SimVLM: Simple Visual Language Model Pretraining with Weak Supervision
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2108.10904
1. Abstract
Vision-Language Pretraining (VLP)
-
Impressive performance on many multimodal downstream tasks
-
Limitation: Expensive annotations including clean image captions and regional labels
Visual Language Model (SimVLM)
Relax these constraints & Present a minimalist pretraining framework
- (1) Reduces the training complexity by exploiting large-scale weak supervision
- (2) End-to-end with a single prefix language modeling objective
2. SimVLM
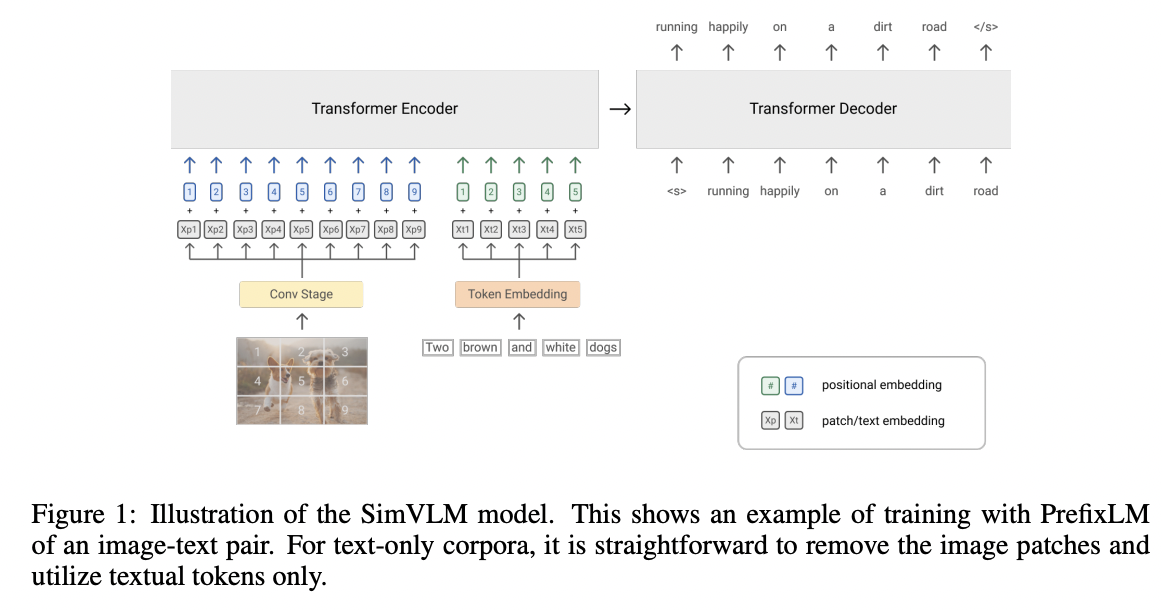
(1) Objective: Prefix LM
Preliminaries: LM loss
- \(\mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{LM}}(\theta)=-\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x} \sim D}\left[\log P_\theta(\mathbf{x})\right]=-\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x} \sim D}\left[\sum_{t=1}^T \log P_\theta\left(\mathbf{x}_t \mid \mathbf{x}_{<t}\right)\right]\).
Proposal: Prefix Language Modeling (PrefixLM)
- During pretraining, a prefix sequence of tokens of (a randomly selected) length \(T_p\) is truncated from input sequence
\(\mathcal{L}_{\text {PrefixLM }}(\theta)=-\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x} \sim D}\left[\log P_\theta\left(\mathbf{x}_{\geq T_p} \mid \mathbf{x}_{<T_p}\right)\right]=-\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x} \sim D}\left[\sum_{t=T_p}^T \log P_\theta\left(\mathbf{x}_t \mid \mathbf{x}_{\left[T_p, t\right]}, \mathbf{x}_{<T_p}\right)\right]\).
Difference with LM?
- Bi-directional attention on the prefix sequence (e.g. \(\mathbf{x}_{<T_p}\) )
- Autoregressive factorization on the remaining tokens (e.g. \(x_{\geq T_p}\) )
Details:
-
Images can be considered as prefix for their textual descriptions!
-
Prepend image feature sequence of length \(T_i\) to the text sequence
( + Enforce the model to sample a prefix of length \(T_p \geq T_i\) )
-
(1) + (2)
- (1) Bidirectional contextualized representation as in MLM
- (2) Text generation similar to LM
(2) Architecture
Backbone: Transformer
- Bidirectional attention within the prefix sequence
- Applicable for both decoder-only & encoder-decoder sequence-to-sequence LMs
Refer to Figure 1
