BLIP-2: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training with Frozen Image Encoders and Large Language Models
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.12597
1. Abstract
Cost of VLP: Expensive!
- Prohibitive due to end-to-end training of large-scale models!
Proposal: BLIP-2
- Generic and efficient pretraining strategy
- Bootstraps VLP from off-the-shelf frozen pre-trained image encoders and frozen LLM
- Q-Former (Querying Transformer)
- Lightweight model to bridge the modality gap
- Pretrained in two stages
- Stage 1) Bootstraps vision-language representation learning
- from a frozen image encoder
- Stage 2) Bootstraps vision-to-language generative learning
- from a frozen language model
- Stage 1) Bootstraps vision-language representation learning
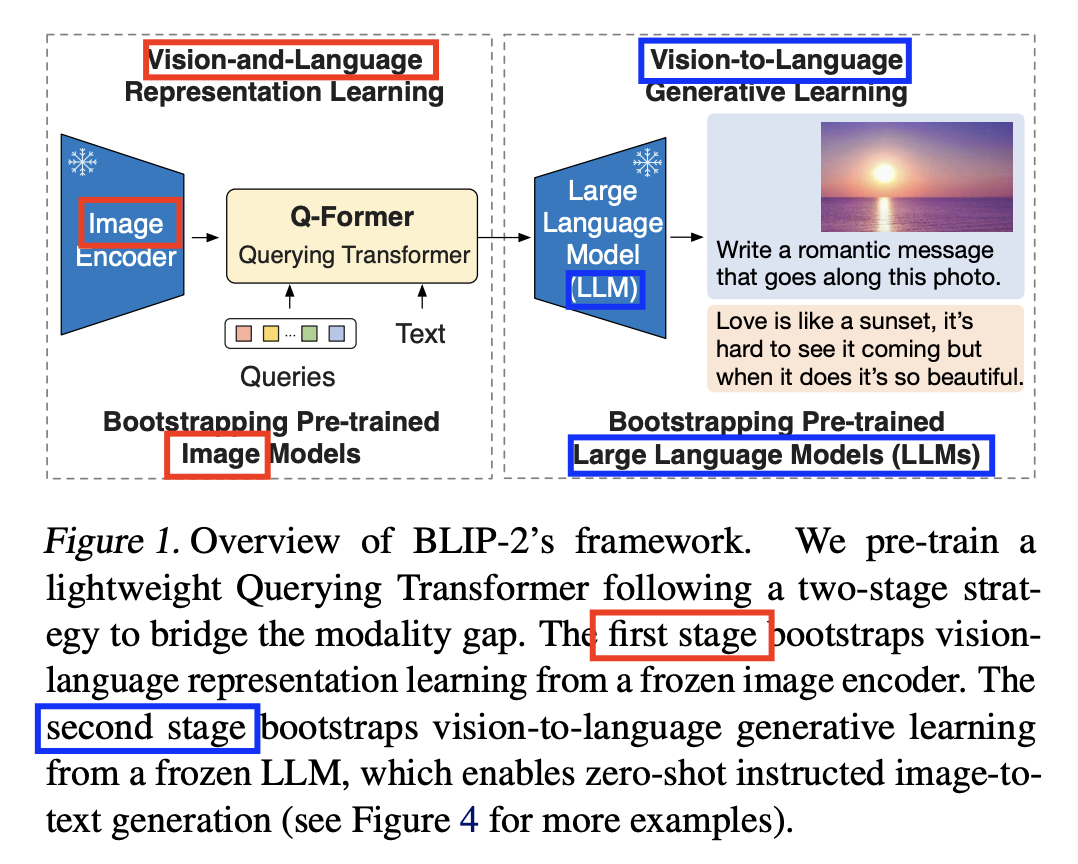
2. Method
New VLP method
- Bootstraps from frozen pre-trained unimodal models
Querying Transformer (Q-Former)
- To bridge the modality gap
- Pre-trained in two stages:
- (1) Vision-language representation learning stage with a frozen image encoder
- (2) Vision-to-language generative learning stage with a frozen LLM
(1) Model Architecture: Q-Former
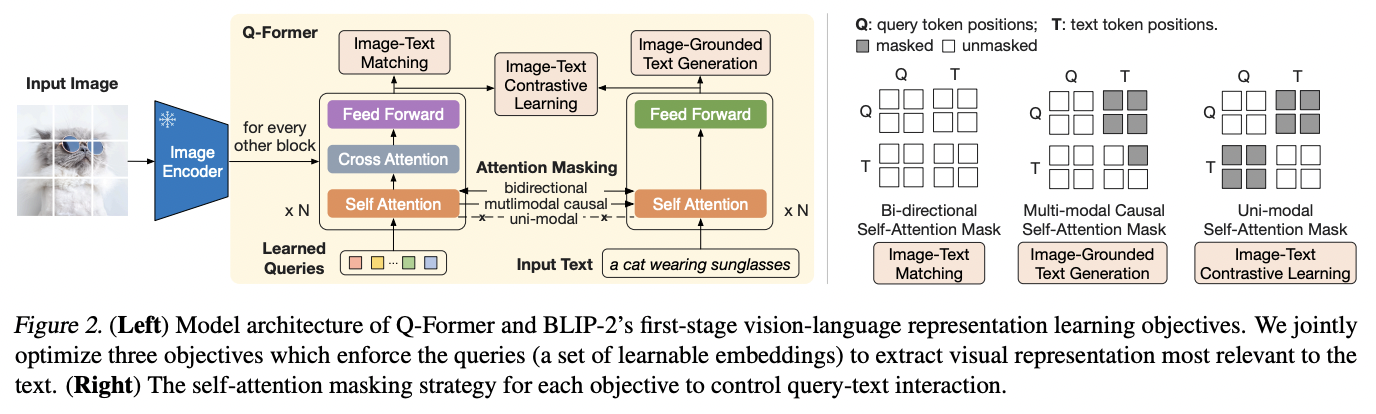
a) Q-Former
-
Trainable module to bridge the gap btw text & image
-
Extracts a fixed number of output features from the image encoder
( independent of input image resolution )
b) Consists of 2 transformer submodules
- Share the same self-attention layers
- (1) Image transformer
- Interacts with the frozen image encoder for visual feature extraction
- Use Cross Attention
- (2) Text transformer
- Function as both a text encoder and a text decoder
c) Details of Image Transformer
- a) Input = Set number of learnable query embeddings
- b) Self-attention
- Queries interact with each other
- c) Cross-attention
- Queries interact with frozen image features
- (optional) Depending on the pretraining task
- Queries can additionally interact with the text through the same self-attention layers.
- Depending on the pre-training task, apply different self-attention masks to control query-text interaction
Initialization
- QFormer = Pre-trained weights of BERTbase
- Cross-attention layers = Randomly initialized
- 32 queries (each with 768 dimension)
(2) Bootstrap Vision-Language Representation Learning from a Frozen Image Encoder
a) Dataset: Pre-train using image-text pairs!
b) Goal: Train the Q-Former such that …
\(\rightarrow\) The queries can learn to extract visual representation that is most informative of the text
c) Loss: Jointly optimize 3pre-training objectives
- Inspired by BLIP (Li et al., 2022)
- c-1) Image-Text Contrastive Learning (ITC)
- c-2) Image-grounded Text Generation (ITG)
- c-3) Image-Text Matching (ITM)
- Each objective employs a different attention masking strategy ( btw queries and text )
(3) Bootstrap Vision-to-Language Generative Learning from a Frozen LLM
Generative pre-training stage
- Connect QFormer (+ frozen image encoder) & frozen LLM
- Projection layer: FC layer
- To linearly project the output query embeddings \(Z\) into the same dimension as the text embedding of the LLM.
- Projected query embeddings:
- Prepended to the input text embeddings
- Function as soft visual prompts that condition the LLM on visual representation
Two types of LLMs
- (1) “Decoder”-based LLMs
- Pre-train with the LM loss
- (2) “Encoder-decoder”-based LLMs
- Pre-train with the prefix LM loss
3. Examples
**
