FNSPID: A Comprehensive Financial News Dataset in Time Series
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2402.06698
0. Abstract
Background in financial market prediction
- [Traditional] Reliance on quantitative factors
- [Recent] + Sentiment data from financial news (feat. LLM)
Limitations of Existing Approaches
- (1) Lack of large-scale datasets
- (2) Insufficient alignment of numerical & sentiment data
[Proposed] FNSPID
- tldr; Financial News & Stock Price Integration Dataset
- Large-scale & time-aligned financial data
- [TS] 29.7M stock price
- [Text] 15.7M financial news
- Coverage
- 4,775 S&P 500 companies
- Time span: 1999–2023
- Sources: 4 stock market news websites
Key Properties
- Larger scale & Higher diversity
- Explicit inclusion of sentiment information
Findings
- a) Dataset size & quality \(\rightarrow\) Improve prediction accuracy
- b) Sentiment scores \(\rightarrow\) Uield modest gains for transformer-based models
1. Introduction
TS regression
- Fundamental to financial forecasting
- For both traditional finance & AI-based financial modeling
Classical financial models
- (e.g., Fama–French Three-Factor Mode, Arbitrage Pricing Theory)
- Rely on linear regression and historical data
- Limitation: Struggle to anticipate market extremes & unprecedented events (e.g., financial crises)
ML/DL methods
- Outperforming traditional models
- Benefit from integrating stock prices with news sentiment
Modern portfolio theory
- Emphasizes market correlations
- Recent studies: Show strong links between sentiment data & stock trends
LLMs in finance
- Multimodal approaches
- Combine numerical & textual data \(\rightarrow\) improve accuracy
- Significantly improve sentiment analysis
- Limitation:
- Information loss from sentiment-only representations
- Lack of large, integrated datasets
Limitation of Existing financial news datasets
- Lack sufficient scale
- Lack aligned stock price data
- Unstructured news formats hinder their use in seq2seq TS modeling
Proposal: Financial News and Stock Price Integration Dataset (FNSPID)
-
Uniquely aligns TS news & Stock prices
-
Contribution
-
(1) Integrating textual & numerical data
- (2) Experiments using FNSPID
-
a) Larger datasets
-
b) High-quality sentiment information
\(\rightarrow\) Enhances forecasting accuracy
-
- (3) Facilitates research in …
- Sentiment analysis
- LLM fine-tuning …
-
2. Related Works
(1) Evolution of Financial Analysis Models
a) Classical factor models
- (e.g., Fama–French Three-Factor Model, Arbitrage Pricing Theory)
- Incorporate factors such as market risk, size, and value
- Strength & Limitation
- [Strength] Effective for long-term asset pricing analysis
- [Limitation] Lack granularity for short-term forecasting (e.g., price peaks and troughs)
b) Statistical TS models
- (e.g., ARIMA, GARCH)
- Widely used for market trend & volatility analysis
- [Limitation] Sensitive to investor subjectivity and behavioral bias
c) ML/DL in finance
- Improves market entry and exit timing
- Evolution:
- Classical ML: Linear Regression, SVM
- Advanced ML/DL: LSTM, RNN, Deep Q-learning
- Reinforcement learning shows promise for trading strategies
d) Data-driven ML/DL advantages
- Leverages heterogeneous data sources
- Real-time news
- Social media sentiment
- Economic indicators
- [Strength]
- Capture non-linear patterns
- Adapt to changing market conditions
e) Role of financial news and sentiment
- Financial news: Strongly influences market movements
- GARCH-based studies: Highlight impact during financial crises
- Sentiment + ML integration:
- Enhances prediction accuracy
- Applied to volatility prediction and relational market analysis
- Limitation of prior work:
- Lack of real-time data
- Limited use of detailed financial metrics
- Neglect of individual investor behavior
f) Pre-trained language models and LLMs
- (e.g., GPT-3.5, FinGPT)
- Used for:
- Generating financial news
- Sentiment-based stock prediction
- Outperform traditional sentiment analysis methods
- Demonstrated strong sentiment–price correlation
g) LLMs for TS forecasting
- Backbone LLMs show strong potential in TS prediction
- Limitation: Scarcity of large, high-quality financial datasets
- Indicates untapped capability of LLMs for financial market applications
(2) Existing Stock Dataset
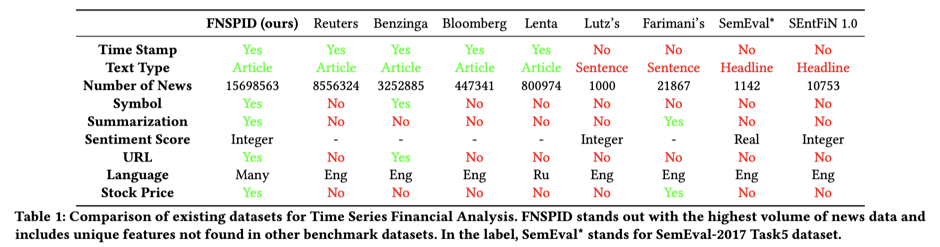
a) Existing stock market datasets
- DL-based sentiment analysis: Performance strongly depends on data volume and quality
- Growing research focus on integrating news sentiment + stock prices
b) Early sentiment-focused datasets
- Lutz dataset
- Binary, sentence-level sentiment (positive / negative)
- Text-only financial news
- Limitation: No company-level financial data
- Cortis dataset
- Fine-grained sentiment for financial news and microblogs
- Includes sentiment scores and lexical/semantic features
- Limitations:
- Very small scale (1,142 headlines)
- Proprietary sentiment scoring method
c) Time-series–oriented datasets
- Farimani dataset
- Integrates latent economic concepts, news sentiment, and technical indicators
- All data structured as time series
- Limitation: Sentiment mainly tied to FX news, limited trading depth
- SEntFiN 1.0 (Sinha et al.)
- Entity-level sentiment annotations
- Rich financial entity coverage
- Limitations:
- Missing timestamps
- Headline-only text
- Insufficient scale for robust training
d) Large-scale news datasets
- Philippe dataset (Bloomberg & Reuters)
- Large financial news time series
- Limitation: No entity-level sentiment labels, raw news only
- Finnhub dataset
- Time-aligned stock prices and related news via API
- Limitation:
- Proprietary access
- No built-in sentiment labels
- Lacks systematic quality evaluation
e) Recent hybrid approaches
- Combine numerical market data with social media text
- Use deep reinforcement learning for stock prediction
- Introduce dynamic datasets for model evaluation
- Limitation: Often dataset-specific and not openly accessible
f) FNSPID dataset
- Covers 1999–2023
- Multilingual news (English & Russian)
- Time-aligned financial news and stock prices
- Designed for:
- Sentiment analysis
- Stock price prediction
- Data quality:
- Sourced exclusively from trusted financial platforms (e.g., NASDAQ)
- Mitigates fake news concerns
- Emphasizes dataset reliability and integrity
g) Open-access challenge
- Many high-quality datasets and models (e.g., FinChat, BloombergGPT)
- Restricted or proprietary
- Limited availability for academic research
- FNSPID objective
- Provide a comprehensive, open, and accessible dataset
- Enable broader and more inclusive research in financial modeling
3. Constructing FNSPID
Curated integration of numerical stock data + sentiment data
Construction divided into three tasks:
- Task 1: “Full sentiment + numerical” dataset
- Task 2: “Summarized” sentiment dataset
- Task 3: “Quantified” sentiment dataset
a) Data sources
- Numerical data
- Stock prices collected via Yahoo Finance API
- Sentiment / news data
- Explored multiple financial news sources
- e.g., Bloomberg, Reuters, Yahoo Finance, Forbes, CNBC
- Due to usage restrictions, primary collection from NASDAQ
- Explored multiple financial news sources
b) NASDAQ data collection pipeline
- Two-stage process:
- Step 1) Collect headlines and URLs for each stock using Selenium
- Step 2) Extract full news content from URLs
- Ensures structured textual data aligned with stock-level information
c) Data diversity and integrity
- To reduce source bias and improve coverage:
- Integrated previously processed datasets from:
- Bloomberg
- Reuters
- Benzinga
- Lenta
- Integrated previously processed datasets from:
- Combined with NASDAQ data to form [FNSPID Task 1]
d) Data ethics and compliance
- Strict adherence to robots.txt and website usage policies
- Only collected content that is:
- Freely accessible
- Not behind paywalls or subscriptions
- Web scraping used only when no official API was available
- Licenses of prior datasets verified before integration
(1) Data mining and processing

a) Data & Goal
- Raw data: Numerical prices, URLs, news headlines, full news text
- Goal:
- (1) Reduce text length
- (2) Preserve sentiment-relevant information
b) News summarization
- Motivation:
- Address token limits
- Improve practicality of downstream sentiment analysis
- Applied 4 rule-based summarization methods:
- LexRank / Luhn / Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA) / TextRank
- via the Sumy Python package
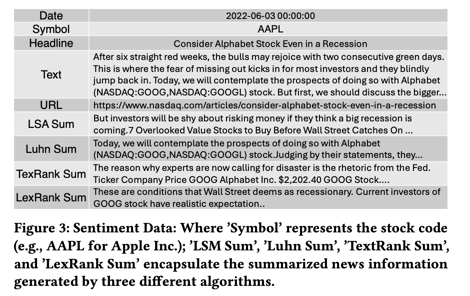
c) Stock-aware summarization
- Introduced a weight model \(W_f\)
- Emphasizes content relevant to the associated stock
- Summary length fixed to 3 sentences
- ≈ 1/8 of original article
- Balances conciseness and specificity
- Benefits:
- Significant reduction in token usage
- Improved ChatGPT prompt stability
- Completion of [FNSPID Task 2]
d) Sentiment quantification
- Limitation:
- Early LLMs and TS-DL models: Struggle with raw language understanding
- Large models (e.g., ChatGPT): Computationally expensive
- Observation:
- DL models can effectively utilize numerical sentiment signals
e) Sentiment labeling strategy
- Constructed a labeled subset:
- News from 50 major S&P 500 stocks
- Used ChatGPT to generate sentiment labels:
- Avoids costly manual annotation
- Outperforms traditional sentiment algorithms
- Input to ChatGPT
- LSA-based summaries for concise yet informative prompts
- Prompt configuration:
- Up to 10 entries per prompt
- Temperature = 0 for output stability
f) Sentiment scoring scheme
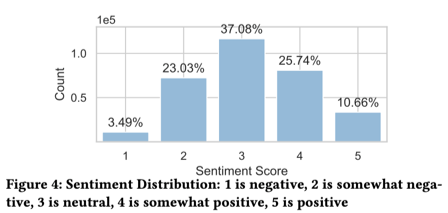
- Adopted a 1–5 discrete scale:
- 1: Negative
- 2: Somewhat negative
- 3: Neutral
- 4: Somewhat positive
- 5: Positive
- Rationale:
- More stable than alternatives (e.g., -1 to 1, 1 to 10)
- Decimal scores lead to unstable representations
- Sentiment distribution:
- Approximately normal
g) Normalization and integration
-
Sentiment scores: Normalized consistently with other features
\(\rightarrow\) Ensures sentiment contributes meaningfully (w/o dominating model training)
h) Handling missing sentiment data
- Issue: Days without news articles
- Solution:
- Exponential decay toward neutral sentiment
- Formula:
- \[S(t) = 3 + (S(0) - 3)\cdot e^{-\lambda t}\]
- Configuration:
- Neutral target = 3
- Decay rate \(\lambda = 0.03\)
i) Daily aggregation
- Multiple news articles on the same day
- Use average sentiment score
- Motivation:
- Balanced representation of daily market sentiment
- Reduces bias from extreme individual news items
4. FNSPID Property
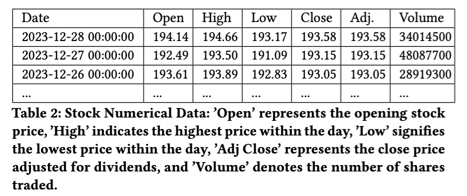
a) Dataset overview
- Large-scale and diverse dataset:
- 30+ GB of processed data
- [TS] Numerical price data (Table 2)
- [Text] Sentiment-related data (Figure 3)
- URLs
- News headlines
- Full news text
- Sentiment scores
- Summaries from four methods
b) Data richness and diversity
- Multi-modal structure:
- Numerical prices
- Textual news (+ quantified sentiment)
c) Computational effort
- For dataset construction…
- ~4 TB of computing resources
- ~45 days of processing time
d) Labeled sentiment subset
- Focused analysis on: Top 50 influential S&P 500 stocks (2024)
- Result: 402,546 news articles with sentiment labels
4-1. Evaluation
Evaluation of FNSPID
- Assesses linguistic, semantic, and temporal properties
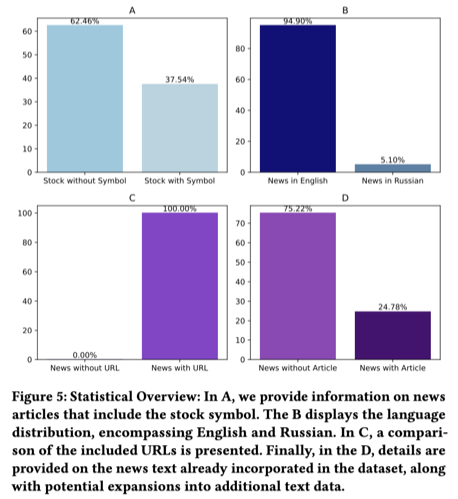
Language distribution
- Pproportions of English Russian content
- Highlights the multilingual nature of FNSPID
News article segmentation
- (1) Stock-symbol–referenced news
- (2) Non–stock-symbol news
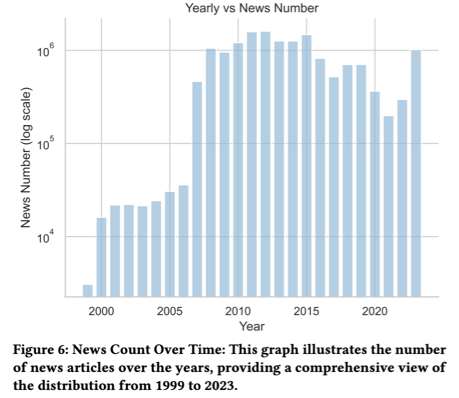
Temporal distribution
- Date: 1999 to 2023
- Identifies long-term trends and fluctuations in financial news coverage
Overall assessment
- a) Large scale
- b) Multilingual coverage
-
c) Long temporal span
-
Well-suited for:
- Financial sentiment analysis
- Time-series forecasting
5. Experiment
- Effectiveness of FNSPID in stock price prediction
- Focuses on how the quantity of news data influences model performance
5-1. Quantity Test
Goal
- Analyze the impact of training data size on short-term stock price prediction
- Use FNSPID Task 3 as the experimental benchmark
Input information
- (1) Numerical features
- Open price
- Close price
- Trading volume
- (2) Sentiment features
- Included or excluded depending on the experiment setting
Models
- Traditional DL methods: RNN / LSTM / GRU / CNN
- TS–oriented models: 4-layer Vanilla Transformer / 4-layer TimesNet
Experimental setup
- Input window: 50 days
- Prediction horizon: 3 days
- Training epochs: 100
- Training dataset sizes
- 5 stocks (n = 11,277)
- 25 stocks (n = 43,192)
- 50 stocks (n = 127,937)
- Evaluation
- Conducted on 5 stocks
- One outlier removed
- Final results reported as averaged values
Test results
-
Evaluation metric: \(R^2\)
-
Experiment settings
- A-Sen: Sentiment info (O)
- A-Non: Sentiment info (X)
Key findings
- Average \(R^2\) improvement of 6.29% when increasing training data from 5 to 25 stocks across all models
Observations
- Transformer-based models > Recurrent models
- Larger training datasets significantly enhance prediction accuracy
- Small datasets limit performance in financial forecasting tasks
Conclusion
- Robustness and applicability of FNSPID
- Importance of data scale in financial TS prediction
- Effectiveness of Transformer-based architectures for stock price forecasting
5-2. Quality Test
Goal
- Evaluate the impact of sentiment quality on model training performance
- Compare sentiment sources derived from FNSPID Task 3, FNSPID Task 2, and TextBlob
Experimental setup
- Sentiment sources
- FNSPID Task 2
- ChatGPT-labeled sentiment
- TextBlob sentiment
- Based on rule-based scoring & lightweight NLP models
- FNSPID Task 2
- Benchmark
- Sentiment information from FNSPID Task 3
Overall findings
- Sentiment quality has a decisive impact on forecasting accuracy
- Results in Table 3
- Part A: FNSPID Task 2 sentiment improves prediction accuracy
- Part B: TextBlob sentiment degrades model performance
Impact on model performance
- Transformer-based comparison
- FNSPID Task 3 sentiment
- Accuracy improvement of +0.2% over non-sentiment input
- TextBlob sentiment
- Accuracy degradation of −1.16%
- FNSPID Task 3 sentiment
Sentiment effectiveness across models
- Transformer: Consistently benefits from high-quality sentiment information
- TimesNet: Occasionally exhibits positive gains
- RNN, LSTM, GRU, CNN
- Treat sentiment features as noise
- Show no consistent performance improvement
Dataset scale effects
-
Small-scale training
- LSTM outperforms Transformer when only 5 news items are available
-
Large-scale training
- Transformer exhibits substantial accuracy gains as data volume increases
<br>
Discussion
-
Hyperparameter alignment
- Uniform hyperparameter settings are used for fair comparison
- This constraint may suppress the optimal performance of individual models
<br>
-
Sentiment representation
- Sentiment scores mapped onto a 5-level scale
- Paragraph-level sentiment compression may discard fine-grained information
- Information loss contributes to limited sentiment effectiveness
<br>
-
Interpretation of limited gains
-
Financial news is known to influence stock prices
-
Marginal improvements arise due to
- Already high baseline prediction accuracy
- Delayed market reactions to news dissemination
-
<br>
Conclusion
-
Key takeaways from the Quality Test
- Dataset quality and quantity jointly determine forecasting performance
- High-quality sentiment information benefits Transformer-based models
- Transformer-based architectures outperform traditional time-series models and recent alternatives such as TimesNet in stock price prediction
