Qwen-VL: A Versatile Vision-Language Model for Understanding, Localization, Text Reading, and Beyond
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2308.12966
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Methodology
- Architecture
- Inputs & Outputs
- Training
- Stage 1: Pre-training
- Stage 2: Multi-task Pre-training
- SFT
1. Abstract
Qwen-VL series
- Set of large-scale VLMs
- Endow Qwen-LM with visual capacity using
- (1) Visual receptor
- (2) Input-output interface
- (3) 3-stage training pipeline
- (4) Multilingual multimodal cleaned corpus.
- Conventional Task
- Image description
- Question-answering
- New Task
- Grounding and text-reading ability of Qwen-VLs by aligning image-caption-box tuples
- Proposed model
- QwenVL
- Qwen-VL-Chat
2. Introduction
P1. Trend of LLM & VLMs
LLMs
- Further aligned with user intent through instruction tuning
Limitation of LLMs
- Lacking the ability to handle other common modalities
Solution: Large Vision Language Models (VLMs)
- Enhance LLMs with the ability to perceive and understand visual signals
P2. Limitation of VLMs
(Current open-source) LVLMs
-
(1) Suffer from inadequate training and optimization
-
(2) Real-world visual scenarios: Complicated
\(\rightarrow\) Fine-grained visual understanding plays a crucial role for VLMs
\(\rightarrow\) But only a few attempts had been made toward this direction!
( Most of them remain in a coarse-grained approach )
P3. Proposal: Qwen-VL series
VLMs based on Qwen-7B
- Empower Qwen with visual capacity
- (1) Visual receptor
- a) Language-aligned visual encoder
- b) Position-aware adapter
- (2) Input-output interface are concise
- (3) 3-Stage training pipeline
P4. Qwen-VL
Qwen-VL
- Pretrained checkpoint = called Qwen-VL
- Capable of perceiving and understanding visual inputs
- Diverse tasks:
- Image captioning
- Question answering
- Text-oriented question answering
- Visual grounding.
Qwen-VL-Chat
- Instruction-tuned VL chatbot based on Qwen-VL

P5. Features of the Qwen-VL series models
- Leading performance
- Top-tier accuracy
- On a vast of vision-centric understanding benchmarks
- Compared to counterparts with similar scales.
- Outperform in both (a) & (b)
- (a) Conventional benchmarks
- e.g., captioning, question-answering, grounding
- (b) Recently introduced dialogue benchmarks
- (a) Conventional benchmarks
- Top-tier accuracy
- Multi-lingual
- (Similar to Qwen-LM) Trained upon multilingual image-text data
- Support English, Chinese, and multilingual instructions
- (Similar to Qwen-LM) Trained upon multilingual image-text data
- Multi-image
- Input = Arbitrary interleaved image-text data
- Compare, understand, and analyze the context when multiple images are given
- Fine-grained visual understanding
- Higher-resolution input size & Fine-grained corpus
- Highly competitive fine-grained visual understanding ability
3. Methodology
(1) Architecture
Three components
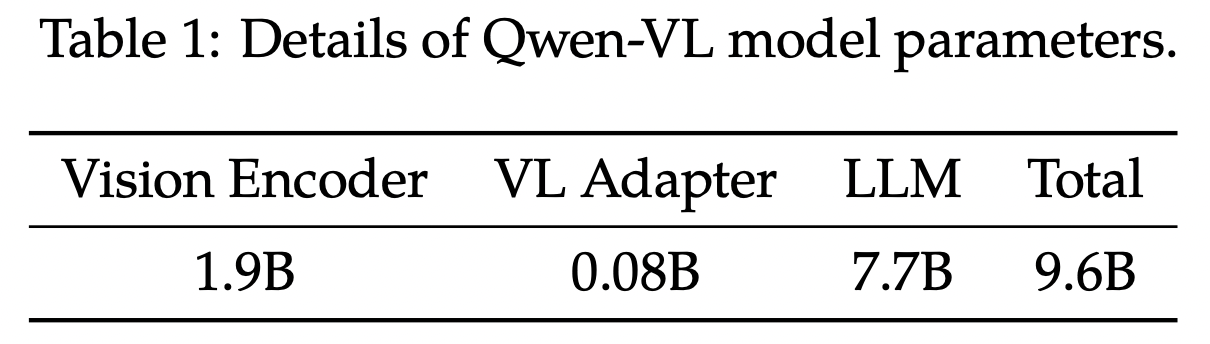
-
(1) LLM: Qwen-7B
-
(2) Visual Encoder: ViT
- Initialized with pre-trained weights from Openclip’s ViT-bigG
- Image is resized to a specific resolution
-
(3) Position-aware Vision-Language Adapter
-
To alleviate the efficiency issues
-
Compresses the image features
-
With single-layer cross-attention module
- Query: Group of trainable vectors
- Keys: Image features from the visual encoder
( + 2D absolute positional encodings (to query-key pairs) )
-
(2) Inputs & Outputs
a) Image (Input)
Processing Images:
-
Model: Visual encoder and adapter,
-
Output: Fixed-length sequences of image features
How to differentiate image & text feature?
- Two special tokens (<img> & </img> ) are appended to the beginning & end of the image feature
b) Bounding Box (Input and Output)
[Goal] Enhance the model’s capacity for fine-grained visual understanding and grounding
[How] Use data in the form of region descriptions, questions, and detections
\(\rightarrow\) Necessitates the model’s accurate understanding and generation of region descriptions in a designated format!
- a) Normalization process: To bbox within the range [0,1000)
- b) Transformation: Into a specified string format: \(\left(X_{\text {topleft }}, Y_{\text {topleft }}\right),\left(X_{\text {bottomright }}, Y_{\text {bottomright }}\right)\)
- c) Tokenization: Tokenize string as text
- d) New tokens: Distinguish btw detection string & text string?
- Two special tokens (<box> and </box>)
- Another set of special tokens (<ref> and </ref>)
- To appropriately associate bounding boxes with their corresponding descriptive words to mark the content referred to by the bounding box.
3. Training
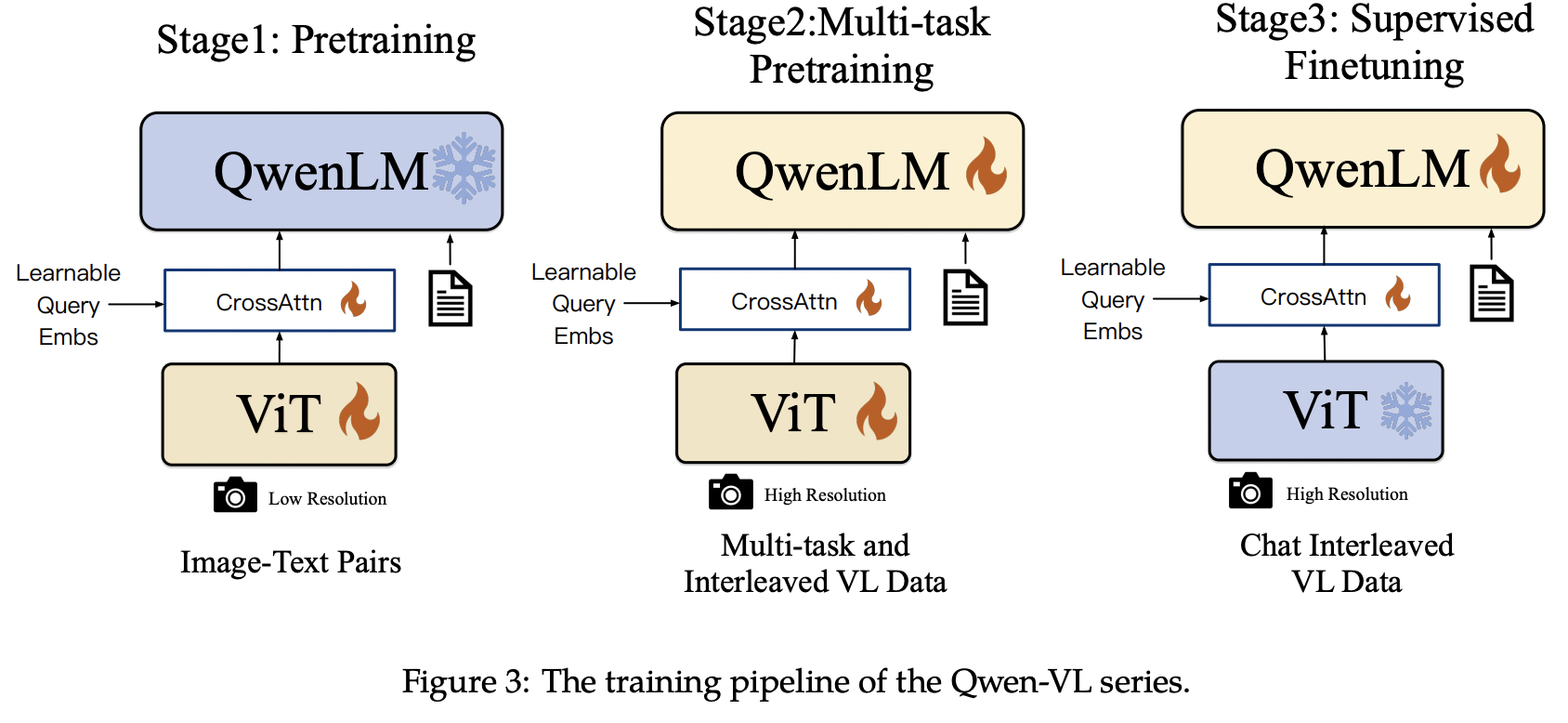
Training process of the Qwen-VL model consists of 3stages
- (1) Two stages of pre-training
- (2) Final stage of instruction fine-tuning
(1) Stage 1: Pre-training
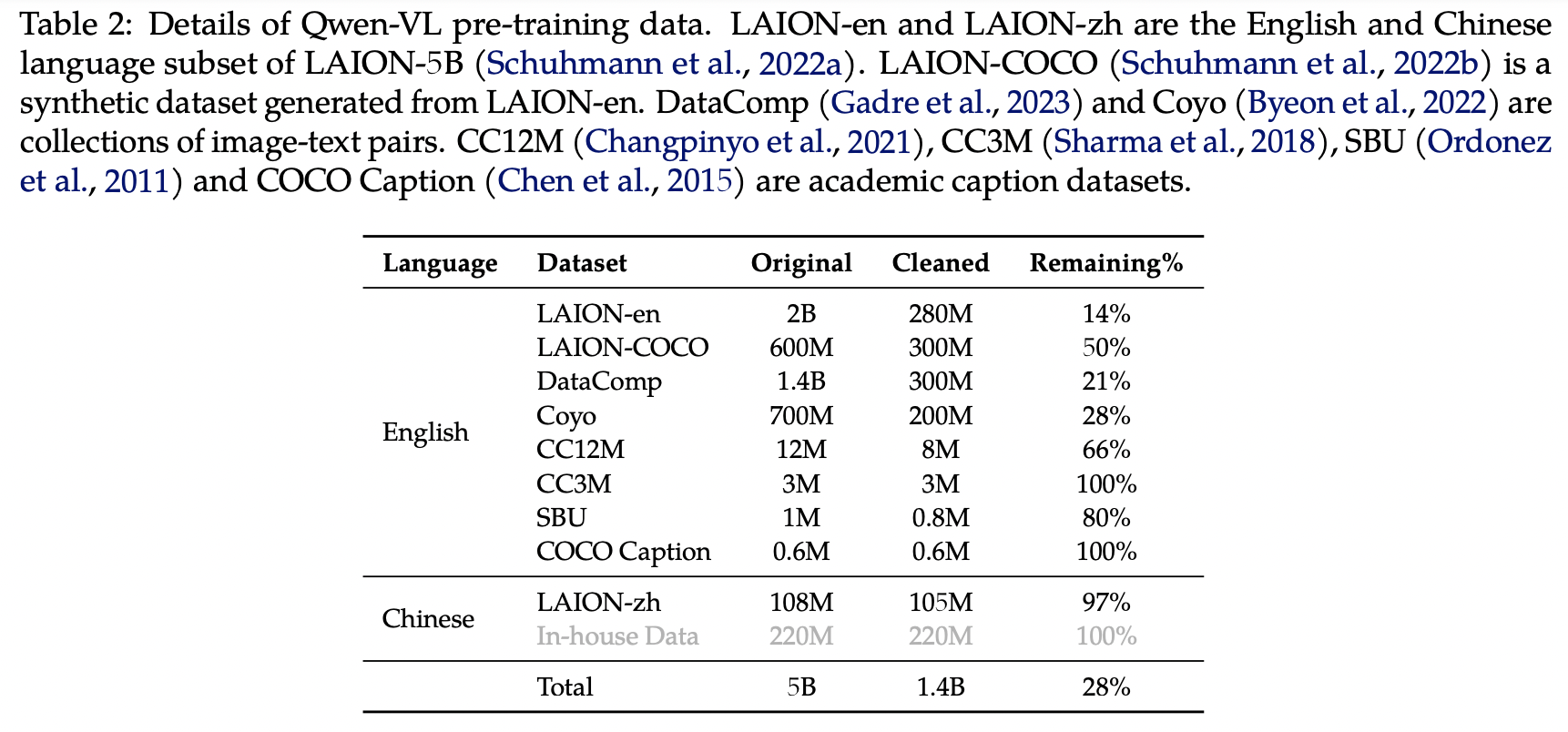
a) Dataset
Large-scale, weakly labeled, web-crawled set of image-text pairs
- Several publicly accessible sources
- Some in-house data.
Clean the dataset of certain patterns
b) Details
-
(1) Freeze & Train
-
Freeze: LLM
-
Train: Vision encoder & VL adapter
-
-
(2) Image size = Resized to 224 × 224
-
(3) Objective = Cross-entropy of the text tokens (LM)
(2) Stage 2: Multi-task Pre-training
a) Dataset
High-quality and fine-grained VL annotation data
- With a larger input resolution
Format: Interleaved image-text data.
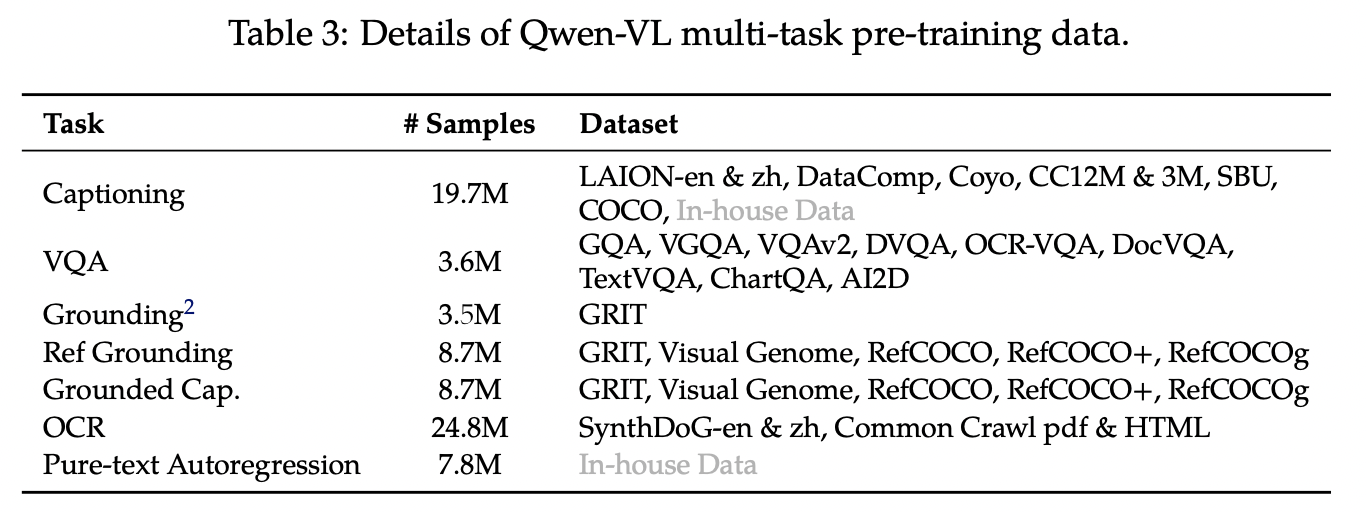
b) Multi-task
Train Qwen-VL on 7 tasks simultaneously
c) Details
-
(1) Freeze & Train
-
Freeze: -
-
Train: All
-
-
(2) Image size = Increase the resolution from 224 × 224 to 448 x 448
-
(3) Objective = Cross-entropy of the text tokens (LM)
(3) SFT
Finetuned the Qwen-VL pre-trained model through instruction fine-tuning
\(\rightarrow\) Too enhance its instruction following and dialogue capabilities
\(\rightarrow\) Result: Interactive *Qwen-VL-Chat model
