DeepSeek-VL: Towards Real-World Vision-Language Understanding
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2403.05525
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Data Construction
- Data 1: Vision-Language pretraining Data
- Data 2: Vision-Language SFT Data
- Approach
- Architecture: 3 modules
- Training Pieplines
Abstract
Open-source Vision-Language (VL) Model
-
(1) Data Construction
-
Diverse, scalable, extensively covers real-world scenarios
- Web screenshots, PDFs, OCR, charts, and knowledge-based content (expert knowledge, textbooks)
-
Create a use case taxonomy from real user scenarios
& Construct an instruction-tuning dataset accordingly
\(\rightarrow\) Fine-tune with this dataset
-
-
(2) Model Architecture
- Hybrid vision encoder
- Efficiently processes high-resolution images (1024 x 1024) within a fixed token budget
- Relatively low computational overhead
- Hybrid vision encoder
-
(3) Training Strategy
- Starting with a focus on text
- Gradually adjust the ratio to facilitate a balanced integration text & image
1. Introduction
P1. Trend of LMMs
Emergence of Large Multimodal Models (LMMs)
- GPT-4V (OpenAI, 2023b)
- Gemini (Team et al., 2023)
P2-3. Performance gap btw LMMs
Performance gap between the majority of LMMs exists!
Due to following reasons:
-
(1) Recent works: Allocate a significant proportion of computational resources to the instruction tuning phase.
\(\rightarrow\) Should be an emphasis on comprehensive pretraining that leverages a broad spectrum of VL data.
-
(2) Often falls short in providing an authentic real-world usage experience.
-
(3) Recent works: Operate on a relatively low resolution, e.g., 336×336 or 448× 448
-
(4) Often overlook the preservation of language skills.
P4. Proposal: DeepSeek-VL
Open-source LMM
- Built upon the DeepSeek LM series
- Pursuit of adept performance in real-world scenarios
- a) Extensive pretraining
- b) Careful data curation based on a use case taxonomy
- c) Model architecture design for high-resolution processing
- d) Training strategy that balances the multi-modalities
P5. Proposal intro: a) Pretraining dataset
-
Compiled from a variety of sources
-
Encompasses real-world scenarios!
P6. Proposal intro: b) Curation
-
Curate our instruction-tuning dataset
\(\rightarrow\) To reflect real-world usage scenarios!
- How?
- Gather authentic test cases for GPT-4V and Gemini from the Internet.
- Systematically organize them into a comprehensive taxonomy
- Use this structured taxonomy to choose prompts for each test image!
P7. Proposal intro: c) Model architecture
Hybrid vision encoder
- To optimize the utilization of high-resolution visual inputs
- While remaining within a fixed token budget to manage inference costs effectively
- Hybrid? Combines (a) & (b)
- (a) Text-aligned encoder
- For coarse semantic extraction at 384 × 384 resolution
- (b) High-resolution encoder
- Captures detailed visual information at 1024 × 1024 resolution
- Eefficiently condenses a 1024×1024 resolution image into 576 tokens
- (a) Text-aligned encoder
P8. Proposal intro: d) Multimodal training
Common challenge
-
Potential degradation of language capabilities
-
Findings: Maintaining a significant proportion of language data—specifically, at least 70%—is essential to preserve the integrity of language knowledge within the model!
“Modality warm-up” strategy
- Adjusts the ratio of modalities during training
- Gradually incorporating more vision-language data.
2. Data Construction
Dataset: Divided into two parts
- (1) Vision-Language pretraining Data
- Visual-text data from various sources
- Goal: Enhance the model’s fundamental cross-modal understanding capabilities
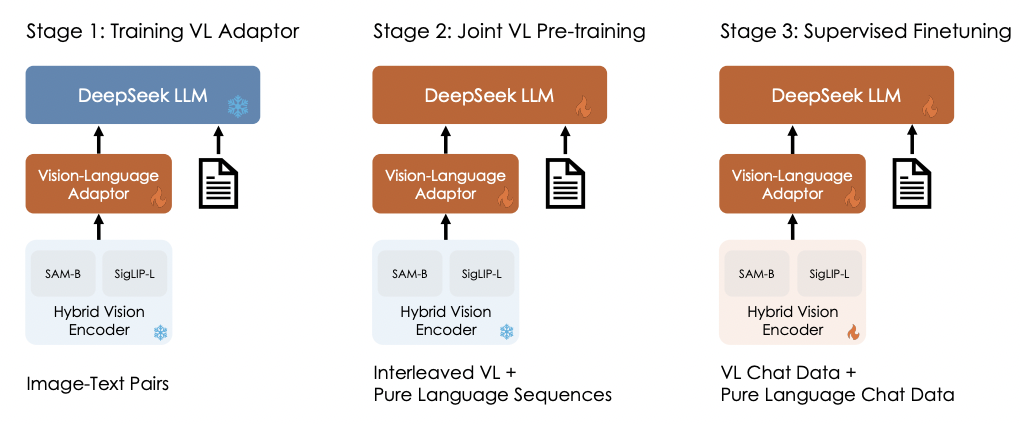
- When? Stage 1 & Stage 2
- (Stage 1) To warm up the vision-language adaptor
- (Stage 2) Jointly pretrain the vision-language model
- (2) Vision-Language SFT Data
- Relatively smaller size
- Goal: Teach the model to complete specific downstream tasks
- When? Stage 3
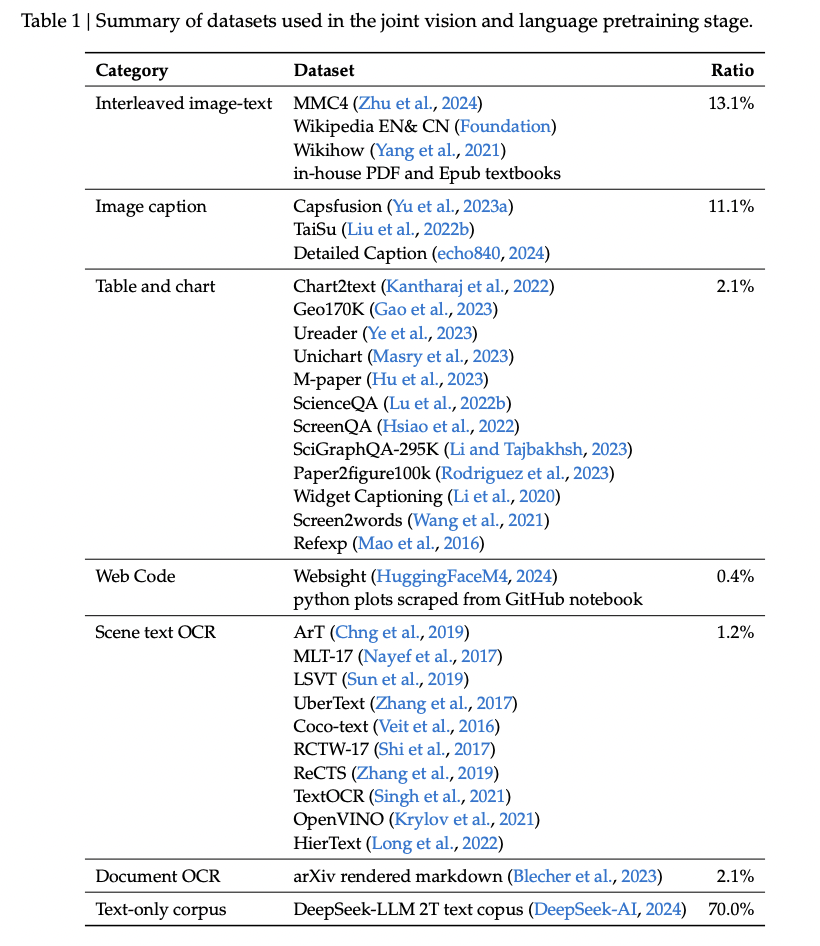
(1) Data 1: Vision-Language pretraining Data
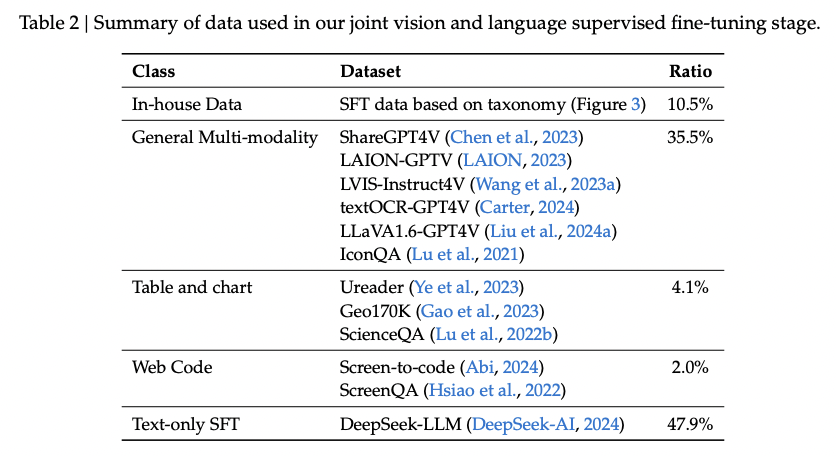
(2) Data 2: Vision-Language SFT Data
3. Approach
(1) Architecture: 3 modules
- Hybrid Vision Encoder
- VL Adaptor
- LM
a) Hybrid Vision Encoder
(1) Architecture: SigLIP
-
Limitation: struggles to address all real-world questions comprehensively
( \(\because\) Primarily designed for semantic visual representations + low-resolution inputs )
(2) Hybrid = SigLIP + SAM-B
-
Recent works: Integration of additional vision-only SSL encoders
\(\rightarrow\) To enhance the visual grounding capabilities
-
Proposal: Utilize a vision-only encoder based on the SAM-B
-
Pre-trained ViTDet image encoder to process low-level features
( Accepts high-resolution 1024 x 1024 image inputs )
-
-
Result: use both (a) & (b)
- (a) SigLIP: for low-resolution
- (b) SAM-B: for high-resolution
b) VL Adaptor
- Two-layer hybrid MLP
- To bridge the vision encoder & LLM
- One for high-resolution feature
- One for low-resolution feature
- Concatenated along their dimensions!
- Transform into the LLM’s input space
- through another layer of MLP.
c) LM
(1) Architecture: Deepseek LLM
- Micro design: follows that of LLaMA
(2) Training Pieplines