( 참고 : “FastCampus, 데이터 엔지니어링 올인원” )
[ Data Engineering ]
Spotify Project
Goal : audio feature를 가져와서 artists 사이의 유사도 확인하기
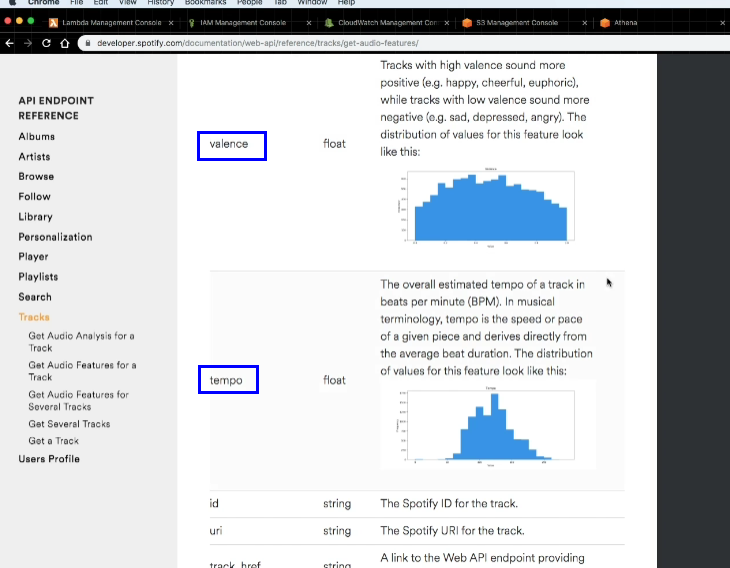
- spotify api의 reference를 확인하면 위와 같은 종류들의 audio feature들이 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
step 1) Athena에서 필요한 데이터 가져오기
step 2) 해당 데이터를 MySQL에 저장하기 ( MySQL안에 있는 table에서 작업할 것이다 )
Artists의 노래들의 average를 구할 것!
- Normalization ( max & min 필요 )
- Euclidean distance
우선, MySQL에서 table을 만든다.
CREATE TABLE related_artists (artist_id VARCHAR(255), y_artist VARCHAR(255), distance FLOAT, PRIMARY KEY(artist_id,y_artists)) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
순서 요약
- step 1) artists 별 average 가져오기
- step 2) max & min 가져오기
- step 3) artists마다 for loop 돌면서, artists 간의 distance 구한다
- step 4) insert row!
Step 1 : Artist 아이디 & audio features 평균값들 가져오기
(1-1) Query 문
query = """
SELECT
artist_id,
AVG(danceability) AS danceability,
AVG(energy) AS energy,
AVG(loudness) AS loudness,
AVG(speechiness) AS speechiness,
AVG(acousticness) AS acousticness,
AVG(instrumentalness) AS instrumentalness
FROM
top_tracks t1
JOIN
audio_features t2 ON t2.id = t1.id AND CAST(t1.dt AS DATE) = DATE('2019-11-18') AND CAST(t2.dt AS DATE) = DATE('2019-11-18')
GROUP BY t1.artist_id
LIMIT 100
"""
(1-2) Query 실행
아래의 코드 세 줄로써 query의 결과를 받을 수 있다.
( 각각의 세부적인 함수는 뒤에 참고 )
r = query_athena(query, athena)
results = get_query_result(r['QueryExecutionId'], athena)
artists = process_data(results)
Step 2. Artist 별 Min & Max 가져오기
- 뒤에 normalization 위해서 필요!
(2-1) Query 문
query = """
SELECT
MIN(danceability) AS danceability_min,
MAX(danceability) AS danceability_max,
MIN(energy) AS energy_min,
MAX(energy) AS energy_max,
MIN(loudness) AS loudness_min,
MAX(loudness) AS loudness_max,
MIN(speechiness) AS speechiness_min,
MAX(speechiness) AS speechiness_max,
ROUND(MIN(acousticness),4) AS acousticness_min,
MAX(acousticness) AS acousticness_max,
MIN(instrumentalness) AS instrumentalness_min,
MAX(instrumentalness) AS instrumentalness_max
FROM
audio_features
"""
(2-2) Query 실행
r = query_athena(query, athena)
results = get_query_result(r['QueryExecutionId'], athena)
avgs = process_data(results)[0]
Step 3. Normalization & Step 4. Insert Rows
metrics = ['danceability', 'energy', 'loudness', 'speechiness', 'acousticness', 'instrumentalness']
for i in artists:
for j in artists:
dist = 0
for k in metrics:
## 1) Normalize
x = float(i[k])
x_norm = normalize(x, float(avgs[k+'_min']), float(avgs[k+'_max']))
y = float(j[k])
y_norm = normalize(y, float(avgs[k+'_min']), float(avgs[k+'_max']))
## 2) Euclidean distance 계산
dist += (x_norm-y_norm)**2
dist = math.sqrt(dist)
data = {
'artist_id': i['artist_id'],
'y_artist': j['artist_id'],
'distance': dist
}
## 3) Insert Row
insert_row(cursor, data, 'related_artists')
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
Functions
1) query_athena :
-
mysql의 경우, (pymysql을 통해) 바로 데이터를 받을 수 있다. athena는 그 형식이 약간 다르다.
-
아래의
qurey_athena라는 함수를 통해, query하는 함수를 만들어준다.( athena의 함수
athena.start_query_execution함수 사용 )
def query_athena(query, athena):
response = athena.start_query_execution(
QueryString=query,
QueryExecutionContext={
'Database': 'production'
},
ResultConfiguration={
'OutputLocation': "s3://athena-panomix-tables/repair/",
'EncryptionConfiguration': {
'EncryptionOption': 'SSE_S3'
}
}
)
return response
2) get_query_result :
-
query_id를 넣어서, query의 결과를 받아낸다.
-
( athena의 함수
athena.get_query_execution함수 사용 )이 결과가 얼마나 소요될 지 알 수 없음. 따라서, while문을 통해 state가 SUCCEEDED일 때 n초 쉬고 계속 받아내기! ( error면 break )
-
( athena의 함수
athena.get_query_result함수 사용 )결과 받아내기
def get_query_result(query_id, athena):
response = athena.get_query_execution(
QueryExecutionId=str(query_id)
)
while response['QueryExecution']['Status']['State'] != 'SUCCEEDED':
if response['QueryExecution']['Status']['State'] == 'FAILED':
logging.error('QUERY FAILED')
break
time.sleep(5)
response = athena.get_query_execution(
QueryExecutionId=str(query_id)
)
response = athena.get_query_results(
QueryExecutionId=str(query_id),
MaxResults=1000
)
return response
3) process_data :
- 위의 2)의 결과 얻어낸 결과( loudness, acousticness, …. )를 input으로 받는다.
- columns를 만든다 ( loudness, acousticness, …. )
- dictionary 형식으로 저장된 데이터에서 정보들 뽑아내서 empty list에 담기
- 정보가 다 담긴 뒤, 해당 list 반환!
def process_data(results):
columns = [col['Label'] for col in results['ResultSet']['ResultSetMetadata']['ColumnInfo']]
listed_results = []
for res in results['ResultSet']['Rows'][1:]:
values = []
for field in res['Data']:
try:
values.append(list(field.values())[0])
except:
values.append(list(' '))
listed_results.append(dict(zip(columns, values)))
return listed_results
4) normalize :
- normalize하는 함수 ( sklearn의 MinMaxScaler와 동일 )
def normalize(x, x_min, x_max):
normalized = (x-x_min) / (x_max-x_min)
return normalized
Result
아래와 같이, artist 별 audio feature에 기반한 유사도 정보(Euclidean Distance)가 잘 저장된 것을 확인할 수 있다!
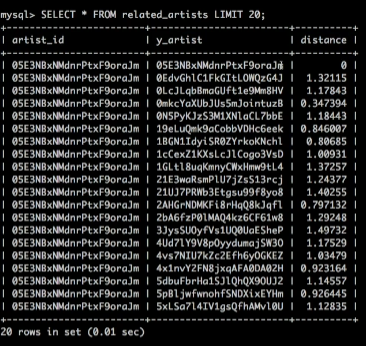
유사도 찾기
SELECT p1.name, p2.name, p1.url, p2.url, p2.distance
FROM artists p1
JOIN (SELECT t1.name, t1.url, t2.y_artist, t2.distance
FROM artists t1
JOIN related_artists t2
ON t2.artist_id = t1.id
) p2
ON p2.y_artist=p1.id
WHERE distance != 0
ORDER BY p2.distance ASC LIMIT 20;
