append vs + []
참고 : 널널한 교수의 코딩 클래스
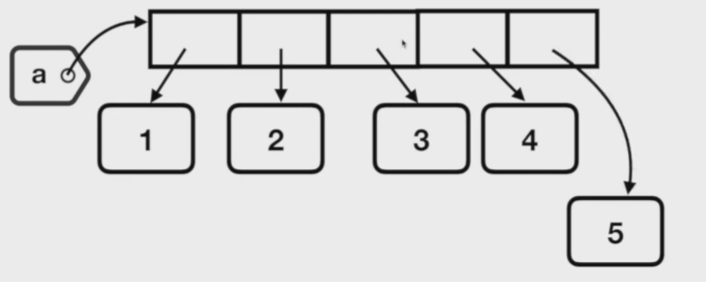
(1) case 1 : .append()
-
리스트 객체의 변경
-
새로운 객체가 생성되고, 해당 새로운 객체를 참조할 수 있는 요소가 생성되는 것
( 리스트는 mutable 객체 )
-
id 변화 없음
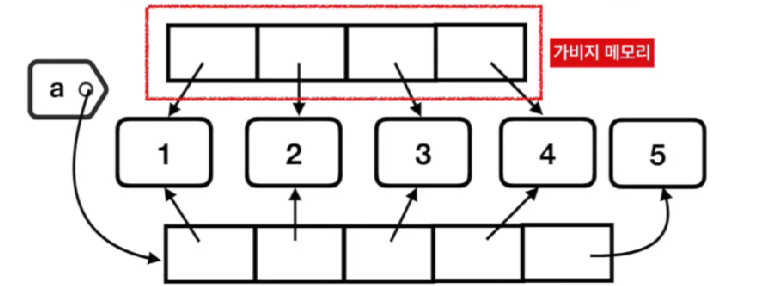
(2) case 2 : + []
- 리스트 객체를 rebinding
- (처음부터) 아예 새로운 참조할 수 있는 요소들이 생성
- garbage memory 가 생성됨
- id 변화 있음
(3) code
case 1. append.py
t1 = time.time()
a=[]
for i in range(100000):
a.append(i)
t2 = time.time()
print(t2-t1)
case 2. rebind.py
- 속도도 느리고
- garbage memory도 발생한다
t1 = time.time()
a=[]
for i in range(100000):
a=a+[i]
t2 = time.time()
print(t2-t1)
case 3. range.py
t1 = time.time()
a=list(range(100000))
t2 = time.time()
print(t2-t1)
case 4. nparange.py
- numpy를 사용하면 C와 비슷한 속도 얻을 수 있다!
t1 = time.time()
a= np.arange(100000)
t2 = time.time()
print(t2-t1)
Comparison
PS C:\Users\LSH\Desktop\advanced_python> python append.py
0.010991334915161133
PS C:\Users\LSH\Desktop\advanced_python> python rebind.py
12.35270643234253
PS C:\Users\LSH\Desktop\advanced_python> python range.py
0.0010008811950683594
PS C:\Users\LSH\Desktop\advanced_python> python nparange.py
0.0
