DeepSeek-VL2: Mixture-of-Experts Vision-Language Models for Advanced Multimodal Understanding
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2412.10302
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Model Architecture
- Dynamic Tiling Strategy
- Vision-Language Adaptor
- DeepSeekMoE LLM
0. Abstract
DeepSeek-VL2
- Advanced series of large MoE VLMs
- DeepSeek-VL + 2 key major upgrades
- (1) [Vision] Dynamic tiling vision encoding strategy
- To process high-resolution images with different aspect ratios
- (2) [Language] DeepSeekMoE models with the MLA mechanism (feat. DeepSeek-V2)
- Efficient inference and high throughput.
- (1) [Vision] Dynamic tiling vision encoding strategy
https://github.com/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-VL2
1. Introduction
P1. Large VLMs
Remarkable capabilities of LLMs to seamlessly process both visual and textual information
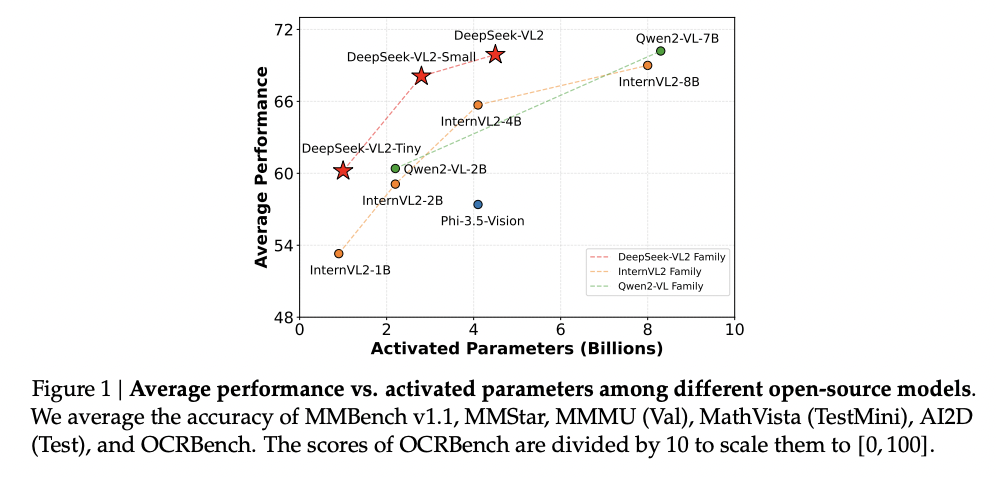
P2. Proposal: DeepSeek-VL2
Open-source VLMs
- (1) Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture
- Improvements in both performance and efficiency (vs. DeepSeek VL)
- (2) Three key aspects
- a) Dynamic, high-resolution vision encoding strategy
- Enhances visual understanding
- b) Optimized language model architecture
- Significantly improves both training and inference efficiency
- c) Refined vision-language data construction pipeline
- a) Dynamic, high-resolution vision encoding strategy
P3. Component 1: Vision
Dynamic tiling vision encoding strategy
- Efficiently processes high-resolution images of varying aspect ratios
- Improves over DeepSeek-VL’s hybrid vision encoder
- DeepSeek-VL vs. DeepSeek-VL2
- (VL) Hybrid vision encoder = two fixed resolution (384 × 384 and 1024 × 1024)
- (VL2) Dynamic tiling vision encoding strategy
- How?
- Step 1) Dynamically segments high-resolution inputs into local tiles
- Step 2) Processes each tile through a shared vision transformer
- Step 3) Integrates the extracted features within the LLM
- Result: Advantages of ViTs with local attention
P4. Component 2: Language
Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) mechanism (feat. DeepSeek V2)
- Significantly reduces computational cost by compressing the KV cache into a latent vector
- Result: Faster inference & Increased throughput capacity
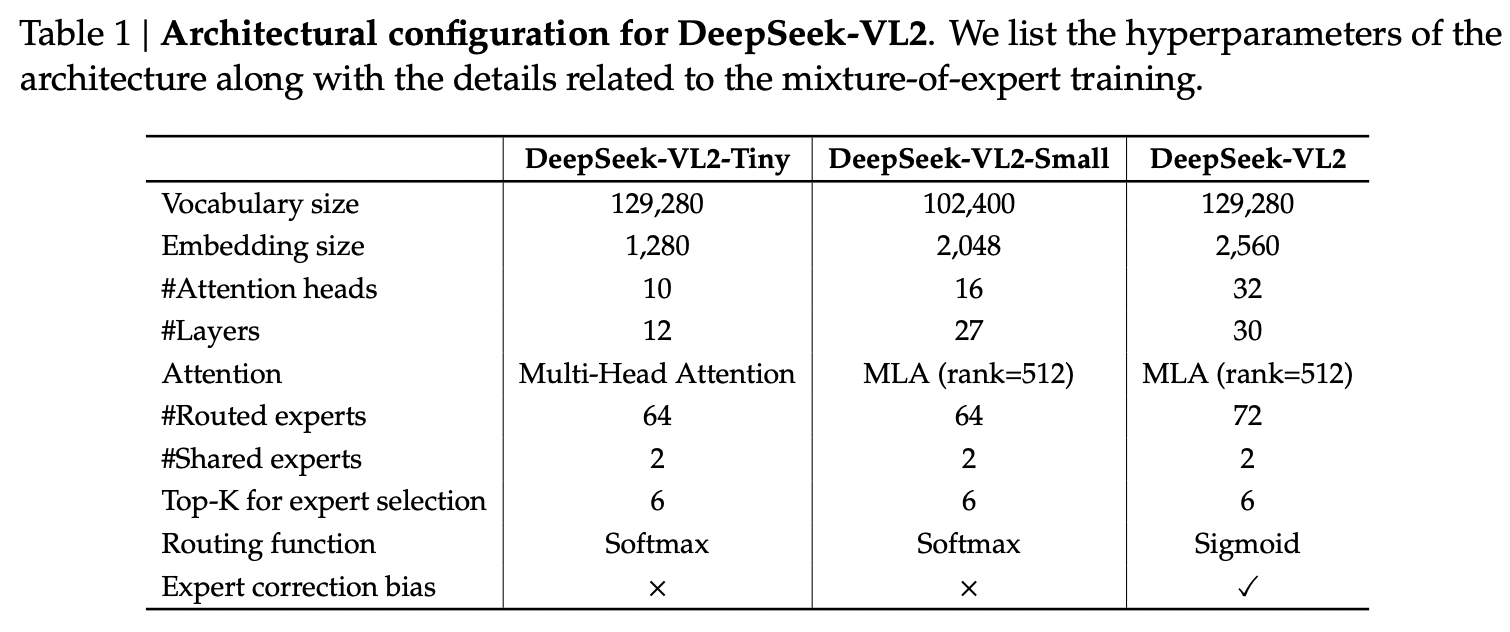
- Details: Three MoE variants
- 3B, 16B, and 27B (total params)
- 0.57B, 2.4B, and 4.1B (activated params)
P5. Component 3: Dataset
Enhance VL training data in terms of…
- Quality, Quantity, Diversity
$\rightarrow$ Better generalization and performance across a broad spectrum of tasks!
- e.g., Visual Question Answering (VQA), Optical Character Recognition (OCR), document/table/chart understanding, visual reasoning, and general chatbot applications.
2. Model Architecture
3 core modules
- (1) Vision encoder
- (2) Vision-language adaptor
- (3) Mixture-of-Experts language model
Two major advancements
Building upon DeepSeek-VL2: the decoder-only LLaVAstyle architecture …
- (1) Dynamic tiling strategy
- (2) DeepSeekMoE
- Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA)

(1) Dynamic Tiling Strategy
a) (Original DeepSeek-VL) Hybrid vision encoder
-
Coarse (1) + Fine-grained (2)
- (1) SigLIP for coarse-grained feature extraction at 384 × 384 resolution
- (2) SAM-B for fine-grained feature extraction at 1024 × 1024 resolution
-
Pros) Rich visual representations suitable for various vision-language tasks
-
Cons) Limited by the fixed 1024 × 1024 resolution constraint
$\rightarrow$ Particularly challenging for processing images with larger resolutions and extreme aspect ratios
b) (Proposed DeepSeek-VL2) Dynamic tiling strategy
- How? Splitting a high-resolution image into tiles
- Effect? Efficient processing of different high-resolution images with varying aspect ratios
- Model: (Pretrained) single SigLIP-SO400M-384 vision encoder
- Resolution & Ratios
- (1) Base resolution = 384x384
- (2) To accommodate different aspect ratios ….
- Set of candidate resolutions: $C_r = {(m\cdot 384, n\cdot 384) \mid m \in N, n \in N, 1 \leq m,n,mn \leq9}$
- $m:n$ = aspect ratio

c) Details of Dynamic tiling strategy
-
Input = Image of size ( $H, W$ )
-
Step 1) Calculate the padding area
- Required for resizing it to each candidate resolution in $C_R$
- How? Select the resolution $\left(m_i-384, n_i-384\right)$ that minimizes the padding area.
-
Step 3) Resize the image
-
Step 4) Divide the resized image into $m_i \times n_i$ local tiles of $384 \times 384$ pixels
( + One global thumbnail tile )
For computational efficiency and context length management, we disable the dynamic tiling strategy when processing multiple (>2) images.
SigLIP-SO400M-384 vision encoder
- Processes all ( $1+m_i \times n_i$ ) tiles!
- Yield $27 \times 27=729$ visual embeddings of 1152 dimensions per tile
(2) Vision-Language Adaptor
2x2 pixel shuffle operation
- To compress each tile’s visual tokens! (1 tile = 196 tokens)
- 27x27=729 tokens $\rightarrow$ 14x14=196 tokens
- Add three special tokens when processing the ( $1+m_i \times n_i$ ) tiles
- Refer to the figure
(3) DeepSeekMoE LLM
Based on DeepSeekMoE
- Incorporates the MLA
- Compressing the Key-Value cache into a latent vector
- Enabling increased throughput capacity!
- Incorporates a MoE architecture
- Introduce a global bias term for each expert
- To cost-effectively improve load balancing between experts.