Transfer Learning with Time Series Data : A Systemetic Mapping Study
Contents
- Abstract
- Overview & Definitions
- Time Series (TS)
- TS problems
- Transfer Learning
- TL solution approachs
0. Abstract
Transfer Learning (TL) :
- relaxes the assumption that train & test data need to be drawn from same distn
- benefits from various TS domains
conduct a study of literature on TL with TS data
1. Overview & Definitions
(1) Time Series (TS)
- Time Series : \(T=\left[x_1, \ldots, x_n\right]\)
- data points \(x_i\) of length \(n\)
- Uni & Multi-variate TS
- Univariate : TS where \(x_i \in \mathbb{R}\).
- Multivariate : TS where each \(x_i\) is a d-dim vector of real values \(\left(x_i^1, \ldots, x_i^d\right), x_i^j \in \mathbb{R}\).
(2) TS problems
-
TS classification
- Assign a TS ( or subsequence TS ) a class \(c_i\), out of \(C=\left\{c_1, \ldots, c_n \mid n \geq 2\right\}\)
-
TS regression
- For TS \(T\), predict numeric value (\(y\)) / values (\(y_1, \ldots, y_n\))
-
TS clustering
-
Assign a TS ( or subsequence TS ) a cluster \(c_i\), out of \(C=\left\{c_1\right. \left.\ldots, c_n \mid n \geq 1\right\}\)
based on similarity measure \(\operatorname{Sim}(a, b)\)
-
-
TS anomaly detection
- Assign a TS ( or subsequence TS ) to one of \(\left\{c_{\text {normal }}, c_{\text {anomaly }}\right\}\)
-
TS forecasting
- Given \(T=\left[x_1, \ldots, x_n\right]\), predict..
- (1) single-step : \(x_{n+1}\)
- (2) multi-step : \(x_{n+1}, \ldots, x_{n+m}\)
- Given \(T=\left[x_1, \ldots, x_n\right]\), predict..
(3) Transfer Learning
-
transfer knowledge from one domain to another simliar domain
-
to improve the generalization ability
Notation
-
(SOURCE) domain
- source domain : \(D_S\)
- source domain learning task : \(T_S\)
- model : \(f_S(\cdot)\)
-
(TARGET) domain
- target domain : \(D_T\)
- target domain learning task : \(T_T\)
- model : \(f_T(\cdot)\)
-
Goal : improve \(f_T(\cdot)\) using the knowledge in \(D_S\) & \(T_S\) ,
where \(D_S \neq D_T\) or \(T_S \neq T_T\)
Types of TL
- (1) Domain Adaptation : \(D_S \neq D_T\)
- (2) Task Adaptation : \(T_S \neq T_T\)
- Combination = (1) + (2)
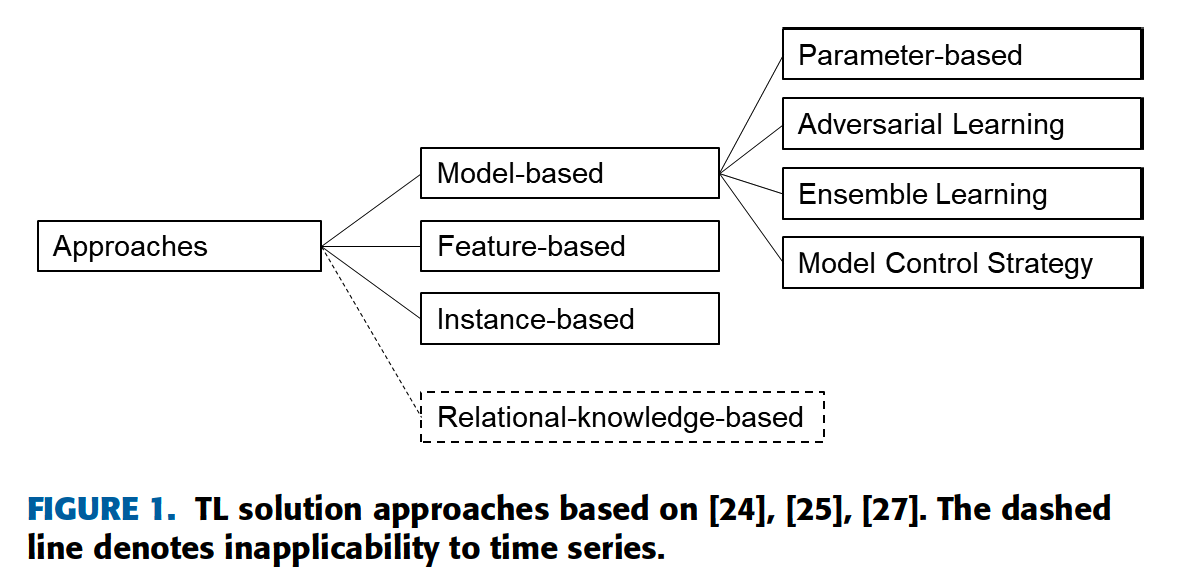
(4) TL solution approachs
-
instance-based
- selection or reweighting of samples from the source domain
- assumption ) instance from source domain are more/less similar to the set of target domain instances
-
feature-representation-based ( = mapping-based )
-
map into common feature space
( place of features, representating characteristics of both domains )
-
-
parameter-based ( = network transfer )
- use pre-trained model
-
relational-knowledge-based
- not applicable to TS