MMICL: Empowering Vision-Language Model with Multi-Modal In-context Learning
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.07915
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- MMICL
- Model Architecture
- Design of Context Scheme of MMICL
Abstract
Vision-language models (VLMs)
-
LLMs = Utilize extensive background knowledge and task information with in-context learning
-
VLMs = still struggle with in-context learning
\(\rightarrow\) Making VLMs less effective in downstream vision-language tasks.
Proposal:
- (1) Introduce VLM with Multi-Modal In-Context Learning (MMICL)
- Allow the VLM to deal with multi-modal inputs efficiently
- (2) Novel context scheme to augment the in-context learning ability of the VLM
- (3) Construct the Multi-modal In-Context Learning (MIC) dataset
- To enhance the VLM’s ability to understand complex multi-modal prompts.
Experiments
- New SOTA zero-shot performance on a wide range of general VL tasks
- Especially for complex benchmarks
- e.g., MME and MMBench.
-
Effectively tackles the challenge of complex multi-modal prompt understanding & emerges the impressive ICL ability
-
Alleviates language bias in VLMs
( = Common issue for VLMs that often leads to hallucination when faced with extensive textual context )
1. Introduction
Recent VLMs
- Augment LLM with a visual encoder
- Impressive zero-shot capacities in various visual tasks
- Limitation:
- LLMs: Can extract rich background knowledge and task information from the prompt with in-context learning (ICL)
- VLMs: Still struggle to understand complex multi-modal prompts that include multiple images.
Previous studies
-
Focus on handling the user queries with a single image
( rather than multi-modal prompts with interleaved multiple images and text )
Flamingo, Kosmos-1
- Handle user queries with multiple images
- Limitation: Their pre-training data can not provide more sophisticated multi-modal prompts than interleaved image and text crawled from the web
\(\rightarrow\) Gap between the prompts used in (1) & (2)
- (1) Pre-training datasets
- (2) User queries in real-world scenarios
- which always contain multiple images & sophisticated text
Three limitations
Limitations making VLMs less effective in downstream tasks
- (1) Hard to Understand Text-to-Image Reference
- (2) Hard to Understand Relationships btw Multiple Images
- (3) Hard to Learn from In-Context Multi-Modal Demonstrations
(1) Hard to Understand Text-to-Image Reference
- Intricate referential relationships between the text and images in user queries, with different words mentioning different images.
- Figure 1(c) & 1(f): Question about multiple images
- Figure 1(d): Use multiple images as exemplars to ask the question only about a specific image
- Limitation of previous works:
- Dataset: crawled from the web & may lack explicit text-to-image references
(2) Hard to Understand Relationships btw Multiple Images
- There are often spatial, temporal, and logical relationships between multiple images
- Limitation of previous works:
- Dataset: collected from the internet & lack close connections among images
(3) Hard to Learn from In-Context Multi-Modal Demonstrations
- ICL ability of current VLMs is limited!!
- (1) BLIP-2, LLaVA: Only support multi-modal prompts with a single image
- (2) Flamingo: Support multi-image inputs during pretraining and emerge ICL abilities, but their context schemes fail to provide text-image references and closely related images

Proposal: MMICL
- (1) MMICL
- To allow VLMs to efficiently deal with multi-modal inputs
- Relationships among multiple images and text-to-image references
- (2) Novel context scheme
- Incorporate an extra image declaration section
- Inclusion of image proxy tokens,
- (3) Multi-modal in-context learning dataset
2. MMICL
(1) Model Architecture
Visual-Prompt Generators (VPG)
-
Most VLMS utilize VPG
(e.g., Resampler (Alayrac et al., 2022), Qformer (Li et al., 2023d))
-
To extract visual embeddings from the image features & use them to help LLMs understand visual inputs!
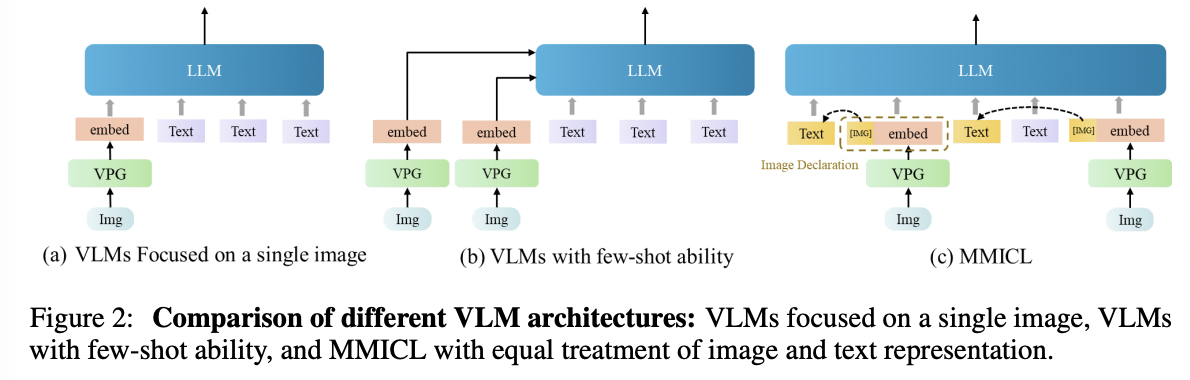
- (a) VLMs that focus on prompts with a single image
- e.g., Blip-2: Places the image at the top of the entire input and can not handle the inputs with multiple images.
- (b) VLMs with few-shot ability
- e.g., Flamingo: Encode images into image embeddings with a fixed number of visual tokens and inserts new gated cross-attention layers into the LLM to inject visual features.
- (c) MMICL
- Treats image and text representations equally
- Establishes the reference between image and text via image declaration
- Effect
- Enables users to have the flexibility to input multiple images and text in any desired order
- No restrictions on the quantity or placement of images in contexts
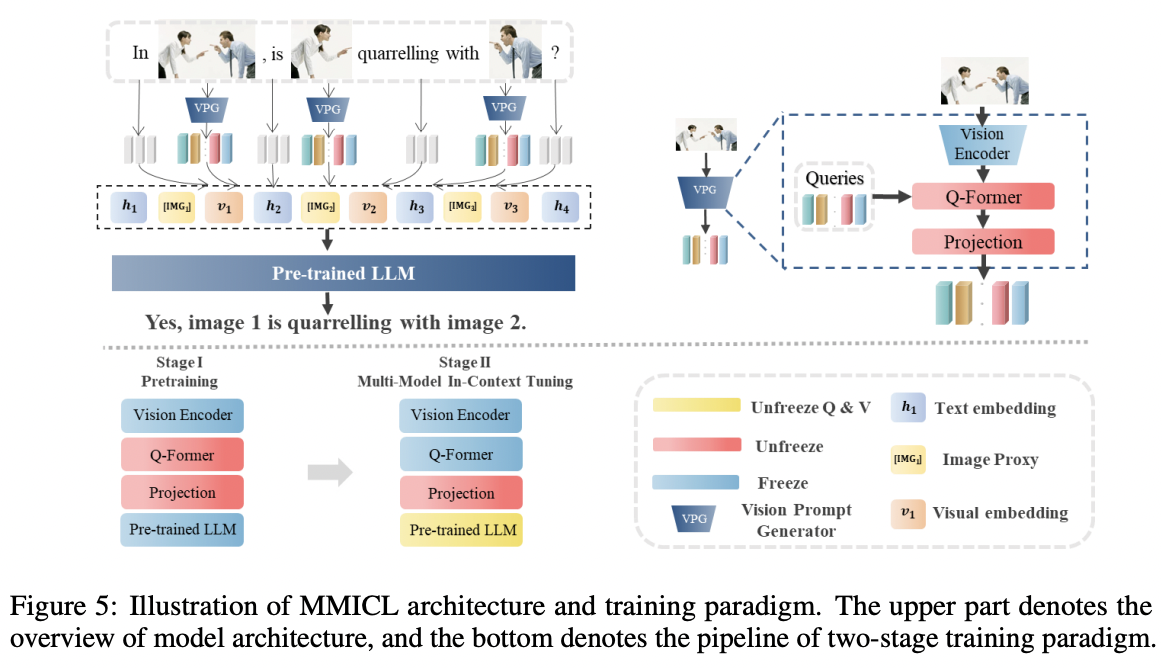
Procedures
- Step 1) Vision encoder (e.g., ViT)
- Step 2) VPG (e.g., Q-former)
- To encode images into embeddings understandable by LLM
- Step 3) FC layer ( = projection layer )
- To convert each visual embedding to the same dimension as the text embedding
- Step 4) Combine the visual and text embeddings
- Into an interleaved style
- Step 5) Feed them into the LLM
(2) Design of Context Scheme of MMICL
To proficiently transform the interleaved image-text data into the training context for MMICL!
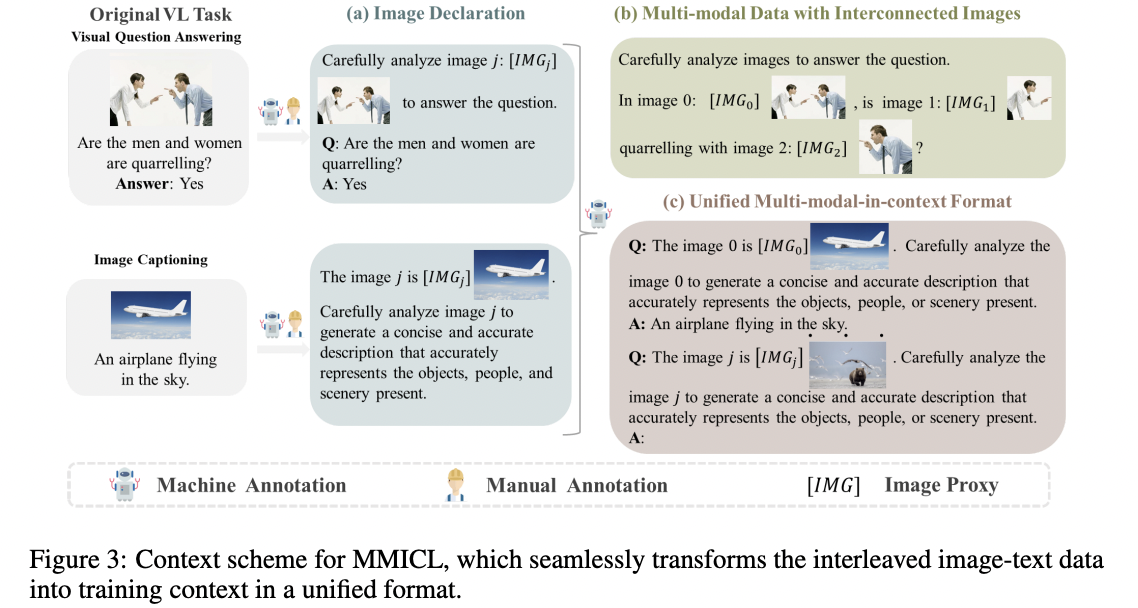
a) Image Declaration
- Step 1) Unique image proxy ([IMG \(j\) ]) to reference the visual embedding of image \(j\),
- Distinguish between visual and text embeddings.
- Step 2) Natural language prompts to establish references between text and image.
- Assists the model in correlating the text with the appropriate image.
Instance \(\mathbf{I}_i=\left(\mathbf{X}_i, \mathbf{q}_i, \mathbf{a}_i\right)\).
- \(\mathbf{X}_i\) = Set of image decorations that can be placed anywhere
- \(\mathbf{q}_i\) and \(\mathbf{a}_i\) = question with instruction & answer
b) Multi-modal Data with Interconnected Images
Multi-image data that includes spatial, logical, and temporal relationships.
Instance \(\mathbf{I}_i=\left(\left\{\mathbf{x}_1, \mathbf{x}_2, \ldots, \mathbf{x}_k\right\}, \mathbf{q}_i, \mathbf{a}_i\right)\)
- Qestion-answer text pair along with \(K\) images
- where the \(\mathbf{x}_{i, k} \in \mathbf{X}_i\) represents the image declaration for the \(k\)-th image
c) Unified Multi-modal In-Context Format for Different Tasks
Instance \(\mathbf{I}_i=\left(\left\{\mathbf{P}_1, \cdots, \mathbf{P}_N\right\}, \mathbf{X}_i, \mathbf{q}_i, \mathbf{a}_i\right)\)
- Exemplar \(\mathbf{P}_j=\left(\mathbf{X}_j, \mathbf{q}_j, \mathbf{a}_j\right)\)
- \(\mathbf{X}_j\) = Image declaration of the \(j\)-th exemplar
- \(\mathbf{q}_j\) and \(\mathbf{a}_j\) = Question and answer for the \(j\)-th exemplar
