CoCa: Contrastive Captioners are Image-Text Foundation Models
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.01917
1. Abstract
Contrastive Captioner (CoCa)
- Minimalist design to pretrain an image-text encoder-decoder foundation model
- Joint training:
- (1) Contrastive loss ( feat. CLIP )
- (2) Captioning loss ( feat. SimVLM )
- CoCa vs. Standard
- Standard standard encoder-decoder transformers: All decoder layers attend to encoder outputs
- CoCa: Omits cross-attention in the first half of decoder layers to encode unimodal text representations
- Pretrained end-to-end and from scratch on both web-scale alt-text data and annotated images by treating all labels simply as text
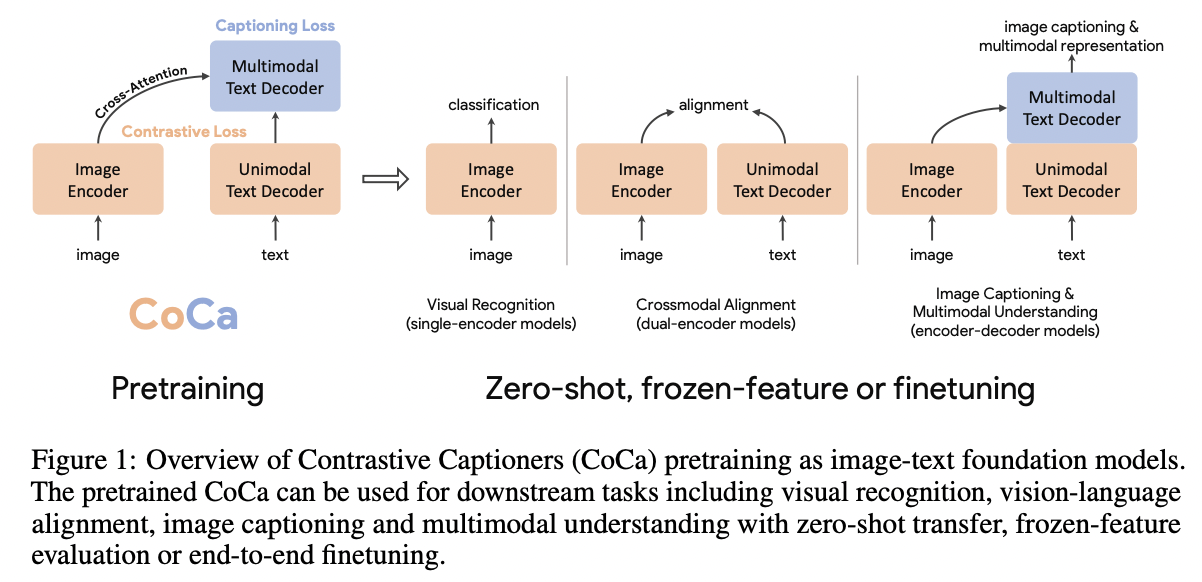
2. CoCa (Contrastive Captioner)
Review of 3 foundation model families
( that utilize natural language supervision differently )
- (1) Single-encoder classification pretraining
- (2) Dual-encoder contrastive learning
- (3) Encoder-decoder image captioning
Contrastive Captioners (CoCa)
- Both contrastive learning & image-to-caption generation
- Simple architecture
(1) Natural Language Supervision
a) Single-encoder classification pretraining
\(\mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{Cls}}=-p(y) \log q_\theta(x)\).
b) Dual-encoder contrastive learning
\(\mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{Con}}=-\frac{1}{N}(\underbrace{\sum_i^N \log \frac{\exp \left(x_i^{\top} y_i / \sigma\right)}{\sum_{j=1}^N \exp \left(x_i^{\top} y_j / \sigma\right)}}_{\text {image-to-text }}+\underbrace{\left.\sum_i^N \log \frac{\exp \left(y_i^{\top} x_i / \sigma\right)}{\sum_{j=1}^N \exp \left(y_i^{\top} x_j / \sigma\right)}\right)}_{\text {text-to-image }}\).
c) Encoder-decoder image captioning
\(\mathcal{L}_{\text {Cap }}=-\sum_{t=1}^T \log P_\theta\left(y_t \mid y_{<t}, x\right)\).
(2) Contrastive Captioners Pretraining
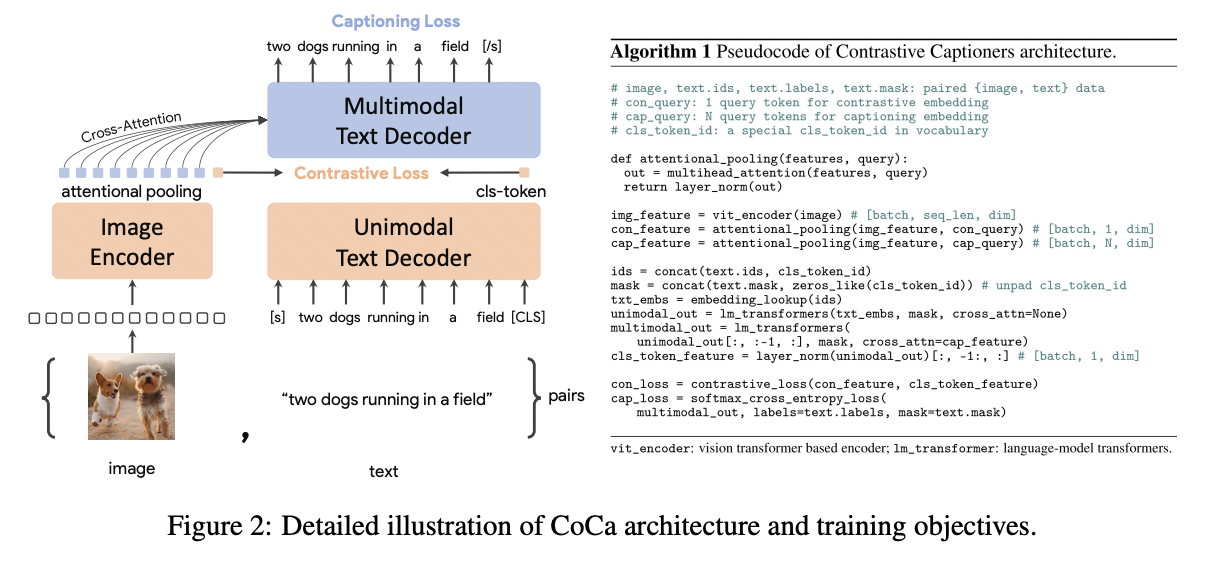
Contrastive captioner (CoCa)
- A simple encoder-decoder approach
- Combines the (above) 3 training paradigms
Details
-
(First half) Omits cross-attention in the first half of the decoder layers
\(\rightarrow\) To encode unimodal text representations
-
(Last half) Cascades the rest of the decoder layers
\(\rightarrow\) Cross-attending to the image encoder for multimodal image-text representations.
\(\rightarrow\) CoCa decoder simultaneously produces both unimodal & multimodal text representations!
Loss function:
- \(\mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{CoCa}}=\lambda_{\mathrm{Con}} \cdot \mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{Con}}+\lambda_{\mathrm{Cap}} \cdot \mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{Cap}}\).
a) Decoupled Text Decoder & CoCa Architecture
Captioning approach
- Optimizes the conditional likelihood of text
Contrastive approach
- Uses an unconditional text representation
\(\rightarrow\) How to combine these two?
Solution: Propose a simple “decoupled decoder” design
- How? Split the decoder into unimodal and multimodal components
- By skipping the cross-attention mechanism in the unimodal decoder layers
Split decoders into two parts!
- (1) Bottom \(n_{\text {uni }}\) unimodal decoder layers:
- Encode the input text as latent vectors with causally-masked self-attention
- (2) Top \(n_{\text {multi }}\) multimodal layers:
- Apply causally-masked self-attention & cross-attention to the output of the visual encoder
b) Attentional Poolers
Two types loss & embeddings
-
(1) Contrastive loss: Uses a single embedding for each image!
-
(2) Captioning loss: Decoder usually attends to a sequence of image output tokens in an encoder-decoder captioner
Single & Multiple embeddings
- (Single) Pooled image embedding
- Helps visual recognition tasks as a global representation
- (Multiple) More visual tokens (thus more fine-grained)
- Beneficial for multimodal understanding tasks which require region-level features
Task-specific attentional pooling (for global representation)
- To be used for different types of training objectives and downstream tasks
- Pooler = Single multi-head attention layer
- (Q) \(n_{\text {query }}\) learnable queries
- (K,V) Encoder outputs
\(\rightarrow\) Can learn to pool embeddings with different lengths for the two training objectives
(3) CoCa for Downstream Tasks
a) Zero-shot Transfer
Leverage both image and text inputs
Tasks
- Zero-shot image classification
- Zero-shot image-text cross-retrieval
- Zero-shot video-text cross-retrieval
b) Frozen-feature Evaluation.
CoCa adopts task-specific attentional pooling (pooler) to customize visual representations for different types downstream tasks
\(\rightarrow\) Enables the model to obtain strong performance as a frozen encoder where we “only learn a new pooler to aggregate features”
c) CoCa for Video Action Recognition
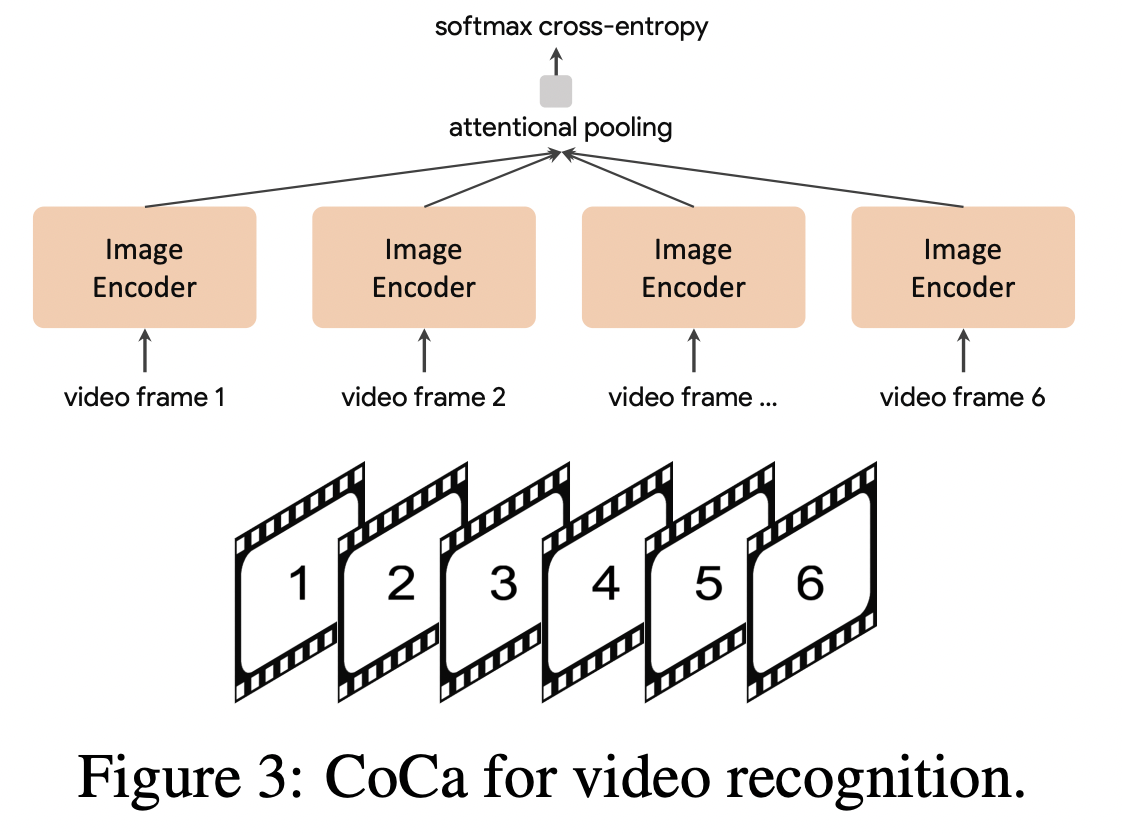
Input = Mmultiple frames of a video
Process
-
Step 1) Feed each frame into the shared image encoder individually
-
Step 2) (For frozen feature evaluation or finetuning) Learn an additional pooler on top of the spatial and temporal feature tokens with a softmax cross-entropy loss
-
Note: Pooler has a single query token
\(\rightarrow\) Computation of pooling over all spatial and temporal tokens is not expensive!
-
