Learning Representations of multivariate time series with missing data (2019)
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Methods
- AutoEncoder
- TCK (Time Series Cluster Kernel)
- TKAE (Temporal Kernelized Autoencoder)
- 도식화
- Experiments
0. Abstract
MTS(multivariate time series)에서 compressed representation 배우기
\(\rightarrow\) 이 논문은 compressed representations of MTS를 생성하기 위한 “RNN에 긱반한 참신한 AE 구조”를 제안한다!
제안한 모델의 특징(장점)
- 1) variable lengths의 input을 받는다
- 2) missing data를 잘 다루기 위함
- 3) fixed-length vectorial representations를 학습함
1. Introduction
RNN :
- long-term dependencies를 잘 포착함
- CNN과 함께 사용되어서 다른 변수(variables)들 과의 relationship도 모델링할 수 있음
Time-series에서의 missing value
-
실생활에서 자주 발생됨
-
pre-processing 단계에서 imputation으로 채워짐
( 하지만 MCAR이 아닌 한, imputation은 유의미한 정보들을 소실시킨다 )
Proper representation of data
- 매우 중요하다!
- (전통적 방식) domain expertise에 의해 manual하게
- (요즈음 방식) automatically produce features
Contributions
참신한 NN구조인 TKAE (Temporal Kernelized Autoencoder)를 제안함
\(\rightarrow\) “missing data”를 포함하고 있는 “real-valued MTS”의 “compressed representation”을 학습한다!
-
Contribution 1 : “Learning compressed representations of MTS with missing data”
- Contribution 2 : “Frameworks for missing data imputation & anomaly detection”
- encoder & decoder구조
- decoder를 사용하여 imputation & reconstruction error 통한 이상치 탐지
- Contribution 3 : “Analysis of how RNNs encode MTS”
Paper Organizations
-
Section 2 : 기존 AE 모델 & 제안한 TKAE 아키텍쳐 소개
-
Section 3 : representation을 잘 학습하는 TKAE’s 능력
( 2개의 framework를 제안함 )
- 1) impute missing data
- 2) building a one-class classifier
-
Section 4 : MTS는 AE+RNNs 구조에서 잘 작동함
2. Methods
(1) Autoencoder
-
non-linear 차원축소
-
2개의 구조 : encoder & decoder
-
AE의 “bottle-neck”구조가 핵심!
-
learn an “under-complete” representation
-
자동적인 regularization 기능 ( limits the variance of the model )
-
하지만, 추가적인 regularization 또한 사용함
\(L=L_{r}+\lambda L_{2}=\operatorname{MSE}(\mathbf{x}, \tilde{\mathbf{x}})+\lambda \mid \mid \mathbf{W} \mid \mid _{2}^{2}\).
-
RNN (Recurrent NN)
- sequence내의 temporal dependencies를 잘 포착함
- seq2seq모델의 핵심
- unequal length 인풋을 받아서 fixed-size representation을 반환함
Attention
-
최근의 seq2seq구조가 많이 사용하는 메커니즘
-
inductive bias를 제공함
- to facilitate the modeling of “long-term” dependencies
- 문장 길이가 매우 다양해도 OK
-
(Time series에 적용)
전체 문장에 대해 1개의 representation을 학습하는 대신,
모든 encoder state를 유지 ( + combined by time-varying decoding vector at each decoding step )
(2) TCK (Time Series Cluster Kernel)
- compute unsupervised kernel similarities among MTS containing missing data
- MAR (Missing At Random) 가정 하
- GMM 앙상블 사용
- data의 local & global 구조를 모두 잘 잡아냄
- imputation을 피하기 위해, missing data는 marginalized away
TCK를 통해 어떻게 \(\mathbf{K}\)를 생성하는지는 appendix A 참고
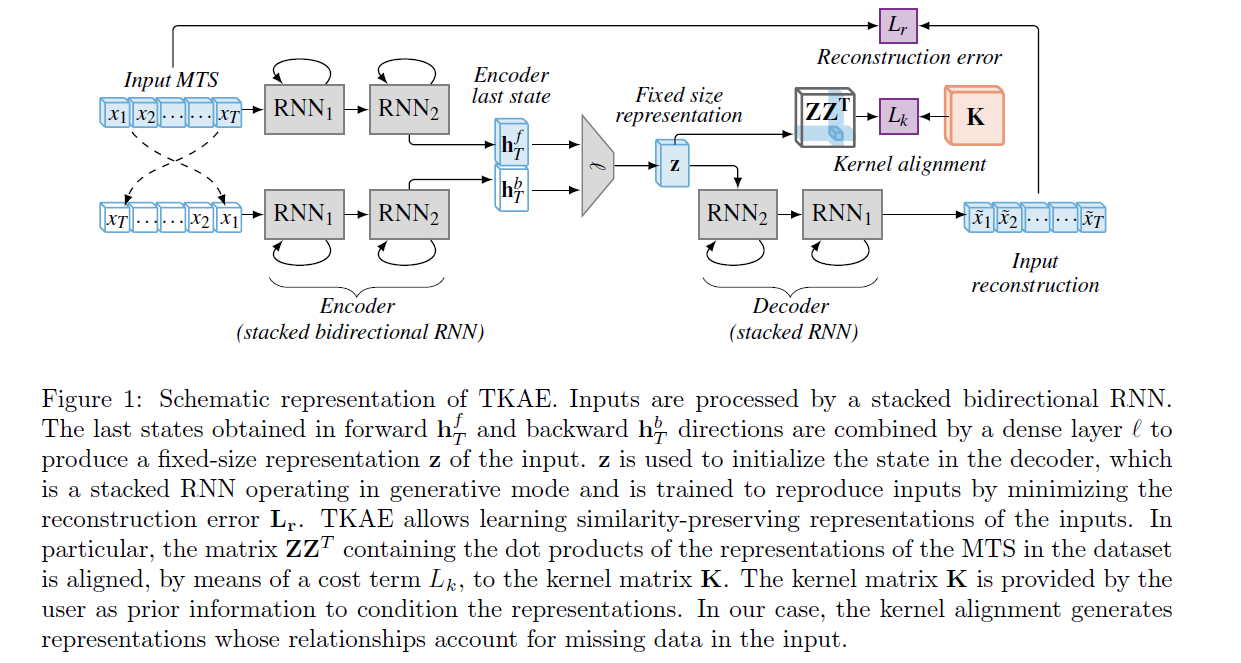
(3) TKAE (Temporal Kernelized Autoencoder)
TKAE = 이 논문에서 제안한 AE 구조
( 알고리즘 한 줄 요약 : learn compressed representations of variable-length MTS that may contain missing values )
MTS data matrix : \(\mathbf{X} \in \mathbb{R}^{V \times T}\)
- \(V\) : 변수 개수
- \(T\) : number of time steps ( 각 MTS마다 다를 수 있음 )
기존 AE의 dense layer를 RNNs로 대체함 ( LSTM, GRU 등 )
매 time step \(t\)마다의 hidden state : \(\mathbf{h}_{t}=\phi\left(\mathrm{x}_{t}, \mathbf{h}_{t-1}, \theta_{E}\right)\)
Encoding 과정
시계열 특징
-
(기존) 직전 time step 이용 가능
-
(시계열) whole input 가능! ( 미래 정보 input도 OK )
\(\rightarrow\) 따라서 stacked bidirectional RNN 사용 가능 ( \(\mathbf{h}_{T}^{f}\) & \(\mathbf{h}_{T}^{b}\) 사용 )
이 둘을 결합하여 \(\mathrm{z} \in \mathbb{R}^{D_{z}}\) 를 생성함 ( = FIXED-sized vector )
Decoding 과정
\(\tilde{\mathrm{x}}_{t}=\psi\left(\mathbf{h}_{t}, \tilde{\mathbf{x}}_{t-1}, \theta_{D}\right)\).
- \(\psi(\cdot, \cdot)\) : stacked RNN with \(M\) layers parametrized by \(\theta_{D}\)
- initial state \(\mathrm{h}_{0}=\mathrm{z}\)
- first input \(\tilde{\mathrm{x}}_{0}=0\),
Iteratively produces outputs for \(T\) steps
- \(T\) being the length of the input MTS
기타 특징
- SGD 사용하여 end-to-end 학습
- 학습 과정에서, \(t\) 시점의 input은
- \(p_s\)의 확률로, decoder output at time \(t-1\) ( = INFERENCE mode )
- \(1-p_{s}\)의 확률로, desired output at time \(t-1\) ( = TEACHER FORCING )
RNNs의 문제점
-
directly process missing value 불가
( 사전에 impute 해줘야 ! with 0, mean, last observed value.. )
\(\rightarrow\) representation의 quality 떨어짐
-
이러한 문제를 극복하기 위해, Kernel Alignment를 소개함
Kernel Alignment
-
allows us to preserve the pairwise similarities of the inputs in the learned representations
-
이 pairwise similarities는 positive semi-definite matrix \(\mathbf{K}\)에 encoded 되어 있음
-
additional regularization term ( \(L_{k}\) )을 사용함으로써 반영함!
\(L=L_{r}+\lambda L_{2}+\alpha L_{k}\).
-
\(L_{k}\) : form of a normalized Frobenius norm of the difference between two matrices: \(\mathrm{K}\) and \(\mathrm{ZZ}^{T}\)
\(L_{k}= \mid \mid \frac{\mathrm{ZZ}^{T}}{ \mid \mid \mathbf{Z Z}^{T} \mid \mid _{F}}-\frac{\mathrm{K}}{ \mid \mid \mathbf{K} \mid \mid _{F}} \mid \mid _{F}\).
-
\(\mathbf{Z} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times D_{z}}\) : matrix of hidden representations relative to the \(N\) MTS
-
(4) 도식화
3. Experiments
2가지로 구성
-
1) Quantitative evaluations of the representations in the presence of missing data
- kernel alignment의 효과를 test해봄
- 결과 : TCK는 missing data가 많을 때 매우 효과적!
-
2) Design and evaluation of decoder-based framework
-
TKAE 디코더를 사용하여
(1) impute missing data
(2) one-class classification
-
Experiment Setup
- TKAE vs PCA / AE / RNN-based 구조
- \(D_x\) : input-dimensionality
- TKAE ) \(D_x = V\)
- AE / PCA ) \(D_x = V \cdot T\)
- \(D_z\) : size of compressed representations
- 3개의 hidden layer 사용 / 5000 epoch / batch size=32 / Adam optimizer
3-1) MTS representations
a) Controlled experiments & sensitivity analysis
- 목적 : kernel alignment의 효과 확인하기 : TAE (\(\alpha=0\) ) vs TKAE (\(\alpha \neq 0\) )
- 데이터 : Jp.Vow ( 원래는 missing 데이터 없어서, 10~90%로 noise 부여 )
- zero imputation
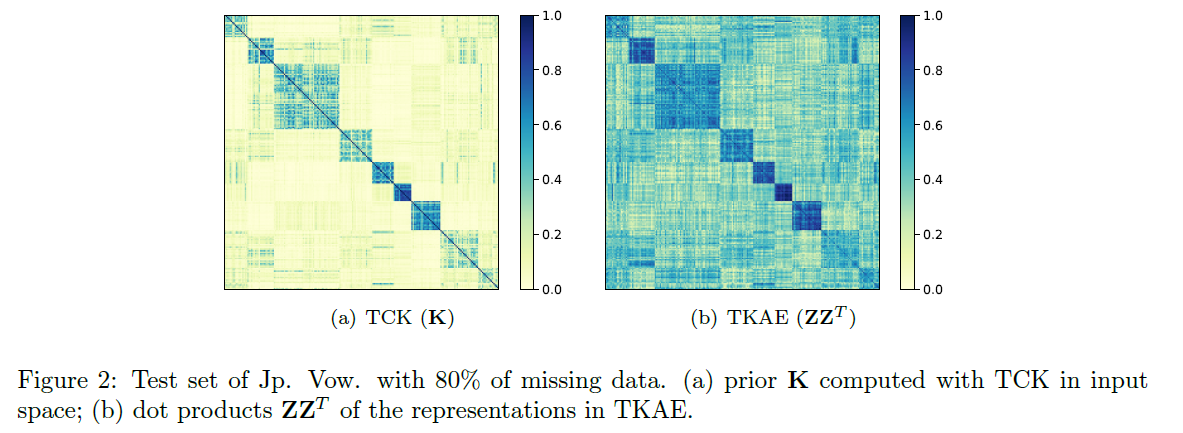
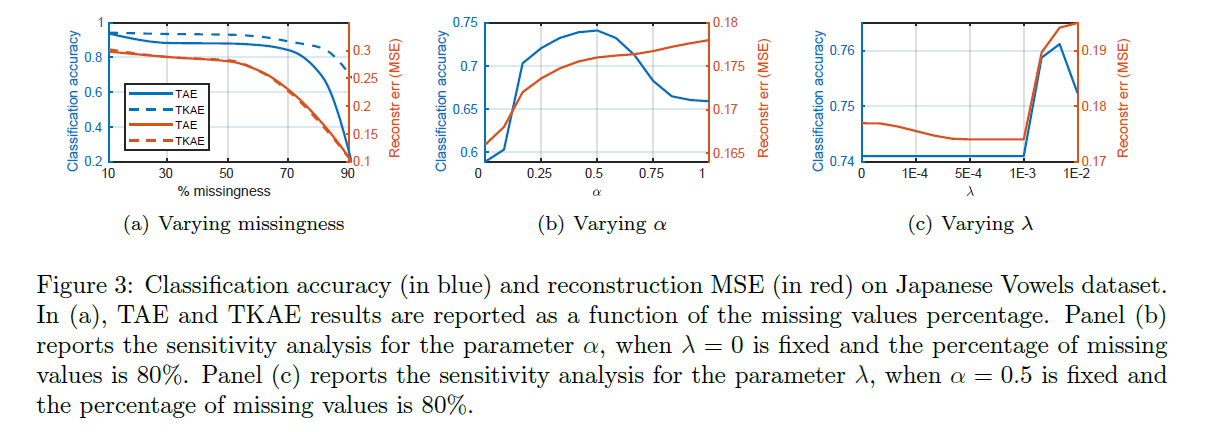
b) Classification of MTS
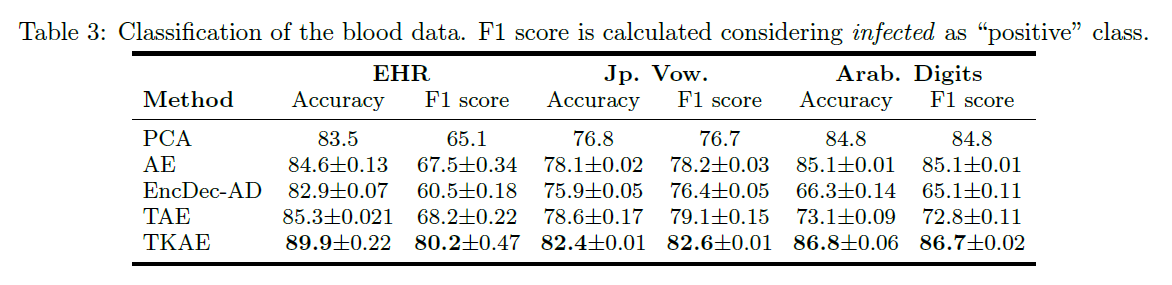
3-2) Decoder-based Frameworks
a) Imputation of missing data
reconstruction MSE
\(L_{r}=-\sum_{t}\left(\left(\mathbf{x}_{t}-\tilde{\mathbf{x}}_{t}\right) m_{t}\right)^{2} / \sum_{t} m_{t},\).
- where \(m_{t}=0\) if \(\mathrm{x}_{t}\) is imputed and 1 otherwise
b) One-class classification
- outlier개수가 너무 적을 때, 정상 데이터만 사용!
- 정상 데이터의 boundary만들고 이를 벗어나면 outlier!
4. Conclusion
TKAE 제안
- RNN-based model for representing MTS with missing values as fixed size vectors
Kernel Alignment
- time series cluster kernel
- similarity measure designed for MTS with missing data
- learn compressed representation that preserve “pairwise relationships” defined in the “original” input space
Supervised & Unsupervised task 모두 성능 good
