[Explicit DGM] 01. Auto Encoders
( 참고 : KAIST 문일철 교수님 : 한국어 기계학습 강좌 심화 2)
Contents
- Implicit vs Explicit distribution model
- Deep Generative Model 소개
- Autoencoder
- Stacked Denoising Autoencoders
1. Implicit vs Explicit distribution model
Explicit : distribution에 대한 명시적 가정 O
- ex) VAE
Implicit : distribution에 대한 명시적 가정 X
- ex) GAN
2. Deep Generative Model 소개
Deep Generative Model (DGM)
- 딥러닝을 활용한 생성모델
- 새로운 데이터를 잘 생성해내기 위해, 딥러닝을 활용
DGM의 갈래
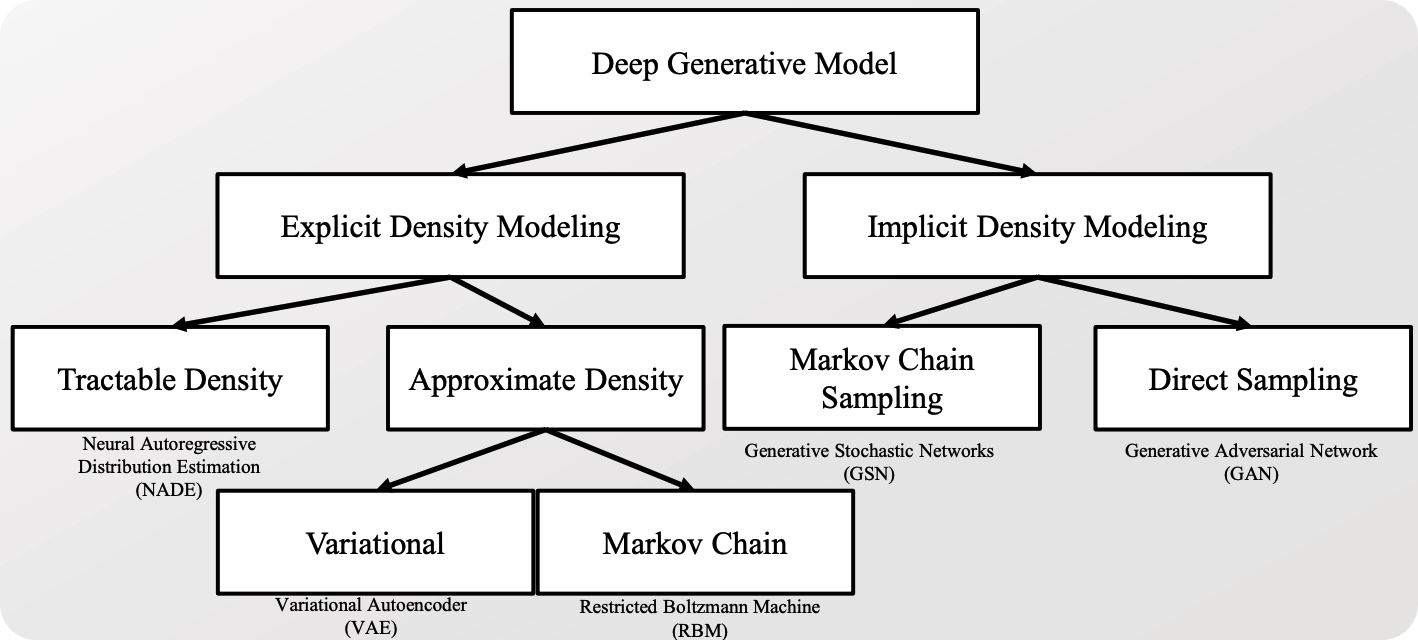
- 대표적인 DGM 모델 :
- Explicit한 방법론에서는 VAE
- Implicit한 방법론에서는 GAN
3. Autoencoder
-
목표 : input과 가장 유사한 output을 만들기
-
핵심 : 데이터의 핵심만을 잘 포착한 저차원으로 임베딩하기
일반적인 구조 : Encoder + Decoder
- Encoder : \(h(\cdot)\)
- \(h(x)=g(a(x))=\sigma(b+W x)\).
- Decoder : \(o(\cdot)\)
- \(\hat{x}=o(\hat{a}(x))=\sigma\left(c+W^{*} h(x)\right)\).
- notation
- \(W,b\) : encoder의 파라미터
- \(W^{*},c\) : decoder의 파라미터
Loss Function
- (1) CE ( Cross Entropy )
- \(l(f(x))=-\sum_{d=1}^{D}\left(x_{d} \log \left(\hat{x}_{d}\right)+\left(1-x_{d}\right) \log \left(1-\hat{x}_{d}\right)\right)\).
- (2) MSE ( Mean Squared Error )
- \(l(f(x))=\frac{1}{2} \sum_{d=1}^{D}\left(\hat{x}_{d}-x_{d}\right)^{2}\).
위 모델에서, encoder & decoder을 NN을 사용하면, DEEP generative model (DGM)이 된다.
4. Stacked Denoising Autoencoders
DENOISING autoencoder
-
이름에서도 알 수 있 듯, 노이즈를 제거 ( 보다 엄밀하겐, 노이즈에 robust한 ) autoencoder이다.
-
이러한 denoising autoencoder을 여러개의 MLP를 쌓아서 만든 것이 Stacked Denoising Autoencoder 이다.
Autoencoder vs DENOISING autoencoder
- Input의 차이
- AE : \(x\)
- DAE : \(x\) + noise ( = \(\tilde{x}\) )
- 그 외에는 전부 동일하다.
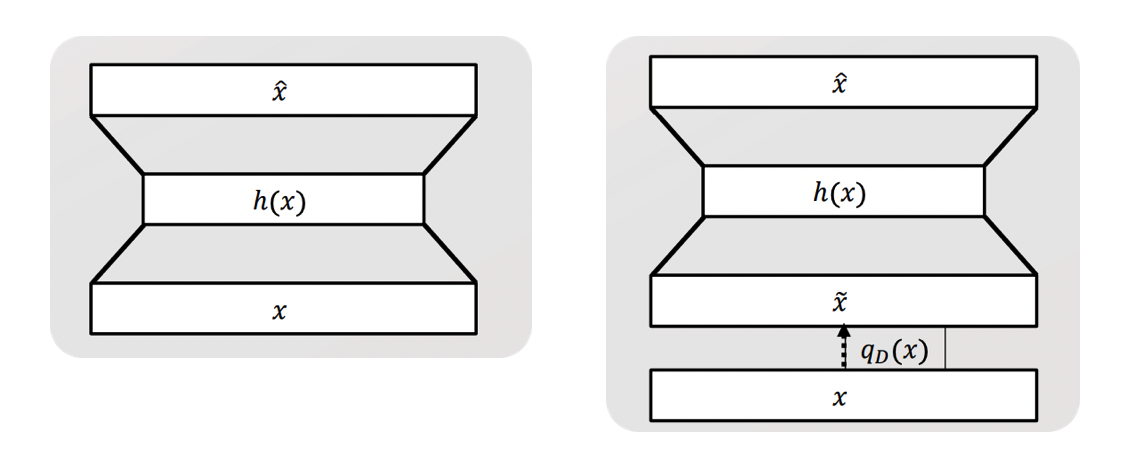
Noise Process : input에 noise를 더해주는 과정
- \(\tilde{x}=q_{D}(x)\).
- 예시 )
- Additive Gaussian noise : \(q_{D}(x)=x+\epsilon, \epsilon \sim N\left(\mu_{D}, \Sigma_{D}\right)\)
- Masking noise : \(q_{D}(x)=x \epsilon_{d}, \epsilon_{d} \sim \operatorname{Bernoulli}(p)\)
수식도, 위의 input이 다르다는 점을 제외하고는 전부 동일하다!
일반적인 구조 : Encoder + Decoder
- Encoder : \(h(\cdot)\)
- \(h(x)=g(a(\tilde{x}))=\sigma(b+W \tilde{x})\).
- Decoder : \(o(\cdot)\)
- \(\hat{x}=o(\hat{a}(\tilde{x}))=\sigma\left(c+W^{*} h(\tilde{x})\right)\).
Loss Function
- (1) CE ( Cross Entropy )
- \(l(f(x))=-\sum_{d=1}^{D}\left(x_{d} \log \left(\hat{x}_{d}\right)+\left(1-x_{d}\right) \log \left(1-\hat{x}_{d}\right)\right)\).
- (2) MSE ( Mean Squared Error )
- \(l(f(x))=\frac{1}{2} \sum_{d=1}^{D}\left(\hat{x}_{d}-x_{d}\right)^{2}\).
요약
- input이 동일하더라도, noise가 더해지는 과정때문에 서로 다른 output이 다를 수 있다 ( stochasticity 부여 )
- 하지만, output 생성 과정은 여전히 deterministic하다. input만 stochastic 할 뿐이다.
