Unified Language-Vision Pretraining in LLM with Dynamic Discrete Visual Tokenization
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.04669
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
Abstract
Previous approaches in VLMs
- (Vision) Regard the visual input as a prompt
- (Language) Focus exclusively on optimizing the text generation process
- Conditioned upon vision content by a frozen LLM
$\rightarrow$ Inequitable treatment of vision and language!
Proposal
-
(1) Propose a new visual tokenizer
-
To translate the non-linguistic image into a sequence of discrete tokens like a foreign language that LLM can read
-
The resulting visual tokens encompass high-level semantics
& support dynamic sequence length varying from the image.
-
-
(2) LaVIT = uses this tokenizer!
-
Handle both image and text indiscriminately
( under the same generative learning paradigm )
-
1. Introduction
Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs)
- Aim at extending the powerful pure-text LLMs to process multi-modality inputs
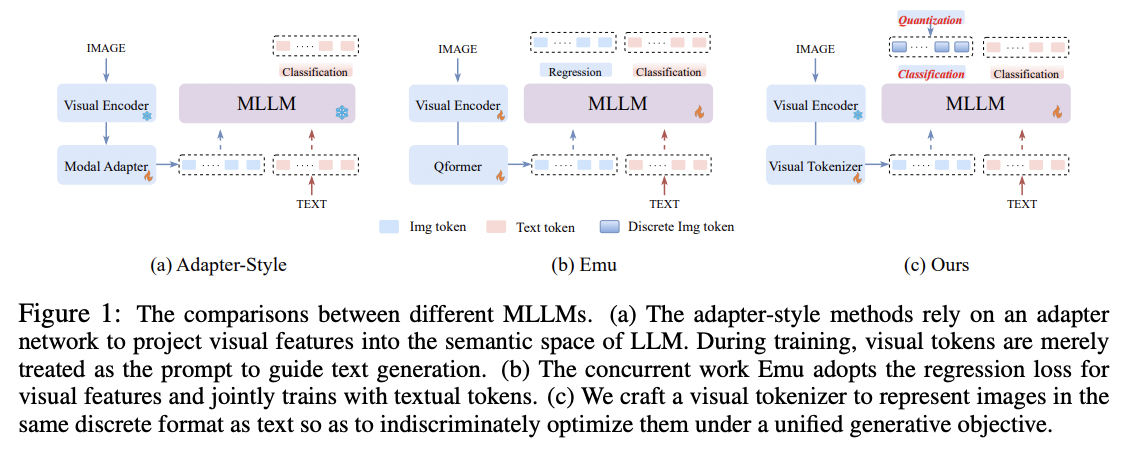
- Prevalent approaches: Figure 1-(a)
- Mostly leverage an adapter architecture to map the visual features to the space of LLM!
- e.g., the Resampler, linear projection, Q-Former
$\rightarrow$ Suffer from inherent design deficiencies!
Limitation of prior works?
-
(1) Training objective
-
Focused on predicting textual descriptions dependent on visual content
( = Visual parts are merely regarded as prompts without any supervision )
$\rightarrow$ Inequitable treatment of different modal inputs!
-
-
(2) Delegate the responsibility of vision-language alignment to the newly added adapter with limited trainable parameters
$\rightarrow$ Fails to leverage the remarkable reasoning capabilities of LLM to learn the interaction across different modalities
Concurrent work: Emu (Figure 1-(b))
-
Proposes to unlock the text-pretrained LLM
$\rightarrow$ By regressing the next visual embedding during pre-training
-
Limitation: The inconsistent optimization objectives for image and text
Proposal: LaVIT (Language-VIsion Transformer)
a novel general-purpose multimodal foundation model that inherits the successful learning paradigm of LLM: predicting the next image/text token in an auto-regressive manner. Our insight is that by employing a unified objective to indiscriminately treat tokens from different modalities, the model can seamlessly achieve “any-toany” multi-modal comprehension and generation. However, the original LLM is specifically crafted to process discrete textual tokens. When dealing with physical signal inputs, such as images, it becomes imperative to embrace a representation seamlessly compatible with text tokens. Therefore, we propose to translate the image into a sequence of tokens like a foreign language that LLM can comprehend, so that both images and texts can be handled simultaneously under the unified generative objective without any specific architectural modification, as shown in Figure 1-(c).
To achieve this goal, a crucial element lies in the development of an efficient visual tokenizer for encoding images, which we contend should adhere to the following principles: (i) discrete visual token: While language models rely on text tokens defined by a dictionary, prior visual tokens, like those derived from ViT, consist of continuous feature vectors encoding a patch. In approaches such as masked image modeling (He et al., 2022) or masked feature prediction (Wei et al., 2022), regressive objectives on continuous features or raw visual pixels are employed for self-supervised pretraining. Here, we advocate for quantizing the visual tokens into a discrete form, aligning them with the next-token prediction objective in language models. This form is particularly advantageous when the target distribution for the next token is multi-mode. (ii) dynamic token allocation. Given the varying semantic complexity of different images, employing a fixed length of tokens to encode all images is compute-uneconomical. Moreover, as a key difference from textual tokens, visual patches exhibit a notable interdependence, making it considerably more straightforward to deduce one token from others. This renders the next-token paradigm less effective in learning visual knowledge through self-supervision. Thus we argue for the token-merging to ensure the least redundancy among visual patches, thereby rendering a dynamic token number for different images.
Following the aforementioned two crucial fundamentals, LaVIT introduces a novel dynamic visual tokenization mechanism consisting of a selector and a merger to process images. The token selector first decides which visual patches carry informative semantics and are necessary to be selected to encode the whole image. In order to maximally preserve the image details, the token merger further compresses the unselected patches onto the retained ones according to their feature similarity. Such a design enables each retained visual token to contain high-level semantics from multiple similar patches and thus reduce the redundancy among tokens. This selecting and merging strategy will produce a dynamic sequence length varying from the image content itself. The retained visual tokens are further quantized into discrete codes by a learnable codebook (Esser et al., 2021), which will serve as the supervision signals for visual tokens during pre-training. Empowered by this visual tokenizer, our LaVIT can be trained with a simple yet unified objective: predicting the next image/text token in the multi-modal sequence. After pre-training, LaVIT can serve as a multi-modal generalist to perform both multi-modal comprehension and generation without further fine-tuning (See Figure 2). The key contributions of this work are summarized as:
- We introduce LaVIT, a new effective, general-purpose multi-modal foundation model that goes beyond the traditional adapter-based architectures. By transforming images into a sequence of discrete tokens like a foreign language that LLM can comprehend and generate, both modalities can be associated indiscriminately under a unified generative training paradigm.
- The developed visual tokenizer can produce discrete visual tokens with dynamic length to reduce the interdependence among visual patches, which enhances the representation compatibility of image and text in LLM and improves computational efficiency.
- Our LaVIT showcases the extraordinary multi-modal understanding and generation potential. It can take any modality combinations as input and perform impressive in-context generation of both images and text. As demonstrated by extensive experiments, LaVIT achieves state-of-the-art zero-shot performance on a wide range of vision-language tasks.
(1) 뛰어난 학업 성적 연세대학교에서 경영학과 및 응용통계학을 복수전공하며 최우등 졸업(상위 1%) 및 조기 졸업(7학기)을 달성하였으며, 석박통합과정에서 GPA 4.29/4.5를 기록하였습니다. 박태영 교수님과 이기복 교수님의 공동 지도를 받으며 Time Series (TS) 딥러닝을 중심으로 Representation Learning, Foundation Models, Diffusion Models, GNN 등 다양한 연구를 수행하였습니다.
(2) 긍정적인 태도, 리더십 긍정적인 태도와 원활한 협업 능력을 갖추고 있으며, 자기 주도적으로 연구를 수행하며 새로운 방법을 탐색하는 데 집중합니다. 다양한 연구 프로젝트에서 공동 연구를 진행하며 효과적인 커뮤니케이션과 팀워크의 중요성을 깊이 이해하고 있습니다. 또한, 교내 데이터사이언스 (Data Science Lab, 2019.01~2020.08) 학회장 을 맡아 연구자 간 협력을 촉진하고 학술 활동을 주도한 경험이 있습니다.
(3) AI 연구 성과 및 강한 모멘텀 최근 1.5년 동안 총 7개의 연구를 수행하며, 이 중 6개에서 제1저자로 기여하였습니다. ICLR 2024에 2편(1편 Spotlight), NeurIPS 2024에 1편, NeurIPS Workshop 2023과 2024에 각각 2편(총 1편의 Oral Presentation), 그리고 현재 ICML 2025에 제출한 4편 (3편 1저자)이 심사 중입니다. 지속적인 연구를 통해 강한 연구 모멘텀을 유지하고 있습니다. 기존에는 TS 분야를 초점으로 연구를 했었지만, 특정 도메인에 국한되지 않고 폭넓은 연구 역량을 갖추고자 다양한 모달리티의 연구를 진행하고 있습니다 (LLM for TS, VLM 등). 또한, 자발적으로 연구를 수행하는 성향이 강하여 (self-motivated), 두 분의 공동 지도 교수님이 TS와 다른 분야를 전공하심에도(교수님 1: 베이지안 통계, 교수님 2: 컴퓨터 비전) 관심 있는 연구 주제(TS)를 제안하고 지도를 받아 여러 탑티어 컨퍼런스에 논문을 제출하였습니다.
(4) 최신 연구 동향 파악
딥러닝의 세계가 빠르게, 다양한 모달리티에서 발전하는 상황을 잘 인지하고 있고, 이에 대해 잘 파악하고자 지난 5년간 약 1400편에 달하는 논문 리뷰를 깃헙 블로그에 올리고 있습니다.
하고 이를 정리하여 GitHub(https://seunghan96.github.io/)에 업로드하며 최신 연구 트렌드를 꾸준히 탐색하고 있습니다.
지원분야와 관련하여 본인의 기술력을 보여줄 수 있는 활동내역을 모두 기재해주세요
나는 “지원분야와 관련하여 본인의 기술력을 보여줄 수 있는 활동내역을 모두 기재해주세요”란에 답변을 해야하는데, 아래는 내가 지원하려는 부서에 대한 소개야.
지원 부서: Vision Foundation Model의 전반적인 성능 향상을 위해 더 정교한 Multimodal LLM Backbone을 개발하고, HyperCLOVA X 이미지 인식 기능을 출시한 부서입니다.
상세 업무: Pretrained Language Model에 Supervised Fine-Tuning을 적용해 Vision 능력을 추가하는 파이프라인은 잘 알려진 VLM 개발 방식임에도, Pretrain 단계에서 다양한 모달리티를 함께 학습해 Vision 역량을 근본적으로 강화하는 Omni Training의 효과는 여러 가설이 있을 뿐, 실제 성능 개선에 대한 Ablation 연구는 충분히 공개되지 않았습니다. 우리 부서는 Vision Foundation Model의 성능을 높이기 위해 더 정교한 Multimodal Backbone 개발에 집중하고 있습니다.
Vision/NLP(LLM)/TS/Tabular/Audio/Multimodal/Diffusion/Mamba/SSL
