Probabilistic Forecasting of Sensory Data with GAN ; ForGAN (2019, 32)
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Mean Regression Forecast
- Probabilistic Forecast
- Methodology
- CGAN
- Probabilistic Forecast with CGAN
0. Abstract
ForGAN
- one-step ahead
- probabilistic forecasting
- with GAN
1. Introduction
Goal : acquire \(\rho\left(x_{t+1} \mid\left\{x_{t}, \ldots, x_{0}\right\}\right)\)
\(\mu\left(\rho\left(x_{t+1} \mid c\right)\right)\) most accurately. There is a broad range of
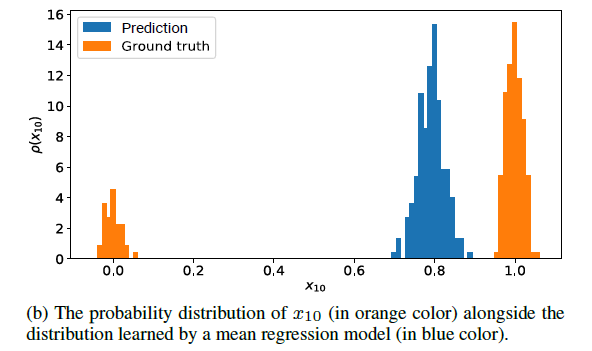
(1) Mean Regression Forecast
predict \(\mu\left(\rho\left(x_{t+1} \mid c\right)\right)\)
- do not include fluctuations around the mean
- unreliable & mis leading
Example :
(2) Probabilistic Forecast
quantify the variance in a prediction
2 common approaches
- 1) conditional quantile regression
- asymmetric piecewise linear scoring function ( \(\alpha\) quantile )
- 2) conditional expectile regression
- asymmetric piecewise quadratic scoring function
OR, collection of point forecasts!
- ex) Dropout ( Gal et al )
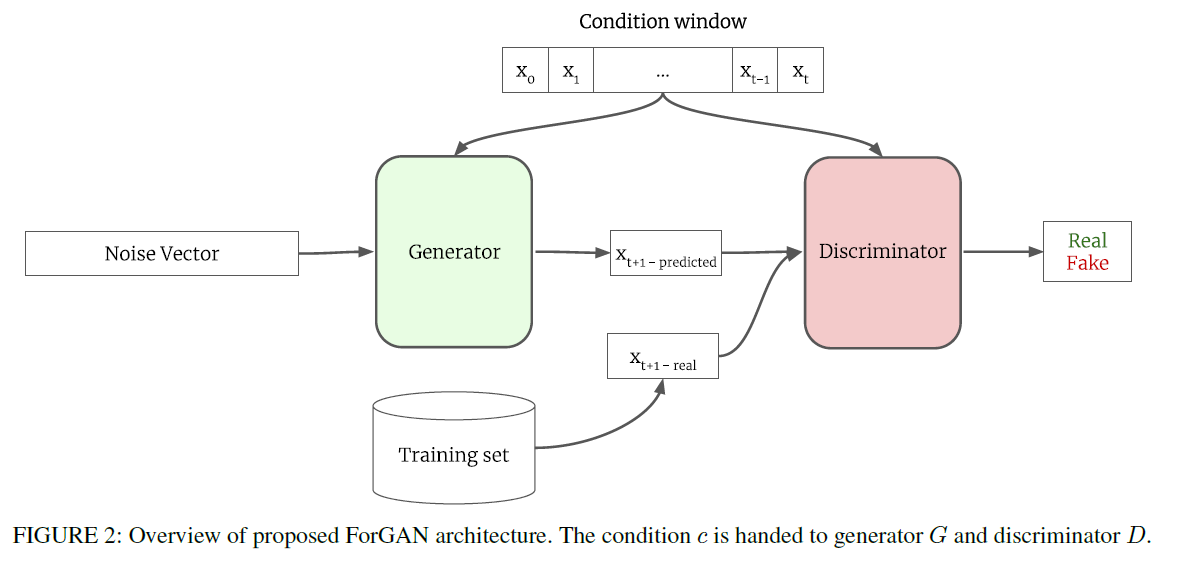
2. Methodology
(a) CGAN
\(\begin{aligned} \min _{G} \max _{D} V(D, G)=& \mathbb{E}_{x \sim \rho_{\text {data }}(x)}[\log D(x \mid y)]+ \mathbb{E}_{z \sim \rho_{z}(z)}[\log (1-D(G(z \mid y)))] . \end{aligned}\).
(b) Probabilistic Forecasting with CGAN
\(\rho\left(x_{t+1} \mid c\right)\).
- model the probability distribution of one step ahead value \(x_{t+1}\) ,
- given the historical data \(c=\left\{x_{0}, . ., x_{t}\right\}\)
use CGAN to model \(\rho\left(x_{t+1} \mid c\right)\)
- discriminator takes \(x_{t+1}\) & determine 1/0
\(\begin{aligned} \min _{G} \max _{D} V(D, G)=& \mathbb{E}_{x_{t+1} \sim \rho_{\text {data }}\left(x_{t+1}\right)}\left[\log D\left(x_{t+1} \mid c\right)\right]+ \mathbb{E}_{z \sim \rho_{z}(z)}[\log (1-D(G(z \mid c)))] \end{aligned}\).