Visual Instruction Tuning
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.08485
1. Abstract
Previous works)
- Instruction tuning with “machine-generated” instruction-following data
- Improve zero-shot capabilities on new tasks
\(\rightarrow\) Limitation: Less explored in the multimodal field
Proposal: LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant)
- (1) Goal: Generate “instruction-following” dataset”
- (2) How: Use language-only GPT-4 to generate “multimodal” language-image instruction-following data
- (3) LLaVA
- Instruction tuned on the above generated data
- End-to-end trained large multimodal model
- Connects a vision encoder & LLM for general-purpose visual and language understanding
2. Contributions
- Multimodal instruction-following data
- Previous) Lack of vision-language instruction-following data
- Proposal: Construct such instruction-following dataset
- With language-only ChatGPT/GPT-4.
- Via a data reformation perspective
- Large multimodal models
- Large multimodal model (LMM)
- Connecting (1) & (2)
- (1) Open-set visual encoder of CLIP
- (2) Language decoder Vicuna
- Fine-tuning end-to-end on our generated instructional vision-language data.
- Multimodal instruction-following benchmark
- Present LLaVA-Bench with two challenging benchmarks
- Open-source
3. GPT-assisted Visual Instruction Data Generation
(1) Lack of multimodal instruction following data
Public multimodal data (e.g., image-text pairs): CC, LAION
\(\rightarrow\) But limited in multimodal instruction following data!
- Creating such data is time-consuming and less well-defined!
Proposal:
Leverage ChatGPT/GPT-4 for multimodal instruction-following data collection
(2) Naive way
-
(1) Image \(\mathrm{X}_{\mathrm{v}}\) & Caption \(\mathrm{X}_{\mathrm{c}}\)
-
(2) Set of questions \(\mathrm{X}_{\mathrm{q}}\)
- To instruct the assistant to describe the image content
\(\rightarrow\) Prompt GPT-4 to curate such a list of questions!
Simple way?
- Human : \(\mathbf{X}_{\mathbf{q}} \mathbf{X}_{\boldsymbol{v}}<\) STOP> Assistant : \(\mathbf{X}_c<\) STOP \(>\)
- Pros & Cons
- Pros) Cheap to construct
- Cons) Lacks diversity and in-depth reasoning!

(3) Proposal
Leverage language-only GPT-4 or ChatGPT as the strong teacher
\(\rightarrow\) Accept only text as input to create instruction-following data involving visual content! How??
To encode an image into its visual features to prompt a text-only GPT…
\(\rightarrow\) Use 2 types of symbolic representations
- (1) Captions
- Typically describe the visual scene from various perspectives
- (2) Bounding boxes
- Usually localize the objects in the scene
- Each box encodes the object concept and its spatial location
\(\rightarrow\) Enables to encode the image as an LLM-recognizable sequence

(Generated) instruction tuning dataset
Dataset used: COCO images
Datasets generated: Three types of instruction-following data!
- (1) Conversation
- (2) Detailed description
- (3) Complex reasoning

4. Visual Instruction Tuning
(1) Architecture
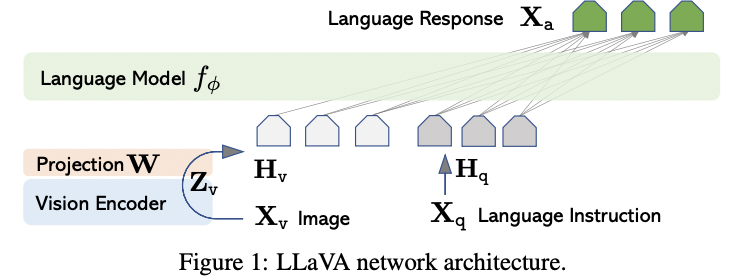
Goal: Leverage the capabilities of both the (1) pre-trained LLM and (2) visual model
Architecture
- (1) LLM (Vicuna): \(f_\phi(\cdot)\)
- Has the best instruction following capabilities in language tasks among publicly available checkpoints
- (2) Vision encoder (CLIP, ViT-L/14)
- Provides the visual feature \(\mathbf{Z}_{\mathrm{v}}=g\left(\mathbf{X}_{\mathrm{w}}\right)\).
- (3) Simple linear layer
- To connect image features into the word embedding space
- Trainable projection matrix \(\mathbf{W}\)
- \(\mathbf{H}_{\mathrm{v}}=\mathbf{W} \cdot \mathbf{Z}_v, \text { with } \mathbf{Z}_v=g\left(\mathbf{X}_v\right)\).
Regarding (3) Simple linear layer…
- LLaVA: Simple
- Cross-attention in Flamingo & Q-former in BLIP-2: Complex
(2) Training
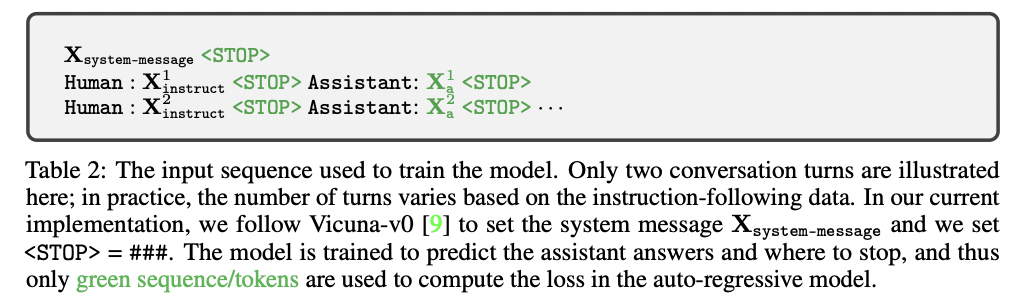
a) Dataset format
For each image \(\mathbf{X}_{\mathrm{q}}\) ….
\(\rightarrow\) Multi-turn conversation data \(\left(\mathbf{X}_q^1, \mathbf{X}_{\mathrm{a}}^1, \ldots, \mathbf{X}_q^T, \mathbf{X}_{\mathrm{a}}^T\right)\)
Instruction \(\mathbf{X}_{\text {instruct }}^t\) at the \(t\)-th turn:
- \(\mathbf{X}_{\text {inatruct }}^t=\left\{\begin{array}{l} \text { Randomly choose }\left[\mathbf{X}_{\mathrm{q}}^1, \mathbf{X}_{\mathrm{v}}\right] \text { or }\left[\mathbf{X}_{\mathrm{v}}, \mathbf{X}_{\mathrm{q}}^1\right], \text { the first turn } t=1 \\ \text { the remaining turns } t>1 \end{array}\right.\).
Result: Unified format for the multimodal instruction-following sequence
b) Loss function
- \(p\left(\mathbf{X}_{\mathrm{a}} \mid \mathbf{X}_{\mathrm{v}}, \mathbf{X}_{\text {inatract }}\right)=\prod_{i=1}^L p_\theta\left(x_i \mid \mathbf{X}_{\mathrm{v}}, \mathbf{X}_{\text {instruct},<i,}, \mathbf{X}_{\mathrm{a},<i}\right),\).
c) [Stage 1] Pre-training for Feature Alignment
- Filter CC3M to 595K image-text pairs
- Freeze & Train
- Freeze: LLM & Visual Encoder
- Train: Projection matrix
d) [Stage 2] Fine-tuning End-to-End
- Freeze & Train
- Freeze: Visual Encoder
- Train: LLM & Projection matrix
