Hierarchical Attention Networks for Document Classification
0. Abstract
Document classification을 위한 HAN(Hierarchical Attention Network) 알고리즘을 제안함
[ 2가지 Key Point ]
- (1) 문서의 계층적 구조(hierarchical structure)를 반영함
- “문서-문장-단어”의 계층적 구조
- (2) Two-level attention을 적용함
- 1) word-level attention
- 2) sentence-level attention
1. Introduction
(1) Text classification : text에 label을 assign하기
- ex) topic labeling, sentiment classification, spam detection
(2) 기존에 사용되던 방법들
- (통계적 방법론) n-gram 등을 사용하여 얻어낸 text representation에, linear model/kernel method 적용
- (딥러닝) CNN, LSTM등으로 text representation를 얻어냄
(3) Key Idea
“문서의 구조 (document structure)”고려 시, 더 나은 text representation을 얻어낸다!
( = 문서의 모든 부분들이, 정답을 맞추는데에 있어서 동일하게 중요하지는 않을 것! )
(4) HAN (Hierarchical Attention Network)의 insight
- (1) Hierarchical structure
- 1) sentence representation을 얻어낸 뒤
- 2) 이를 aggregate하여 document representation을 얻어내자!
-
(2) different words & sentences \(\rightarrow\) differently informative!
-
1) word level attention
-
2) sentence level attention
-
example)

위의 예시에서, 정답(=”긍정”)을 예측하는데에 있어서 delicious & amazing이 기여를 많이 했을 것!
-
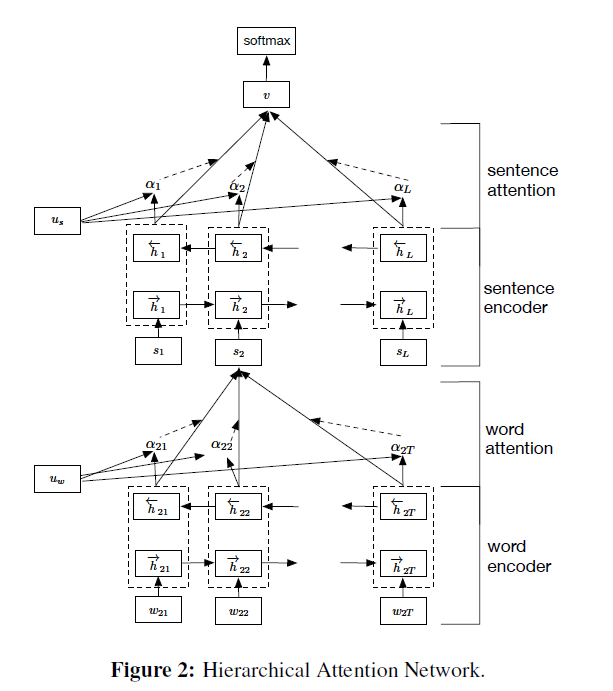
2. Hierarchical Attention Networks
아래의 4가지의 구조로 이루어짐
- (1) WORD sequence encoder
- (2) WORD-level attention layer
- (3) SENTENCE encoder
- (4) SENTENCE-level attention layer
GRU 간단 소개
-
memory cell을 사용하여 중요한/중요하지 않은 정보 선별적으로 저장
-
두 가지 gate 사용 : reset gate \(r_t\) & update gate \(z_t\)
-
\(t\) 시점에 나오게 되는 hidden state (=\(h_t\)) :
\(h_{t}=\left(1-z_{t}\right) \odot h_{t-1}+z_{t} \odot \tilde{h}_{t}\).
- previous state \(h_{t-1}\) 와 current new state \(\tilde{h}_{t}\) 의 linear interpolation
- \(z_{t}\) : 과거의 정보를 얼마나 기억할지, 새로운 정보를 얼마나 추가할지를 결정하는 역할
- \(z_{t}=\sigma\left(W_{z} x_{t}+U_{z} h_{t-1}+b_{z}\right)\).
- \(\tilde{h}_{t}=\tanh \left(W_{h} x_{t}+r_{t} \odot\left(U_{h} h_{t-1}\right)+b_{h}\right)\).
- \(r_t\) ( reset gate ) : 과거의 state가 현재의 candidate state에 얼마나 contribute할 지 조절
- \(r_{t}=\sigma\left(W_{r} x_{t}+U_{r} h_{t-1}+b_{r}\right)\).
Notation
- \(L\) : 문장의 개수
- (계층 1) \(s_i\) : \(i\)번째 문장
- (계층 2) \(T_i\) : \(i\)번째 문장이 가지는 단어의 개수
- (계층 3) \(w_{it}\) : \(i\)번째 문장의 \(t\)번째 단어
- (계층 2) \(T_i\) : \(i\)번째 문장이 가지는 단어의 개수
- 최종 goal : “문서 전체에 대한 representation”이 input으로 들어가, \(y\)를 예측
2-1. Word Encoder
\(w_{it}\)를 embedding matrix \(W_e\)를 사용하여 embedding ( \(x_{i j}=W_{e} w_{i j}\) )
사용하는 모델 : bidirectional GRU
- \(h_{i t}=\left[\vec{h}_{i t}, \overleftarrow{h}_{i t}\right]\).
- \(\vec{h}_{i t}=\overrightarrow{\operatorname{GRU}}\left(x_{i t}\right), t \in[1, T]\).
- \(\overleftarrow{h}_{i t} =\overleftarrow{\operatorname{GRU}}\left(x_{i t}\right), t \in[T, 1]\).
- \(x_{i t} =W_{e} w_{i t}, t \in[1, T]\).
2-2. Word Attention
모든 단어가 “동일하게 중요하지는 않다” \(\rightarrow\) Attention 수행
sentence vector \(s_{i} =\sum_{t} \alpha_{i t} h_{i t}\)
- attention score : \(\alpha_{i t} =\frac{\exp \left(u_{i t}^{\top} u_{w}\right)}{\sum_{t} \exp \left(u_{i t}^{\top} u_{w}\right)}\)
- \(u_{i t} =\tanh \left(W_{w} h_{i t}+b_{w}\right)\).
2-3. Sentence Encoder
( 2-1. Word Encoder와 동일한 구조 )
\(h_{i}=\left[\vec{h}_{i}, \overleftarrow{h}_{i}\right]\).
- \(\vec{h}_{i} =\overrightarrow{\operatorname{GRU}}\left(s_{i}\right), i \in[1, L]\).
- \(\overleftarrow{h}_{i} =\overleftarrow{\operatorname{GRU}}\left(s_{i}\right), t \in[L, 1]\).
2-4. Sentence Attention
( 2-2. Word Attention과 동일한 구조 )
\(v =\sum_{i} \alpha_{i} h_{i}\).
- \(\alpha_{i} =\frac{\exp \left(u_{i}^{\top} u_{s}\right)}{\sum_{i} \exp \left(u_{i}^{\top} u_{s}\right)}\).
- \(u_{i} =\tanh \left(W_{s} h_{i}+b_{s}\right)\).
위의 과정들을 통해, 최종적으로 DOCUMENT vector \(v\)를 얻어냄
( 이를 사용하여 최종적으로 document classification 수행 )
2-5. Document classification
Model : softmax
- \(p=\operatorname{softmax}\left(W_{c} v+b_{c}\right)\).
Loss function : NLL
- \(L=-\sum_{d} \log p_{d j}\) .
