( 출처 : 연세대학교 데이터베이스 시스템 수업 (CSI6541) 강의자료 )
Chapter 1. Introduction
(1) DBMS
- provides environment that is both convenient & efficient to use
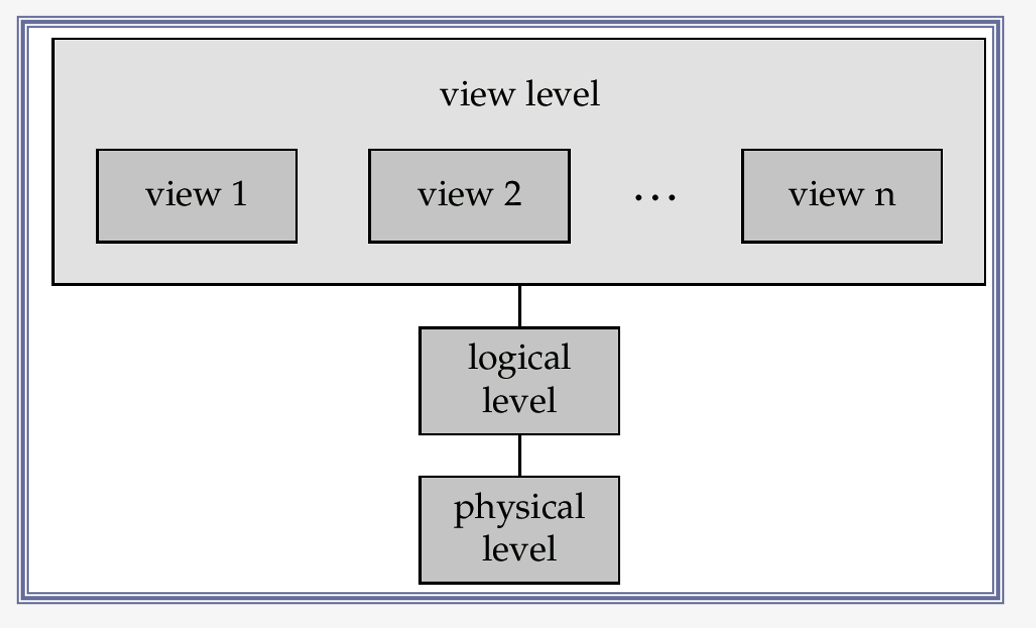
(2) Architecture of DB system
(3) Data Models
Data Models ?
- collection of tools, for describing data, data relationships, data semantics, data constraints
- ex 1) ER model ( Entity-Relationship model )
- ex 2) Object-oriented model, Semi-structured data model, Network mdoel, Hierarchical model
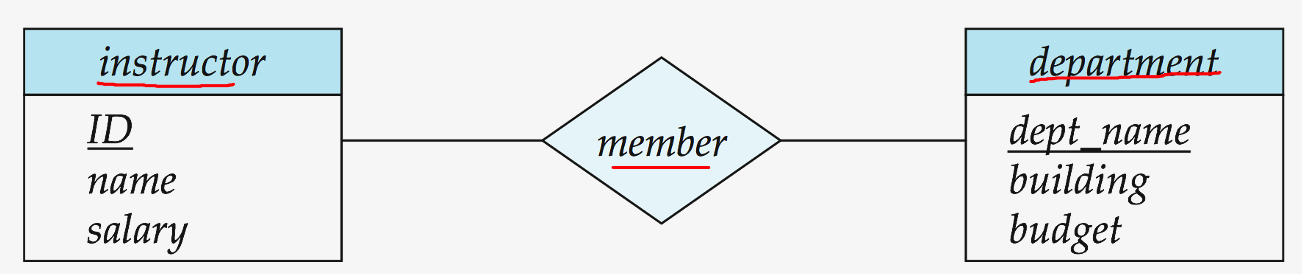
ER model ( Entity-Relationship model )
(4) DDL, DML
DDL ( Data DEFINITION Language )
-
for defining DB structure
- ex) CREATE TABLE
- In addition, it updates a special set of tables called the “data dictionary”
DML ( Data MANIPULATION Language )
- for accessing & manipulating data
- Procedural vs Declarative DML
- [ Procedural ] user need to specify “WHAT” data are needed & “HOW” to get them
- [ Declarative ] user need to specify only “WHAT” data are needed
- (term) query language \(\approx\) DML
- mostly used query language : SQL
(5) DB access from applications
Application programs?
-
programs used to interact with DB
-
usually written in host language ( ex. Python, Java … )
-
access DB via one of…
- (1) language extensions to allow embedded SQL
- (2) API ( Application Program Interface )
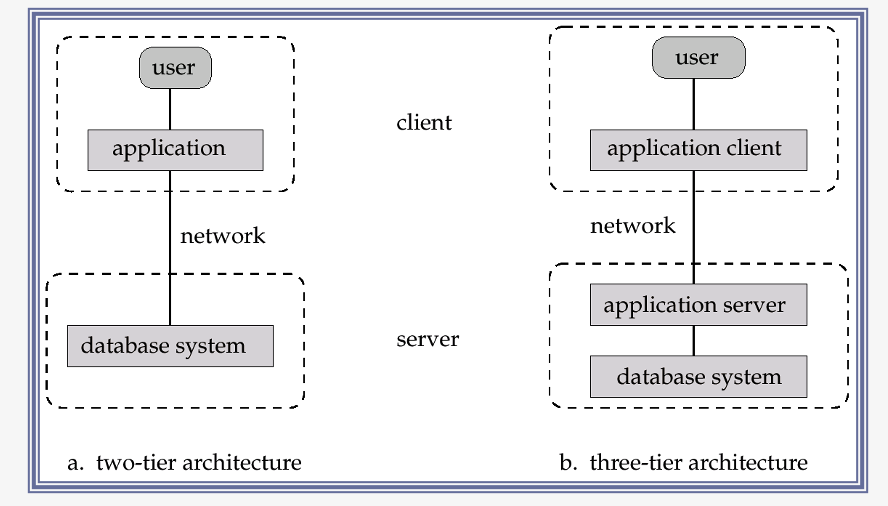
Application architecture
- 2-tier architecture
- ex) client programs using ODBC/JDBC to communicate with a database
- 3-tier architecture
- ex) web-based applications
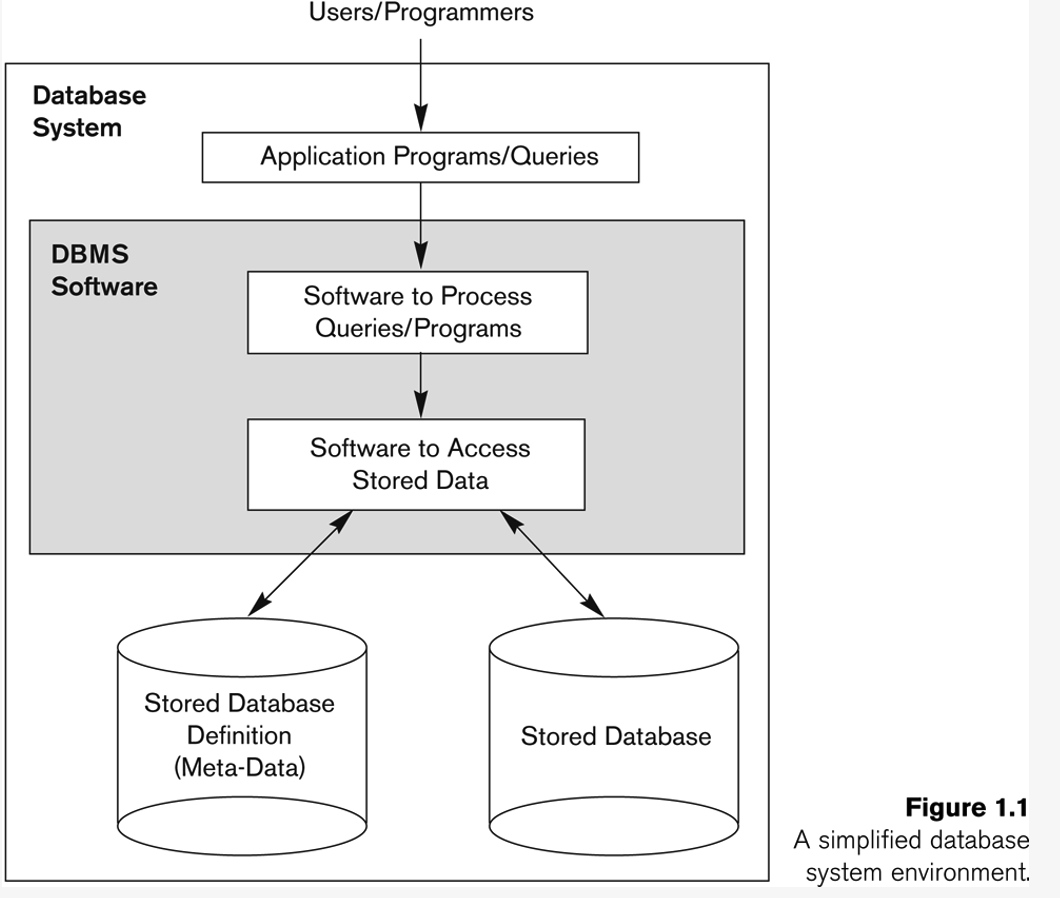
(6) Overall DB system structure
(7) Query Processing
- step 1) parsing & translation
- step 2) optimization
- step 3) evaluation
(8) Storage Management
- program module that provides the interface between ..
- (1) low-level data ( stored in DB & application programs )
- (2) queries ( submitted to the system )
- issues : storage access, file organization, indexing/hashing
(9) History of DB system
-
1960s~1970s :
-
network & hierarchical data models
-
relational data model
-
-
1980s :
- SQL
- parallel & distributed DB
- Objected-oriented DB
-
1990s :
- decision support & data mining applications
- data warehouses
-
2000s :
- XML & XQuery
-
2010s
-
Big data
-
Giant data storage systems
( Google BigTable, Hadoop, …)
-
