Modelling Context and Syntactical Features for Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis (2020)
Contents
- Abstract & Introduction
- Proposed Method
- AE (Aspect Extraction)
- ASC (Aspect Sentiment Classification)
1. Abstract & Introduction
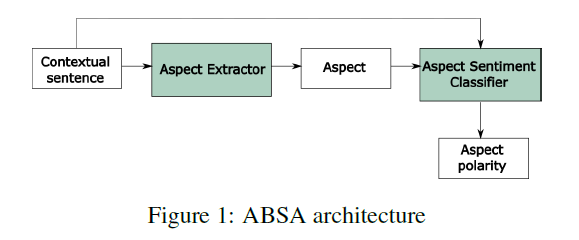
ABSA의 2가지 task
- AE ( Aspect Extraction )
- ASC ( Aspect Sentiment Classification )
두 가지의 task를 각각(separately)풀지 않고, (1) end-to-end 방식으로 풀기를 제안
+ 기존의 연구들은 (2) syntactic information를 사용하지 않아서, 이를 활용하는 알고리즘 제안
This paper explores the
- (1) grammatical aspects of the sentence
- (2) and employs the self-attention mechanism for syntactical learning
CSAE ( Contextualized Syntactic-based Aspect Extraction )
보다 구체적으로, aspect extractor의 성능을 높이기 위해, 아래 3개의 embedding을 combine한다.
- 1) POS embeddings
- 2) dependency-based embeddings
- 3) contextualied embeddings ( e.g. BERT, ROBERTa )
SRD ( syntactic relative distance )
- 무관한 단어를 de-emphasize하기 위해!
- idea) shortest path between words in dependency parsing tree
- 이 방법을 LCFS-ASC (Local Context Focus on ASC)라고 한다
[ Contributions ]
- 1) propose multi-channel CASE
- ( which distils grammatical aspects into contextualized features )
- 2) contribute the LCFS-ASC
- ( which analyze syntactical connections between words to better understand local contexts that are relevant to target aspect terms )
- 3) study the importance of SRD
- ( by exploring attention score )
2. Proposed Method
Notation
- contextual sentence \(S\) : \(S=\left\{w_{i} \mid i \in[1, n]\right\}\)
- E2E ABSA task의 목적 : extract \(A\)& determine \(y_p\)
- \(A=\left\{a_{i} \mid i \in[1, m]\right\}\).
- \(y_{p} \in\) \(\{\) Positive, Negative, Neutral \(\}\)
2-1) AE (Aspect Extraction)
AE 문제 = sequence labeling problem
-
input token \(w_{i}\) 에 대하여, label \(y_{i}\)를 assign하기
( \(y_{i}\) : values from the set \(\{B, I, O\}(\) Begin, Inside, Outside) )
제안된 CASE ( Contextualized Syntax-based Aspect Extraction ) model :
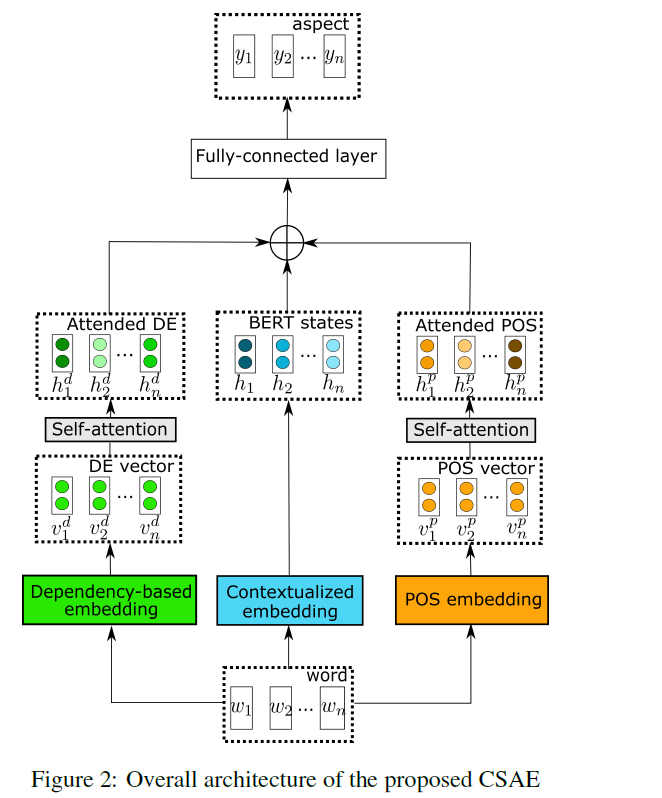
- 1) POS embeddings
- 2) dependency-based embeddings
- 3) contextualied embeddings ( e.g. BERT, ROBERTa )
(a) Input Representation
- “[CLS]”+ Input Sequence + “[CLS]”
(b) POS Embedding
- part-of-speech (POS) embedding
- Embedding Layer의
- input : \(P=\left\{p_{1}, p_{2}, \ldots, p_{n}\right\}\)
- output : \(V^{P}=\left\{v_{i}^{p} \mid i \in[1, n]\right\}\)
- 그런 뒤, self-attention layer를 사용하여 input sentence의 grammatical dependencies를 잡아내!
(c) Dependency-based Embeddings
-
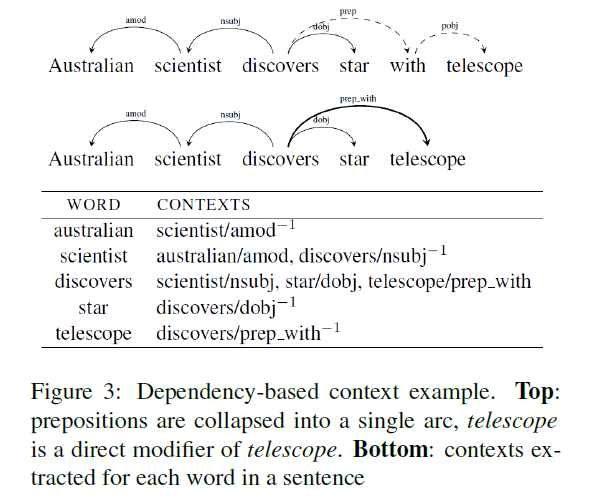
sentence를 parse하기 위해, dependency tree를 사용해!
-
target word \(w\) 와, 이와 관련된 modifiers \(m_{1}, m_{2}, \ldots, m_{n}\)에 대해,
context \(C=\left\{\left(m_{1}, r e l_{1}\right),\left(m_{2}, r e l_{2}\right), \ldots,\left(m_{n}, r e l_{n}\right)\right\}\)를 construct한다.
- 여기서 \(r e l_{i}\) 는 (\(w\)와 \(m_i\) 사이의) dependency relation이다 (e.g., subj, amod, pobj)
-
final context를 뽑아내기 전에, relations consisting of a preposition are collapsed
( 아래 그림 참고 )
(d) Fine-tuning Procedure
- loss : CE loss
- regularization : L2
\(\mathcal{L}(\theta)=-\sum_{i=1}^{n} \hat{y}_{i} \log y_{i}+\lambda \sum_{\theta \in \Theta} \theta^{2}\).
2-2) ASC (Aspect Sentiment Classification)
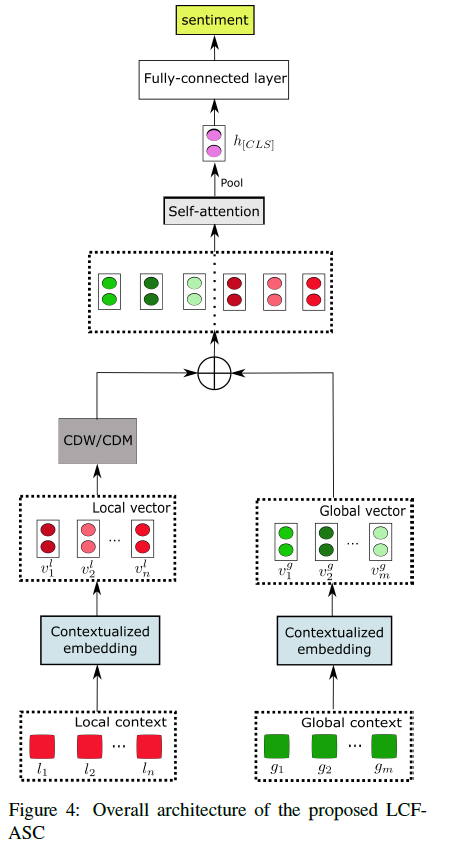
Notation :
- contextual sentence \(S=\left\{w_{i} \mid i \in\right.\) \([1, n]\}\)
- extracted aspect terms \(A=\left\{a_{i} \mid i \in\right.\) \([1, m]\}\)
\(\rightarrow\) \(S\)와 \(A\)가 주어졌을 때, 이에 해당하는 polarity \(\{\) Positive, Neutral, Negative \(\}\) 를 찾아내기!
(a) Input Representation
global context \(G\)
-
\(S\)와 \(A\)가 결합되어 global context \(G\)를 만들어낸다.
-
\(G=[C L S]+S+[S E P]+A+[S E P]\).
local context \(L\)
- \(L\) = contextual sentence \(S\)
- \(L = [CLS] + S + [SEP]\).
(b) Local Context Focus
local context가 contextualized embedding에 들어가서 local context vectors가 나온다
- local context vectors \(V^{l}=\left\{v_{i}^{l} \mid i \in[1, n]\right\}\)
그런 뒤, apply CDW/CDM
- CDW : Context feature Dynamic Weight
- CDM : Context feature Dynamic Mask
Relative Distance
-
SRD between words :
“shortest distance” between nodes in dependency-parsed tree
Context Dynamic Masks (CDM)
-
mask out less-semantic context features
( whose SRD to target words is greater than the pre-defined threshold )
-
즉, 어느정도 거리 넘어가는 애들은 mask out시켜버려!
\(\begin{gathered} v_{i}^{m}= \begin{cases}O & S R D_{i}>\alpha \\ I & S R D_{i} \leq \alpha\end{cases} \\ M=\left[v_{1}^{m}, v_{2}^{m}, \ldots, v_{n}^{m}\right] \\ V^{C D M}=V^{l} \odot M \end{gathered}\).
Context Dynamic Weighting (CDW)
-
retains the contribution of less-semantic-relative context features,
but de-emphasizes them!
( based on their distance to aspect terms )
\(\begin{gathered} v_{i}^{w}= \begin{cases}\left(1-\frac{S R D_{i}-\alpha}{N}\right) \cdot I & S R D_{i}>\alpha \\ I & S R D_{i} \leq \alpha\end{cases} \\ W=\left[v_{1}^{w}, v_{2}^{w}, \ldots, v_{n}^{w}\right] \\ V^{C D W}=V^{l} \odot W \end{gathered}\).
Fine-tuning Procedure
hidden state of “CLS” \(h_{pool}\) is pooled out
& fed into softmax
\(\rightarrow\) Positive / Neutral / Negative 중 하나로!
( AE 모델과 마찬가지의 loss function )
