3. Unsupervised Representation Learning
(1) Motivation
- Representation Learning : key of success in visual recognition
- problem : requires labeled data ( = supervision )
\(\rightarrow\) solution : UNsupervised Representation Learning
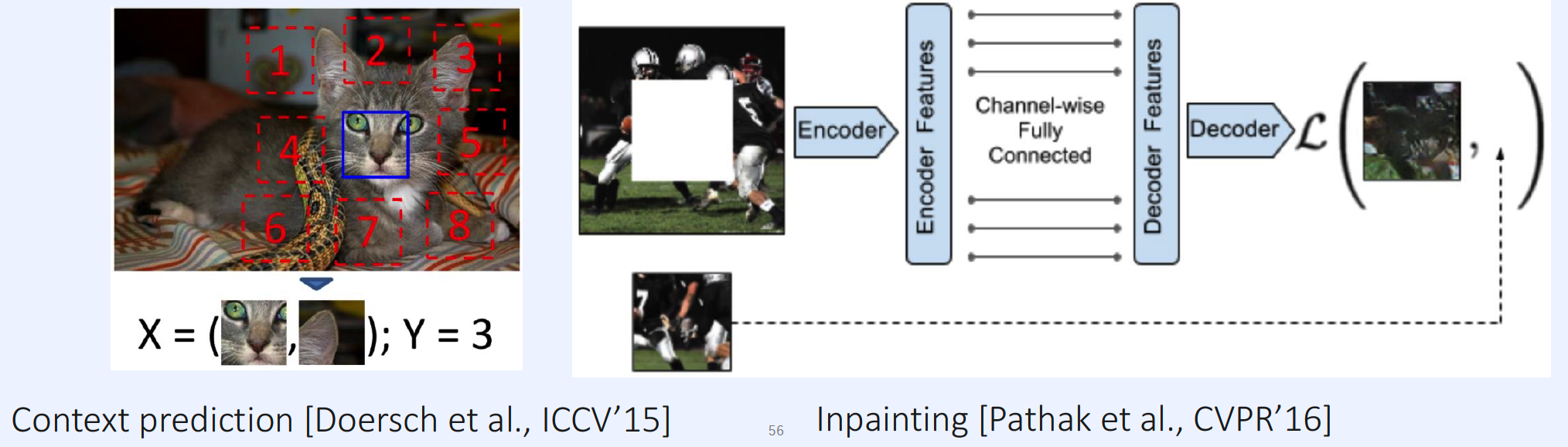
Example )
- context prediction (2015)
- inpaiting (2016)
(2) Face Recognition : faceNet (2015)
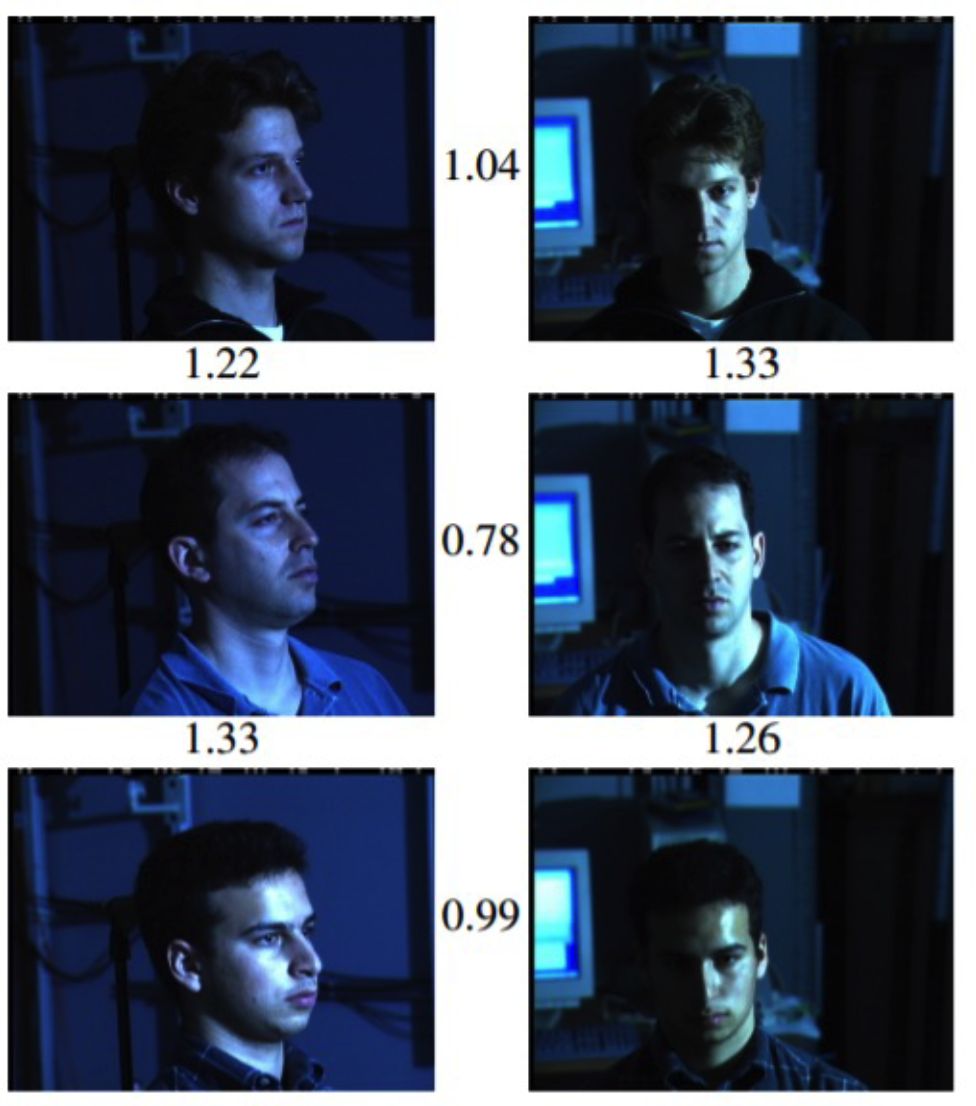

- Motivation : different pose, illumination \(\rightarrow\) but if same person, HIGH similarity !!
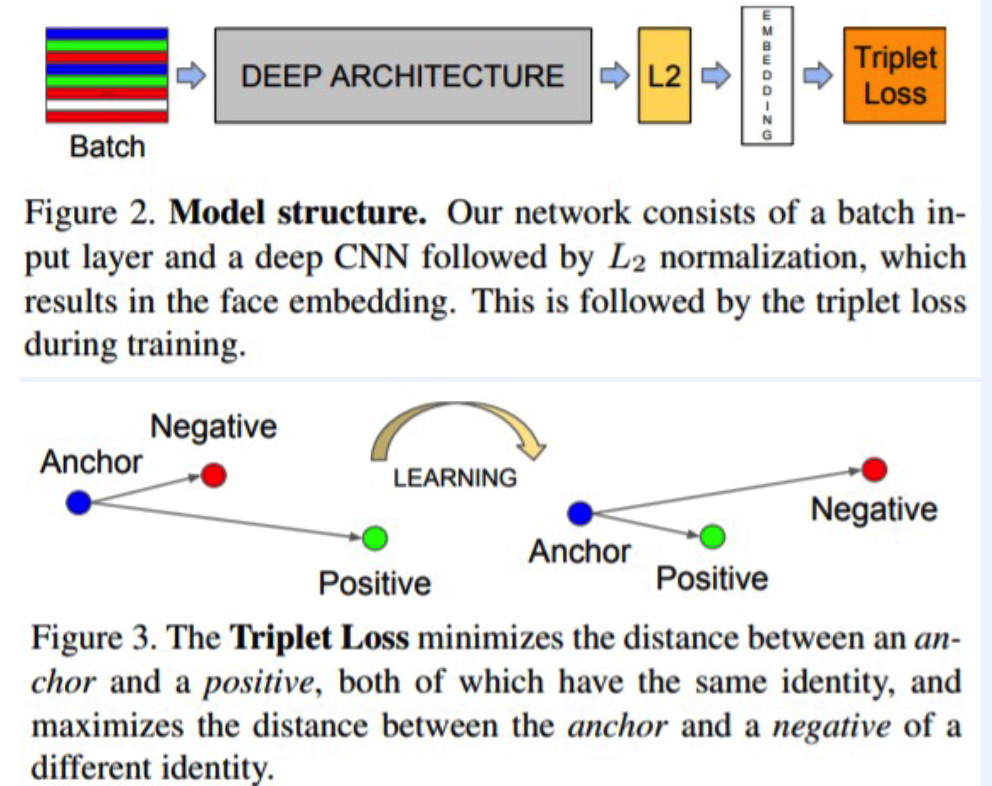
Loss Function
\(\begin{gathered} \sum_{i}^{N}\left[ \mid \mid f\left(x_{i}^{a}\right)-f\left(x_{i}^{p}\right) \mid \mid _{2}^{2}- \mid \mid f\left(x_{i}^{a}\right)-f\left(x_{i}^{n}\right) \mid \mid _{2}^{2}+\alpha\right]_{+} \end{gathered}\).
( Triplet Loss ) Code - TF
- https://github.com/davidsandberg/facenet/blob/master/src/facenet.py
def triplet_loss(anchor, positive, negative, alpha):
with tf.variable_scope('triplet_loss'):
pos_dist = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(tf.subtract(anchor, positive)), 1)
neg_dist = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(tf.subtract(anchor, negative)), 1)
basic_loss = tf.add(tf.subtract(pos_dist,neg_dist), alpha) # alpha = MARGIN
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.maximum(basic_loss, 0.0), 0)
return loss
( Triplet Loss ) Code - Pytorch (scratch)
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.nn.modules.distance import PairwiseDistance
from torchvision.models import resnet18
class TripletLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, alpha):
self.margin = alpha
self.pdist = PairwiseDistance(p = 2)
def forward(self, anchor, pos, neg):
pos_dist = self.pdist.forward(anchor, pos)
neg_dist = self.pdist.forward(anchor, neg)
hingle_loss = torch.clamp(self.margin + pos_dist - neg_dist, min = 0.0)
loss = torch.mean(hinge_loss)
return loss
class FacenNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_dim = 128, pretrained = False):
self.backbone = resnet18(pretrained = pretrained)
# get input dimension
input_dim = self.backbone.fc.in_features
self.model.fc = nn.Linear(input_dim, hidden_dim)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.backbone(x) # get Embedding
x = F.normalize(x, p = 2, dim = 1) # L2 normalization
return x
( Triplet Loss ) Code - Pytorch (built-in)
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.TripletMarginLoss.html
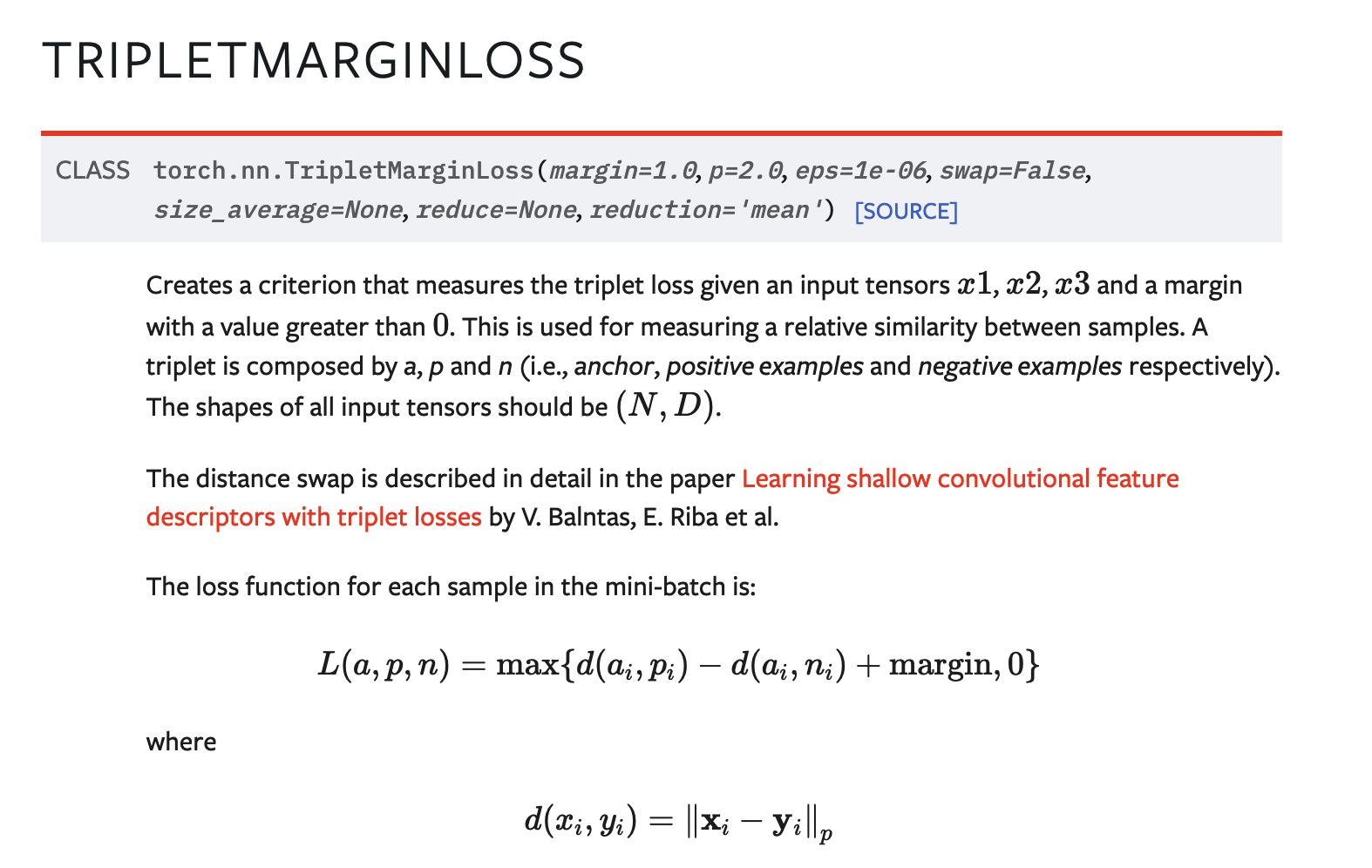
loss_fn = nn.TripletMarginLoss(margin = 0.2)
loss = loss_fn(anchor_embed, pos_embed, neg_embed)
(3) Image Retrieval
Image Retrieval의 종류
-
Content-based Image Retrieval
-
ex) finding closest content/object image from DB
-
Dataset
- Cars196 : http://ai.stanford.edu/~jkrause/cars/car_dataset.html
- CUB-200 : https://paperswithcode.com/dataset/cub-200-2011
- Stanford Online Products : https://cvgl.stanford.edu/projects/lifted_struct/
- In-Shop : https://mmlab.ie.cuhk.edu.hk/projects/DeepFashion/InShopRetrieval.html
-
-
Instance-based Image Retrieval
- ex) Landmark
[ Content-based Image Retrieval ]
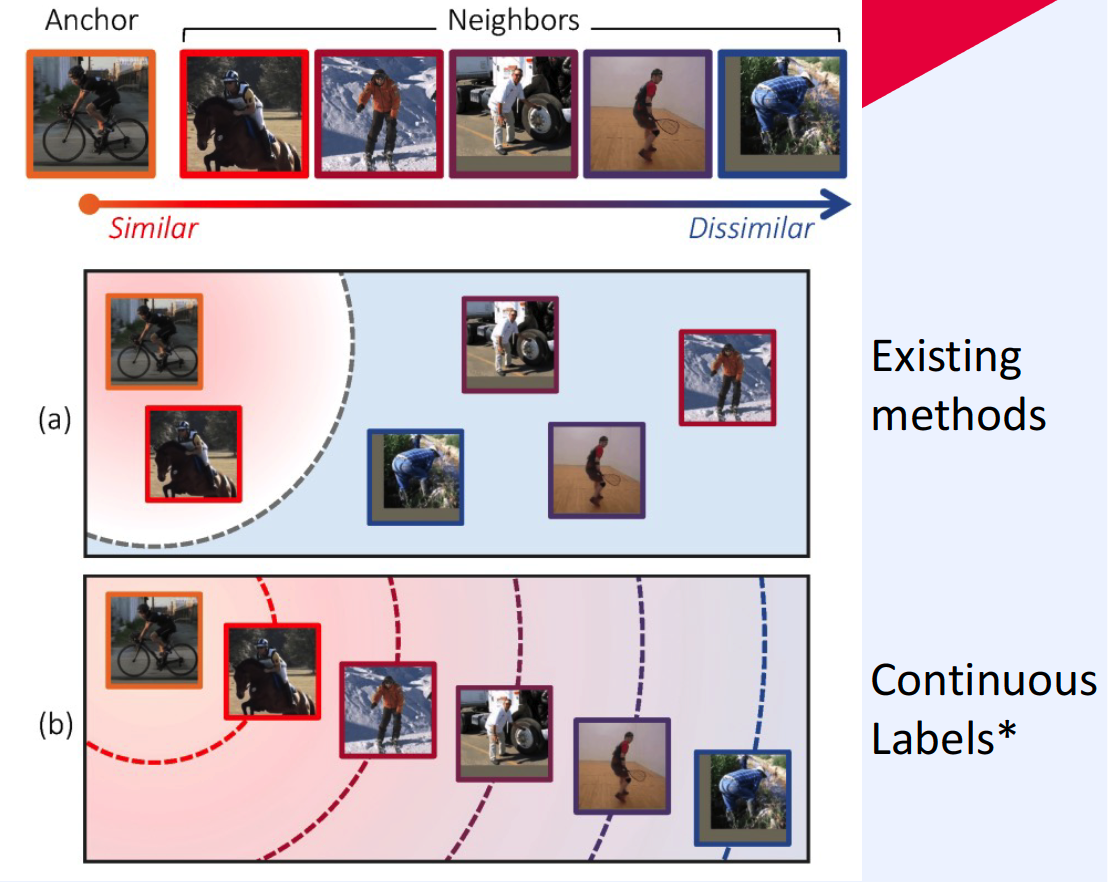
1. Beyond Binary Supervision (2019)
( Deep Metric Learning Beyond Binary Supervision (Kim et al., CVPR 2019) )
- continuous label ( discrete (X) )
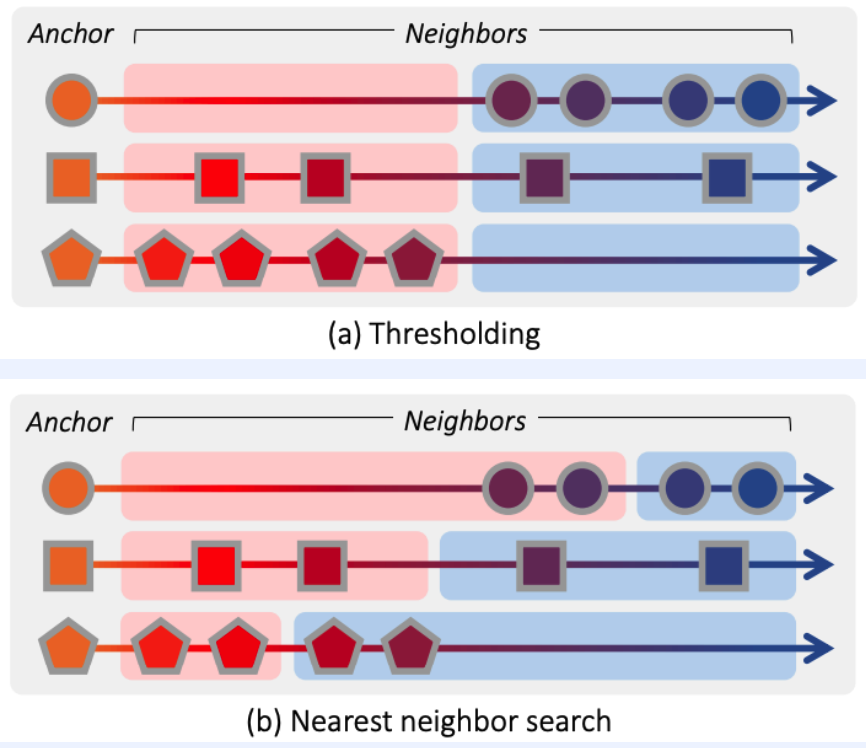
- loss function : \(\ell_{\operatorname{lr}}(a, i, j)=\left\{\log \frac{D\left(f_{a}, f_{i}\right)}{D\left(f_{a}, f_{j}\right)}-\log \frac{D\left(y_{a}, y_{i}\right)}{D\left(y_{a}, y_{j}\right)}\right\}^{2}\)
- \(a\) : anchor
- \(i\) : similar
- \(j\) : dissimilar
Code
- https://github.com/tjddus9597/Beyond-Binary-Supervision-CVPR19/tree/master/code
( Naive version )
class Naive_TripletLoss(Function):
def __init__(self, mrg=0.2):
super(Naive_TripletLoss, self).__init__()
self.mrg = mrg
def Squared_L2dist(self, x1, x2, norm=2):
eps = 1e-4 / x1.size(0)
diff = torch.abs(x1 - x2)
out = torch.pow(diff, norm).sum(0)
return out + eps
def forward(self, input):
a = input[0] # anchor
p = input[1] # positive
n = input[2] # negative
N = a.size(0) # #acnhor
Li = torch.FloatTensor(N)
for i in range(N):
Li[i] = (self.Squared_L2dist(a[i],p[i])-self.Squared_L2dist(a[i],n[i])+self.mrg).clamp(min=1e-12)
loss = Li.sum().div(N)
return loss
( Proposed version )
class Dense_TripletLoss(Function):
"""Log ratio loss function. """
def __init__(self, mrg=0.03):
super(Dense_TripletLoss, self).__init__()
self.mrg = mrg
self.pdist = Squared_L2dist(2)
def forward(self, input, gt_dist):
# "CONSIDERS DISTANCE"
m = input.size()[0]-1 # paired
a = input[0] # anchor
p = input[1:] # paired
# auxiliary variables
idxs = torch.arange(1, m+1).cuda()
indc = idxs.repeat(m,1).t() < idxs.repeat(m,1)
dist = self.pdist.forward(a,p)
# uniform weight coefficients
wgt = indc.clone().float()
wgt = wgt.div(wgt.sum())
loss = dist.repeat(m,1).t() - dist.repeat(m,1) + self.mrg
loss = loss.clamp(min=1e-12)
loss = loss.mul(wgt).sum()
return loss
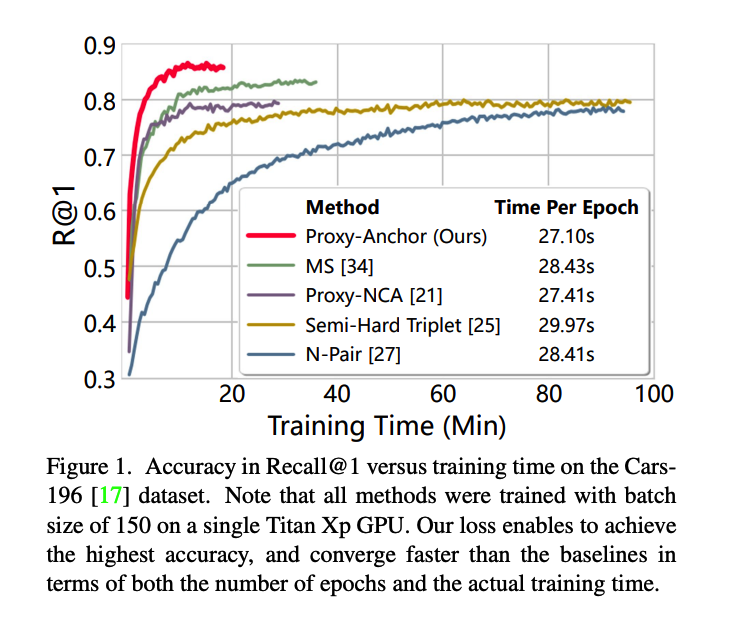
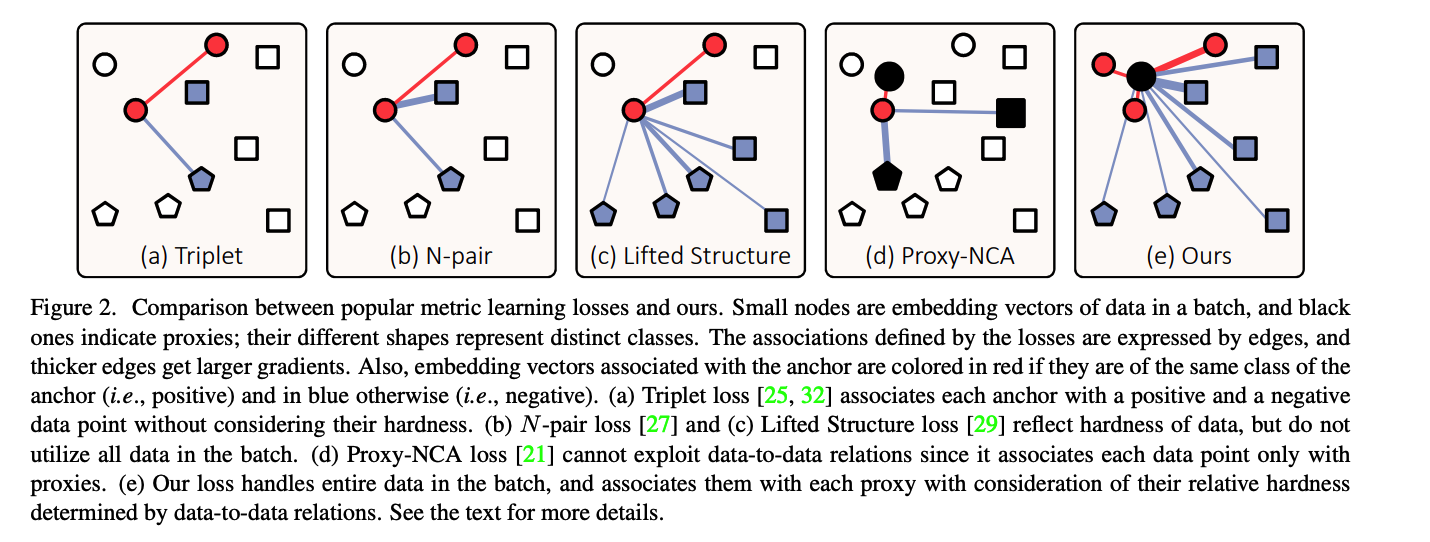
2. **Proxy Anchor Loss **(2020)
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/2003.13911.pdf
Exisiting metric learning losses
- (1) pair-based
- (2) proxy-based
Faster convergence!
Comparison with previous works
Loss Function (Proxy-NCA)
\(\begin{aligned} \ell(X) &=\sum_{x \in X}-\log \frac{e^{s\left(x, p^{+}\right)}}{\sum_{p^{-} \in P^{-}} e^{s\left(x, p^{-}\right)}} \\ &=\sum_{x \in X}\left\{-s\left(x, p^{+}\right)+\underset{p^{-} \in P^{-}}{\left.\operatorname{LSE} s\left(x, p^{-}\right)\right\}}\right. \end{aligned}\).
- Notation
- \(X\) : batch of embedding vectors
- \(x\) : embedding vector of input
- \(p^{+}\) : positive proxy
- \(P^{-}\) : set of negative proxies
- \(p^{-}\) : negative proxy
- \(s(\cdot, \cdot)\) : cosine similarity
- \(X\) : batch of embedding vectors
Loss Function (Proxy-Anchor)
\(\begin{aligned} \ell(X)=& \frac{1}{ \mid P^{+} \mid } \sum_{p \in P^{+}}[\operatorname{Softplus}(\operatorname{LSE}-\alpha(s(x, p)-\delta))] \\ &+\frac{1}{ \mid P \mid } \sum_{p \in X_{p}^{+}}\left[\operatorname{Softplus}\left(\operatorname{LSE}_{x \in X_{p}^{-}} \alpha(s(x, p)+\delta)\right)\right] \end{aligned}\).
- Notation
- \(\delta>0\) : margin
- \(\alpha>0\) : scaling factor
- \(P\) : set of ALL proxies
- \(P^{+}\) : set of POSITIVE proxies
- for each proxy \(p\), a batch of embedding vectors \(X\) is divided into…
- (1) \(X_{p}^{+}\) : positive embedding vectors of \(p\)
- (2) \(X-X_{p}^{+}\)
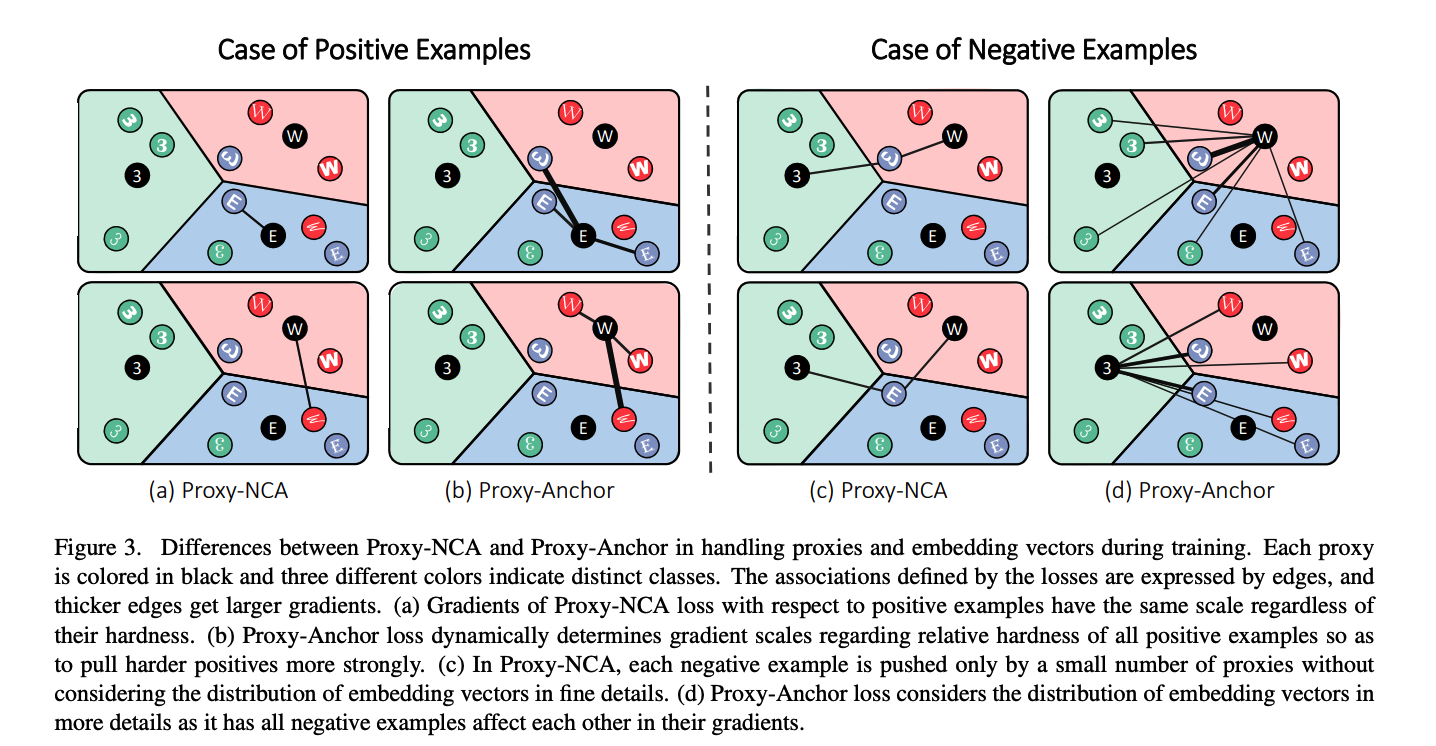
Comparison between..
- (1) Proxy-NCA
- (2) Proxy-Anchor