[Paper Review] 03.On Buggy Resizing Libraries and Surprising Subtleties in FID Calculation
Contents
- Abstract
- Preliminaries
- FID Calculation
- Image Resizing
- Clean FID
0. Abstract
Investigate the sensitivity of FID score
- FID score : widely used to evaluate generative models
- BUT, each FID implementation uses a different low-level image processing process
Numerous subtle choices need to be made for FID calculation!
( lack of consistencies….lead to vastly different FID scores )
make comparison difficult! only meaningful WITHIN the same paper
Choices
- 1) selecting what image resizing library to use
- 2) choosing what interpolation kernel to use
- 3) what encoding to use when representing images
1. Preliminaries
(1) FID Calculation
measure the gap between 2 distributions
- 1) training set
- 2) samples from generator
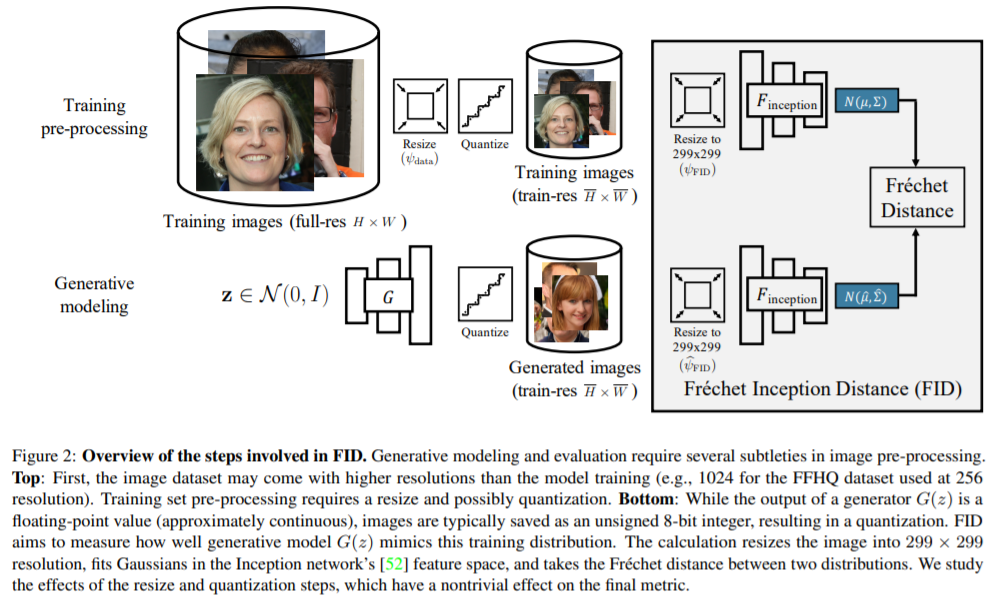
Dataset pre-processing
real image : \(\mathbf{x} \sim p_{\text {data }}(\mathbf{x})\)
- where \(x \in \mathbb{Z}^{H \times W \times 3}\)
- training GANs at original resolution is often prohibitively expensive
\(\rightarrow\) lower resolution versions of original dataset is common! downsample
( resize function : \(\psi_{\text {data }}\) )
Downsampling
- 1) antialiasing step
- integer \(\rightarrow\) floating point number ( \(\mathbb{Z} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) )
- 2) quantization step
- added afterwards to cast back to \(\mathbb{Z}\)
- images can be potentially saved to disk
Result
-
low-res real images : \(\overline{\mathbf{x}} \sim p_{\text {data }}(\overline{\mathbf{x}})\)
( where \(\overline{\mathbf{x}} \in \mathbb{Z}^{\bar{H} \times \bar{W} \times 3}\) )
Evaluating a generator
common method for evaluating generator :
-
pass both REAL & GENERATED images through a FEATURE EXTRACTOR \(\mathcal{F}\) ,
fitting a Gaussian distribution and measure FID score
-
feature extractor \(\mathcal{F}\) = Inception V3 model
These operations are represented by…
- \(Q\) for reference images \(\mathrm{x}\)
- \(\mathbf{f} =\mathcal{F}\left(\psi_{\mathrm{FID}}\left(Q\left(\psi_{\mathrm{data}}(\mathbf{x})\right)\right)\right)\).
- \(\widehat{Q}\) for synthesized images \(G(\mathbf{z})\)
- \(\hat{\mathbf{f}} =\mathcal{F}\left(\widehat{\psi}_{\mathrm{FID}}(\widehat{Q}(G(\mathbf{z})))\right)\).
FID
- the mean \((\mu, \hat{\mu})\) and covariance matrix \((\Sigma, \widehat{\Sigma})\) of the corresponding set of features \(\mathbf{f}\) and \(\hat{\mathrm{f}}\)
- \(\mathrm{FID}= \mid \mu-\hat{\mu} \mid _{2}^{2}+\operatorname{Tr}\left(\Sigma+\widehat{\Sigma}-2(\Sigma \widehat{\Sigma})^{1 / 2}\right)\).
(2) Image Resizing
- \(\psi_{\mathrm{FID}}\) & \(\hat{\psi_{\mathrm{FID}}}\) could be either DOWN/UP sampling
- Libraries
- 1) PIL v8.0.1
- 2) OpenCV v3.4.2
- 3) Tensorflow v2.0
- 4) PyTorch v1.3.1
2. Clean FID
provide an easy-to-use library, clean-fid at..
github.com/GaParmar/clean-fid
