GAFormer: Enhancing TS Transformers Through Group-Aware Embeddings
Contents
- Abstract
- Preliminaries
0. Abstract
Novel approach for learning data-adaptive position embeddings
\(\rightarrow\) Incorporate learned spatial and temporal structure
How?
-
Introduces “group tokens”
-
Constructs an instance-specific “group embedding (GE) layer”
-
Assigns input tokens to a select number of learned group tokens
\(\rightarrow\) Incorporating structural information into the learning process.
-
Group-Aware Transformer (GAFormer)
Both spatial and temporal group embeddings
\(\rightarrow\) Significantly enhance the performance of several backbones
1. Introduction
Position embeddings (PE)
- Encode the relative ordering between channels and over different points in time
Standard PE can be problematic for the following reasons
- (1) No predetermined ordering or “spatial position” for different channels in TS
- (2) Relationships across channels and time segments might be instance-specific
\(\rightarrow\) These characteristics of TS make conventional PE inadequate!
GAFormer
Learn both channel and temporal structure in TS
\(\rightarrow\) Integrate this information into our tokens through “group embeddings”
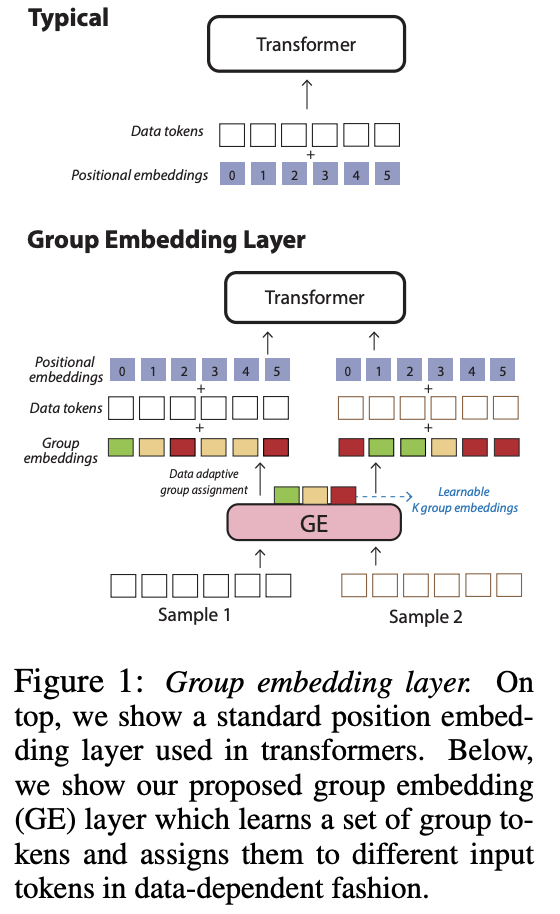
Details
- Learns a concise set of group-level tokens
- Determines how to adaptively assign them to individual samples
- How? Based on the similarity between …
- (1) Group embedding
- (2) Specific sample embeddings
- How? Based on the similarity between …
- Integrate both spatial and temporal group embeddings
- By decomposing grouping into either the spatial or temporal dimension, leads to enhanced interpretability
2. Method
(1) Group Embeddings
Conventional approach
- Input: Sequence of tokens \(X=\left[\mathbf{x}_1, \ldots, \mathbf{x}_N\right] \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times D}\)
- PE: \(P=\left[\mathbf{p}_1, \ldots, \mathbf{p}_N\right] \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times D}\)
- Input + PE = \(X_{P E}=\left[\mathbf{x}_1+\mathbf{p}_1, \ldots, \mathbf{x}_N+\mathbf{p}_N\right]\).
Result in \(X_{P E} \leftarrow X+P\).
Proposal
In contrast to this fixed scheme for PEs …
Group embeddings (GEs)
- In a data-adaptive manner
- Pass the input sequence to Enc \((\cdot)\)
- Obtain \(\left[\operatorname{Enc}(X)_1, \ldots, \operatorname{Enc}(X)_N\right]\).
- Procedure
- (1) Projection
- Projected to \(K<D\) dimensions with \(W \in \mathbb{R}^{D \times K}\).
- (2) Softmax
- Effectively sparsify the coefficients that assign group tokens to input tokens
- Select a small number of group embeddings to each token
- (1) Projection
Summary) Group embedding operation \(\mathrm{GE}(X)\)
- \(\operatorname{GE}(X)=\operatorname{SoftMax}(\operatorname{Enc}(X) \cdot W) \cdot G\).
- \(X_{G E} \leftarrow X+\operatorname{GE}(X)\).
(2) GAFormer: A Group-Aware SpationTemporal Transformer
Spatiotemporal transformer
- Concurrently extracts both temporal and spatial grouping structures, through learning group embeddings
a) Tokenization Layer
- Patchify: \(X \in \mathbb{R}^{C \times P \times L}\),
- Token Embedding: \(Z=\operatorname{Token}(X) \in \mathbb{R}^{C \times P \times D}\).
- via Transformer + learnable PE, in a CI manner
b) Spatial Group Embeddings
For Channel-wise interactions
- Slice TS spatially
- Result: \(Z_S\) = Set of \(P\) sequences of length \(C\).
- Use group embedding strategy to learn spatial structure
- with spatial group embedding (SGE) layer
- Result: Spatial set of group tokens \(G_S \in \mathbb{R}^{K_S \times D}\),
- where \(K_S\) is the number of groups
- Spatial operations: \(Z^{\prime}=\operatorname{Trans-S}\left(Z_S+\operatorname{SGE}\left(Z_S\right)\right)\).
- Trans-S \((\cdot)\): Spatial transformer encoder
- Operates on sequences of tokens that are at the same point in time but vary across their channel
- Effect: Extract different spatial groupings for each time period.
- Trans-S \((\cdot)\): Spatial transformer encoder
c) Temporal Group Embeddings
For Temporal interactions
-
Use dimension reduction layer \(H(\cdot)\)
- Result: \(Z_T=\) \(H\left(\left[Z_1^{\prime}, \ldots, Z_P^{\prime}\right]\right) \in \mathbb{R}^{P \times D^{\prime}}\),
- where \(C\) channels of \(D\)-dim tokens are bottlenecked into one token of \(D^{\prime}\)-dim
- Result: \(Z_T=\) \(H\left(\left[Z_1^{\prime}, \ldots, Z_P^{\prime}\right]\right) \in \mathbb{R}^{P \times D^{\prime}}\),
-
Use group embedding strategy to learn temporal structure
- with temporal group embedding (TGE) layer
-
Temporal operation: \(Z^{\text {final }}=\text { Trans- } \mathrm{T}\left(Z_T+\operatorname{TGE}\left(Z_T\right)\right)\)
- Trans-T : Temporal transformer encoder
GAFormer maintains a temporal set of group tokens:
- \(G_T \in \mathbb{R}^{K_T \times D^{\prime}}\) with \(K_T\) groups.
