1.Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space (2013)
목차
- Abstract
- Introduction
-
Model Architectures
- NNLM ( Feedforward NNLM )
- RNNLM ( Recurrent NNLM )
- New Log-Linear Models
- CBOW
- Skip-gram
Abstract
Word2Vec : (1) Skip-gram & (2) CBOW
- able to capture the similarity of words
- improvement in accuracy & speed
1. Introduction
Previous models : N-gram … similarity (X) & use indices (O)
Proposes “distributed representations of words”
( \(\leftrightarrow\) previous ones were “SPARSE” representation….one-hot encoded vector )
2. Model Architectures
This paper focuses on “distributed representations” of words, learned by NN
Training Complexity : \(O=E \times T \times Q\)
- \(E\) : training epoch
- \(T\) : number of words
- \(Q\) : (defined further for each model architecture)
use SGD & BP
2-1. NNLM (Feedforward NNLM)
consists of 1) input, 2) projection, 3) hidden, 4) output layers
1) Input layer
- \(N\) words are one-hot encoded ( = 1-of-V coding )
2) Projection layer
- dimension : \(N \times D\)
- shared projection matrix
3) Hidden layer
-
projection-hidden layer : complex computation
( since values in projection layer are dense )
-
compute “probability distribution” over all the words in vocabulary
4) Output layer
- dimension : \(V\)
Time complexity : \(Q=(N\times D) + (N\times D \times H) + (H \times V)\)
-
last term \((H \times V)\) is the dominating term
\(\rightarrow\) use Negative Sampling, Hierarchical softmax to reduce this!
\(\rightarrow\) from \(V\) to \(\log_2V\)
2-2. RNNLM (Recurrent NNLM)
overcome limitation of NNLM ( = need to specify context length, N )
RNN :
-
input, hidden, output layer (no projection layer)
-
information from past can be represented by “hidden layer state” \(h_t\)
( updated by \(x_t\) and \(h_{t-1}\) )
Time complexity : \(Q=(H\times H) + (H \times V)\)
-
last term \((H \times V)\) is the dominating term
\(\rightarrow\) use Negative Sampling, Hierarchical softmax to reduce this!
\(\rightarrow\) from \(V\) to \(\log_2V\)
3. New Log-Linear Models
propose 2 models, (1) CBOW & (2) Skip-gram
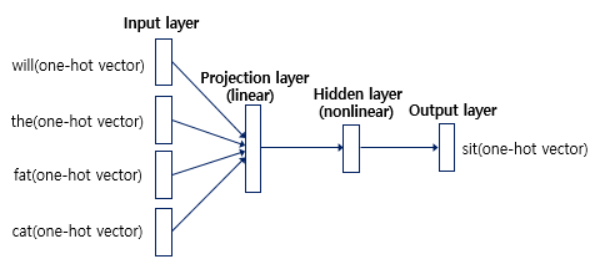
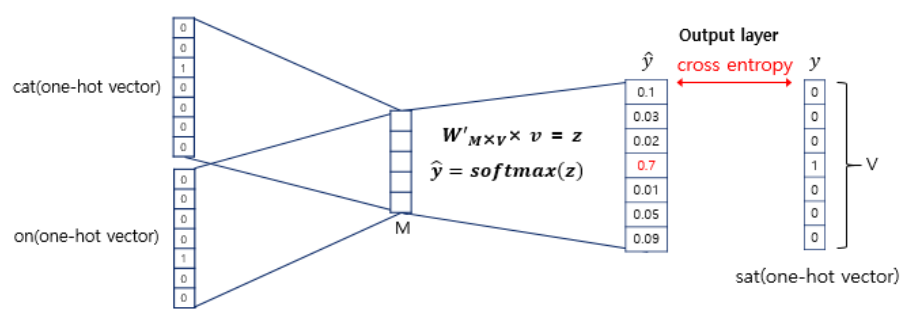
3-1. CBOW
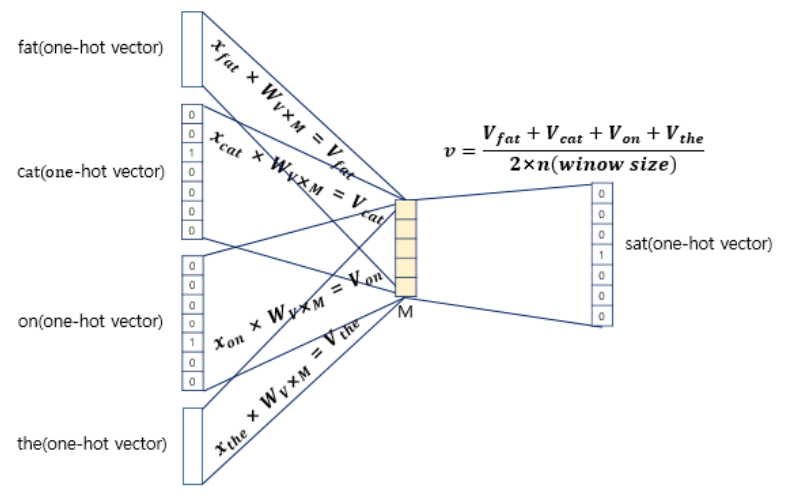
\(Q = (N \times D) + (D \times \log_2(V))\).
3-2. Skip-gram
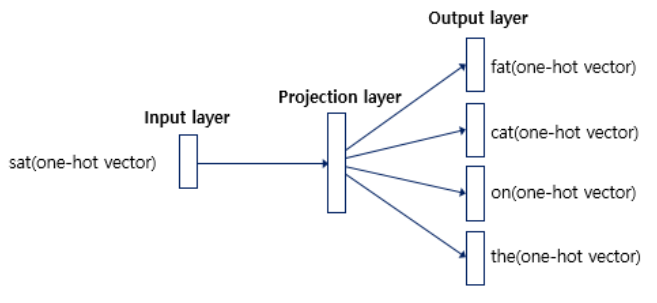
\(Q = C \times (D + D \times \log_2(V))\).
