HydraLoRA; An Asymmetric LoRA Architecture for Efficient Fine-Tuning (NeurIPS 2024)
Tian, Chunlin, et al. "HydraLoRA: An Asymmetric LoRA Architecture for Efficient Fine-Tuning." NeurIPS (2024)
( https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.19245 )
Contents
- (1) Abstract
- (2) Limitation of LoRA
- (3) HydraLoRA
- LoRA
- HydraLoRA
- (4) Workflow of HydraLoRA
- Fine-tuning
- Inference
1. Abstract
(1) LoRA: Widely used Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) technique
(2) Limitation of LoRA: Often underperform compared to full fine-tuning
- ( especially in complex datasets )
(3) Proposal: HydraLoRA
- LoRA framework with an asymmetric structure that eliminates the need for domain expertise
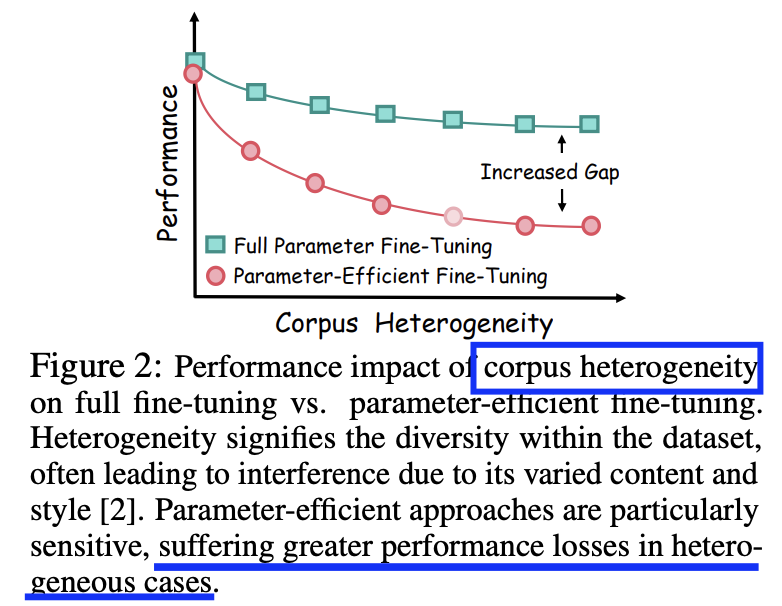
2. Limitation of LoRA
Underperform compared to full fine-tuning, especially in heterogeneous datasets
3. HydraLoRA
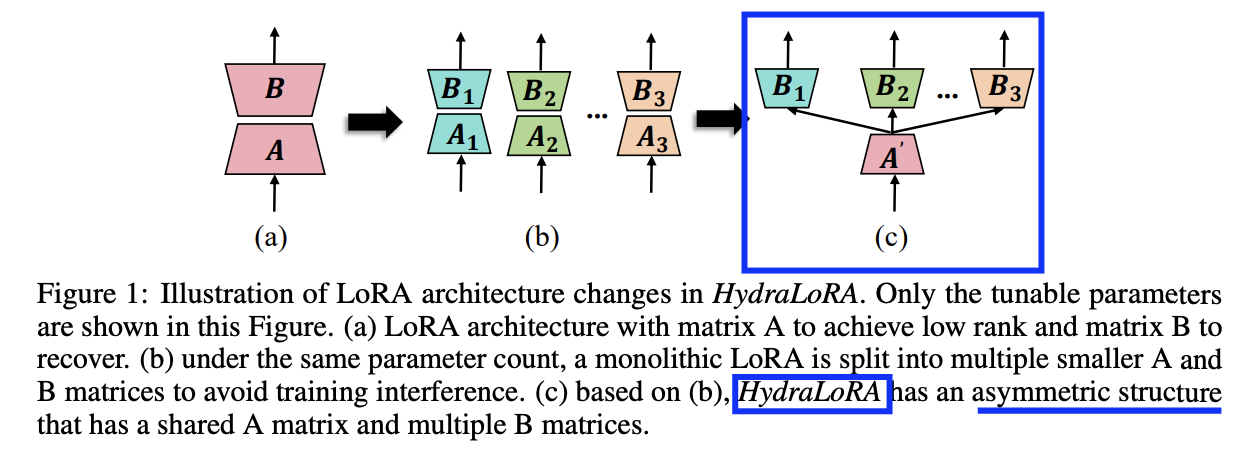
(1) LoRA
\(y \prime=y+\Delta y=W_0 x+B A x\),
-
\(y \in R^{\mathrm{d}}\): output
-
\(x \in R^{\mathrm{k}}\): input
-
\(B \in R^{\mathrm{d \times r}}, A \in R^{\mathrm{r \times k}}\) with \(r \ll \min (d, k)\).
-
\(B\) is initialized with zeroes
-
\(A\) is initialized with Kaiming Uniform [14]
\(\rightarrow\) to force \(\Delta y=0\) at the beginning
-
(2) HydraLoRA
\(\begin{aligned} W & =W_0+\Delta W \\ & =W_0+\sum_{i=1}^N \omega_i \cdot B_i A \end{aligned}\).
- \(B_i \in \mathbb{R}^{d \times r}\) \(\rightarrow\) \(N\) matrices
- \(A \in \mathbb{R}^{r \times k}\). \(\rightarrow\) single matrix (shared)
- \(\omega_i\): modulates these contribution weights for head \(B_i\)
4. Workflow of HydraLoRA
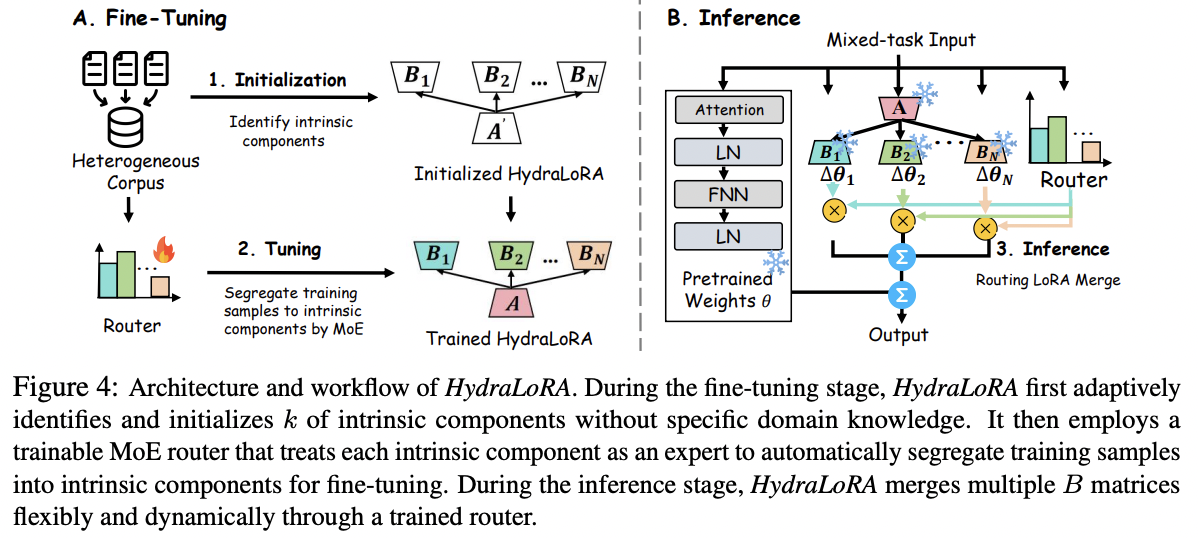
(1) Fine-tuning
MoE (Mixture-of-Experts) = Experts are selectvely activated by a gating mechanism (router)
a) Set of experts
To achieve a unified approach of multiple \(B\) matrices…
\(\rightarrow\) Define a set of experts: \(\left(E_1, \ldots, E_N\right)\)
Interpretation
- (1) Shared matrix \(A\) : inherently captures collaborative knowledge to augment intra-gains
- (2) Different matrices \(B\) : foster knowledge modularity to mitigate fine-tuning inter-offsets
b) Router
\(\omega_i=\operatorname{softmax}\left(W_g^T x\right)\).
- trainable weights (transformation matrix) \(W_g \in \mathbb{R}^{r \times N}\)
\(\rightarrow\) becomes a gating scores \(\left(\omega_1, \ldots, \omega_N\right)\)
c) HydraLoRA
\(y=W_0 x+\sum_{i=1}^N \omega_i E_i A x \quad(M o E)\).
- where \(N\) denotes the number of experts, i.e., \(B\) matrices.
(2) Inference
Merges adapters by enabling routing computation based on the input!
