From Sparse to Soft Mixture of Experts (ICLR 2024)
Puigcerver, Joan, et al. "From sparse to soft mixtures of experts." ICLR 2024
( https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.00951 )
참고:
- https://aipapersacademy.com/from-sparse-to-soft-mixture-of-experts/
Contents
- Background
- Sparse vs. Soft MoE
- Sparse MoE
- Soft MoE
- Architecture
- Notation
- Details
1. Background
Trend: 점점 더 커지는 모델
\(\rightarrow\) 높아지는 computational cost
\(\rightarrow\) Mixure of Experts (MoE)의 등장! (used by GPT-4)
2. Sparse vs. Soft MoE
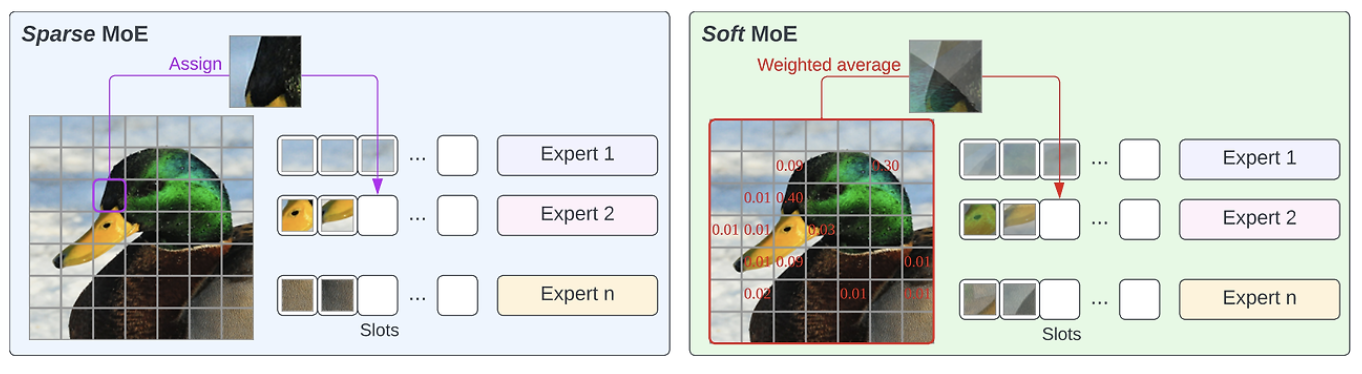
3. Sparse MoE
데이터를 적절한 expert에 할당(hard, sparse, discrete)해서 풀자!
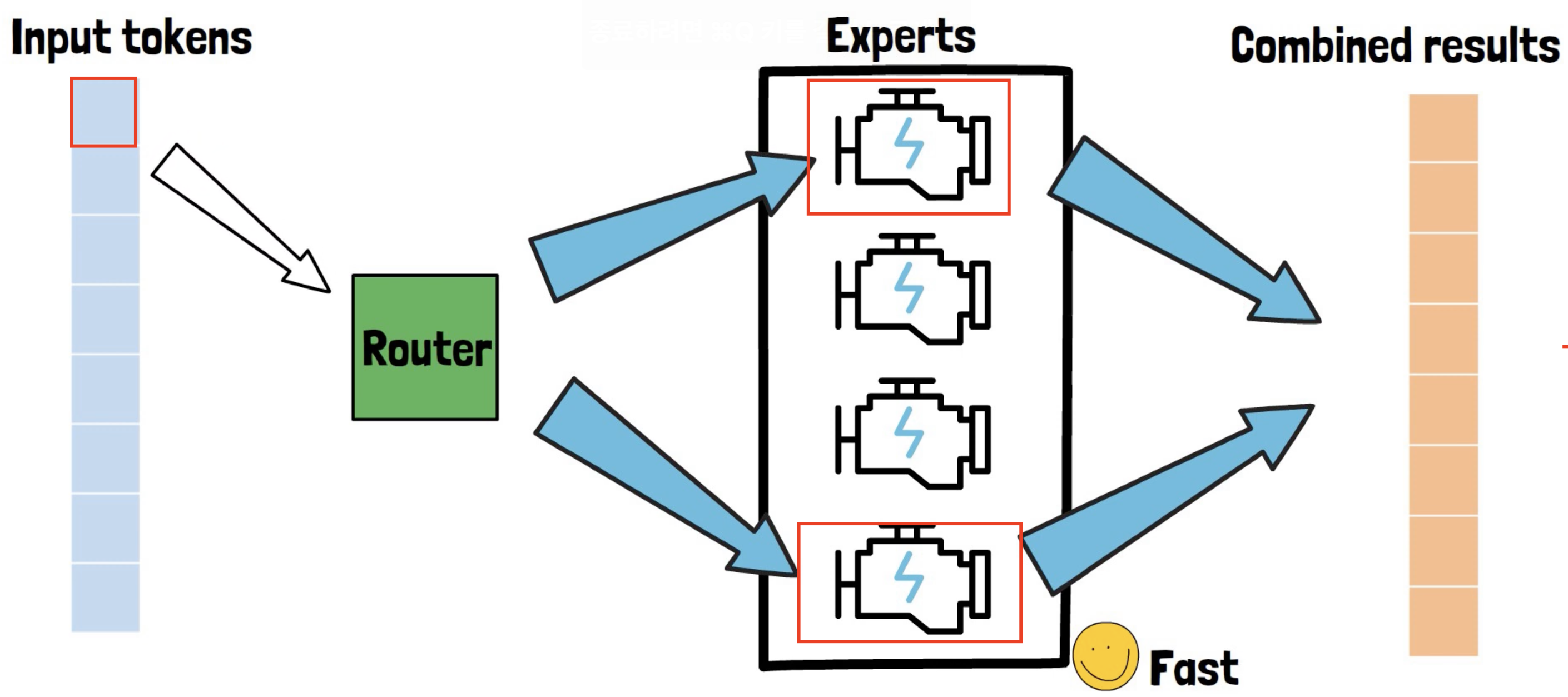
Router의 역할 = token을 적절한 expert에 할당해줌
Sparse MoE의 Issue?
- Discrete optimization
- Hard to scale the # of experts
3. Soft MoE
Goal = MoE의 한계점을 극복
핵심
- 기존) 하나의 token \(\rightarrow\) K개의 expert에 할당
- 제안) 모든 token의 combination \(\rightarrow\) 모든 expert에 할당
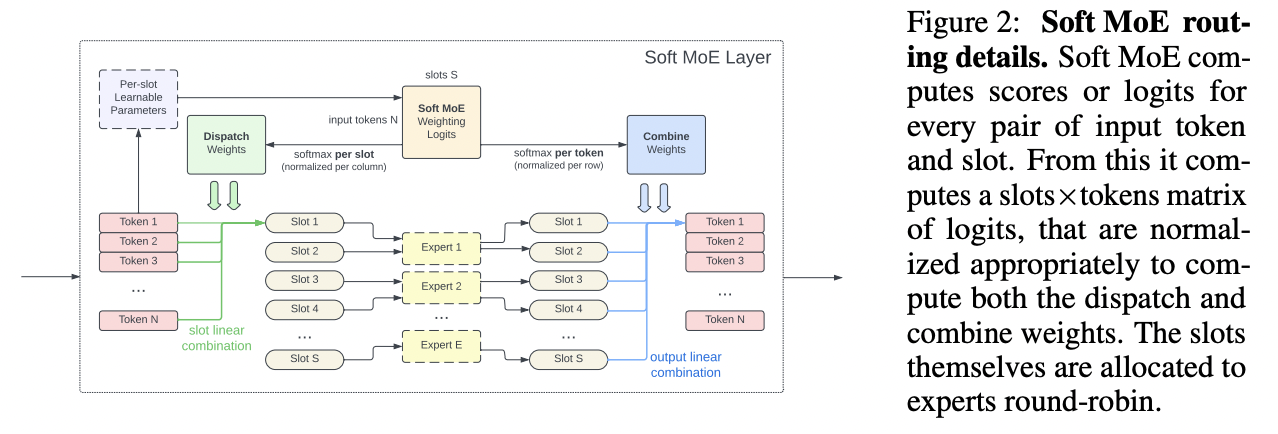
(1) Architecture
(2) Notation
- Input token: \(\mathbf{X} \in \mathbb{R}^{m \times d}\)
- \(m\): token의 개수
- \(d\): dimension
- \(n\)개의 expert
- \(\left\{f_i: \mathbb{R}^d \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^d\right\}_{1=n}\).
(3) Details
Expert는 (token)대신 slot을 process한다
- 각 expert는 \(p\)개의 slot을 처리함 (\(\Phi \in \mathbb{R}^{d \times(n \cdot p)}\))
[Step 1] Input slots: \(\tilde{\mathbf{X}} \in \mathbb{R}^{(n\cdot p) \times d}\)
-
Convex combinations of all the \(m\) input tokens
-
\(\tilde{\mathbf{X}}=\mathbf{D}^{\top} \mathbf{X} \in \mathbb{R}^{n\cdot p \times d}\).
-
Dispatch weights = \(\mathbf{D} \in \mathbb{R}^{m\times n\cdot p}\): token & slot과의 관계
-
where \(\mathbf{D}_{i j}=\frac{\exp \left((\mathbf{X} \boldsymbol{\Phi})_{i j}\right)}{\sum_{i^{\prime}=1}^m \exp \left((\mathbf{X} \boldsymbol{\Phi})_{i^{\prime} j}\right)}\)
( = Softmax over the columns of \(\mathbf{X} \Phi\). )
-
[Step 2] Expert가 slot을 처리함 (on rows of \(\tilde{\mathbf{X}})\)
- Output slots: \(\tilde{\mathbf{Y}}_i=f_{\lfloor i / p]}\left(\tilde{\mathbf{X}}_i\right)\).
[Step 3] Output에 대해 linear combination (\(\mathbf{Y}=\mathbf{C} \tilde{\mathbf{Y}}\))
-
Convex combination of all ( \(n \cdot p\) ) output slots
-
\(\mathbf{C}_{i j}=\frac{\exp \left((\mathbf{X} \Phi)_{i j}\right)}{\sum_{j^{\prime}=1}^{n-p} \exp \left((\mathbf{X} \Phi)_{i j^{\prime}}\right)}\).
-
Combine weights = \(\mathbf{D} \in \mathbb{R}^{m\times n\cdot p}\)
( = Softmax over the rows of \(\mathbf{X} \Phi\). )
-
기타
- (Sparse MoEs와 마찬가지로) Transformer’s MLP blocks를 Soft MoE blocks로 대체함
- Typically replace the second half of MLP blocks
- # slot = key hyperparameter of Soft MoE layers
- \(\because\) Time complexity가 (# expert보다) # slot에 의존함
