Variational Inference
( 이론 참고 : https://seunghan96.github.io/bnn )
( 코드 참고 : https://www.ritchievink.com/blog/2019/09/16/variational-inference-from-scratch/ )
1. Import Packages
Variational Inference 구현을 위한 주요 패키지들을 불러온다. ( Pytorch, Numpy … )
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.distributions as dist
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from dataclasses import dataclass
import numpy as np
GPU 사용 여부
-
torch.tensor( ).to(device)를 계속 사용하는 것을 피하기 위해Tensor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor를 사용한다.
cuda = True if torch.cuda.is_available() else False
Tensor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor if cuda else torch.FloatTensor
2. 가상 데이터 생성
아래와 같은 임의의 데이터를 생성한다.
Y_real: noise가 없는 YY_noise:Y_real에 \(\epsilon \sim N(0,\sigma)\)의 noise가 낀 값
def func(x):
return 0.2*np.power(x, 3)-2*np.power(x, 2+1)+8*x
n=10000
sigma=1.5
X = np.linspace(-3, 3, n)
Y_real = func(X)
Y_noise = (Y_real+np.random.normal(0,sigma,n))
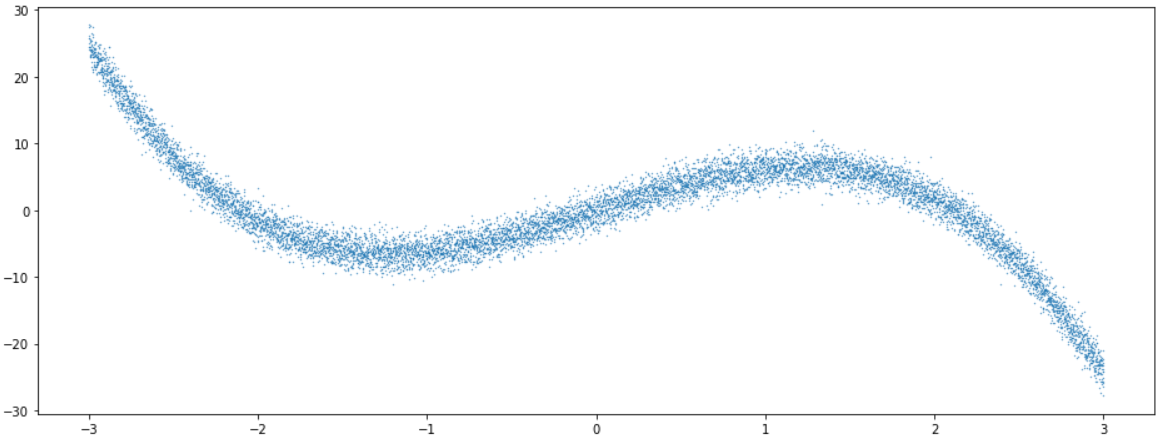
데이터의 모양을 보면 아래와 같다.
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 6))
plt.scatter(X, Y_noise,s=0.1)
생성한 데이터를 tensor로 변환해준다.
X = Tensor(X).view(-1,1)
Y_real = Tensor(Y_real).view(-1,1)
Y_noise = Tensor(Y_noise).view(-1,1)
Train & Test split ( 8 : 2 )를 한다.
np.random.seed(1996)
val_idx = np.sort(np.random.choice(n, int(n*0.2),replace=False))
train_idx = np.array(list(set(np.arange(n))-set(val_idx)))
x_train,x_val = X[train_idx],X[val_idx]
y_train,y_val = Y_noise[train_idx],Y_noise[val_idx]
3. Train 함수
2가지 방법으로, 아래와 같이 각기 다른 모델을 생성할 것이다.
( 방법 1 ) MLE
- frequentists의 방법
- maximum likelihood estimator
- uncertatainty 측정 불가
- 우리가 흔히 loss function를 MSE로 잡는 방법
( 방법 2 ) Variational Regression
- Q를 사용해서 true posterior를 근사
\(Q*_{\theta}(y)\) = \(Q_*{\theta}\left(\mu, \operatorname{diag}\left(\sigma^{2}\right)\right)\).
\[P(y)=\mathcal{N}(0,1)\] \[\left.Q(y \mid x)=\mathcal{N}\left(g*_{\theta}(x)_*{\mu}, \operatorname{diag}\left(g*_{\theta}(x)_*{\sigma^{2}}\right)\right)\right)\]이 두 모델을 생성하여 학습시키는 공통적인 함수인 train을 아래와 같이 구현한다.
-
[INPUT] model , loss function, number of epochs, optimizer, datasets, print interval, type
- type = 1 : ( 방법 1 ) MLE모델을 학습할 경우
- type = 2 : ( 방법 2 ) Variational Regression모델을 학습할 경우
( MLE 모델을 사용하느냐, Variational Regression을 사용하느냐에 따라 손실함수 및 손실함수에 들어가는 input 또한 다르다 )
def train(model,loss_fn,n_epoch,opt,x_train,y_train,x_val,y_val,print_,type=1):
for epoch in range(1,n_epoch+1):
if type==1:
y_pred = model(x_train)
y_val_pred = model(x_val)
train_loss = loss_fn(y_pred,y_train)
val_loss = loss_fn(y_val_pred,y_val)
else:
y_pred,y_mu,y_logvar = model(x_train)
y_val_pred,y_val_mu,y_val_logvar = model(x_val)
train_loss = loss_fn(y_pred,y_train,y_mu,y_logvar)
val_loss = loss_fn(y_val_pred,y_val,y_val_mu,y_val_logvar)
opt.zero_grad()
train_loss.backward()
opt.step()
if epoch%print_==0:
print('Epoch %d, Train Loss %f, Val Loss %f' %(epoch,float(train_loss/x_train.shape[0]),float(val_loss/x_val.shape[0])))
4. Model & Loss Function 구현
( 방법 1 ) MLE
( 방법 2 ) Variational Regression
4-1. MLE
(1) Model
- single hidden layer ( hidden unit 20개 )
class MLE_model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.out = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(1, 20),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(20, 1)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.out(x)
(2) Loss Function
- MSE를 사용한다 (Mean Squared Error)
def MSE(y_pred,y_real):
return (0.5 * (y_pred - y_real)**2).mean()
4-2. Variational Regression
(1) Model
- reparameteriztation을 위한 함수도 함께 구현을 한다.
class VI_model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.q_mu = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(1, 40),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(40, 20),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(20, 10),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(10, 1)
)
self.q_log_var = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(1, 40),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(40, 20),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(20, 10),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(10, 1)
)
def reparam(self, mu, log_var):
sigma = torch.exp(0.5 * log_var) + 1e-5
eps = torch.randn_like(sigma)
return mu + sigma * eps
def forward(self, x):
mu = self.q_mu(x)
log_var = self.q_log_var(x)
return self.reparam(mu, log_var), mu, log_var
(2) Loss Function
-
(함수 1) gauss_LL(gaussian Log Likelihood)
-
(함수 2) neg_ELBO (negative Evidence Lower Bound)
\(\rightarrow\) 최종적인 loss function :
neg_ELBO
최종적인 Loss Function
\[\begin{aligned}\text{negative ELBO}&=-(E_{Z \sim Q}[\log P(D \mid Z)]+E_{Z \sim Q}[\log P(Z)-\log Q(Z)])\end{aligned}\]def gauss_LL(y, mu, log_var):
sigma = torch.exp(0.5 * log_var)
return -0.5 * torch.log(2 * np.pi * sigma**2) - (1 / (2 * sigma**2))* (y-mu)**2
prior_mean = y_train.mean().item()
prior_var = y_train.var().item()
def neg_ELBO(y_pred, y, mu, log_var,prior_mean=prior_mean,prior_var=prior_var):
likelihood = gauss_LL(y, mu, log_var) # (1) likelihood of observing y ( given Variational mu and sigma )
log_prior = gauss_LL(y_pred, prior_mean, torch.log(torch.tensor(prior_var))) # (2) prior probability of y_pred
log_prob_q = gauss_LL(y_pred, mu, log_var) # (3) variational probability of y_pred
ELBO = (likelihood+log_prior-log_prob_q).mean()
return -ELBO
mle_model = MLE_model()
vi_model = VI_model()
if cuda:
vi_model.cuda()
mle_model.cuda()
5. 학습시키기
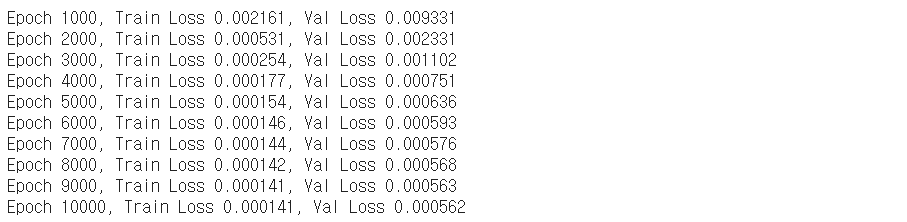
5-1. MLE 모델
epochs = 10000
print_ = 1000
optim = torch.optim.Adam(mle_model.parameters())
train(model=mle_model,
loss_fn=MSE,
n_epoch=epochs,
opt=optim,
x_train=x_train,y_train=y_train,
x_val=x_val,y_val=y_val,
print_=print_,type=1)
with torch.no_grad():
Y_mle_pred = mle_model(X)
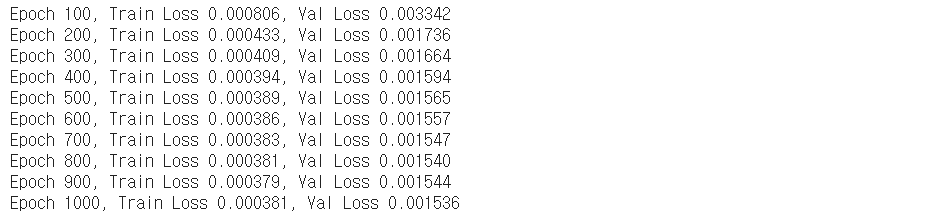
5-2. Variational Regression 모델
epochs = 1000
print_ = 100
optim = torch.optim.Adam(vi_model.parameters())
train(model=vi_model,
loss_fn=neg_ELBO,
n_epoch=epochs,
opt=optim,
x_train=x_train,y_train=y_train,
x_val=x_val,y_val=y_val,
print_=print_,type=2)
Variational Regression의 ouptut값은 deterministic하지 않다.
이를(feed forward) 1000번 반복하여, 각 data당 1000개의 결과값을 출력하여 저장한다.
with torch.no_grad():
Y_vi_pred = torch.cat([vi_model(X)[0] for _ in range(1000)], dim=1)
6. Visualization
( xxx.detach().cpu()를 통해 다시 cpu에서 흐르게끔 바꾼 뒤 시각화를 해줘야 한다 )
6-1. MLE 모델
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 6))
plt.scatter(X.detach().cpu(), Y_noise.detach().cpu(),color='blue',s=0.1)
plt.scatter(X.detach().cpu(), Y_mle_pred.detach().cpu(),color='red',s=0.1)
#plt.plot(X, mu)
#plt.fill_between(X.detach().cpu().flatten(), q1, q2, alpha=0.2)
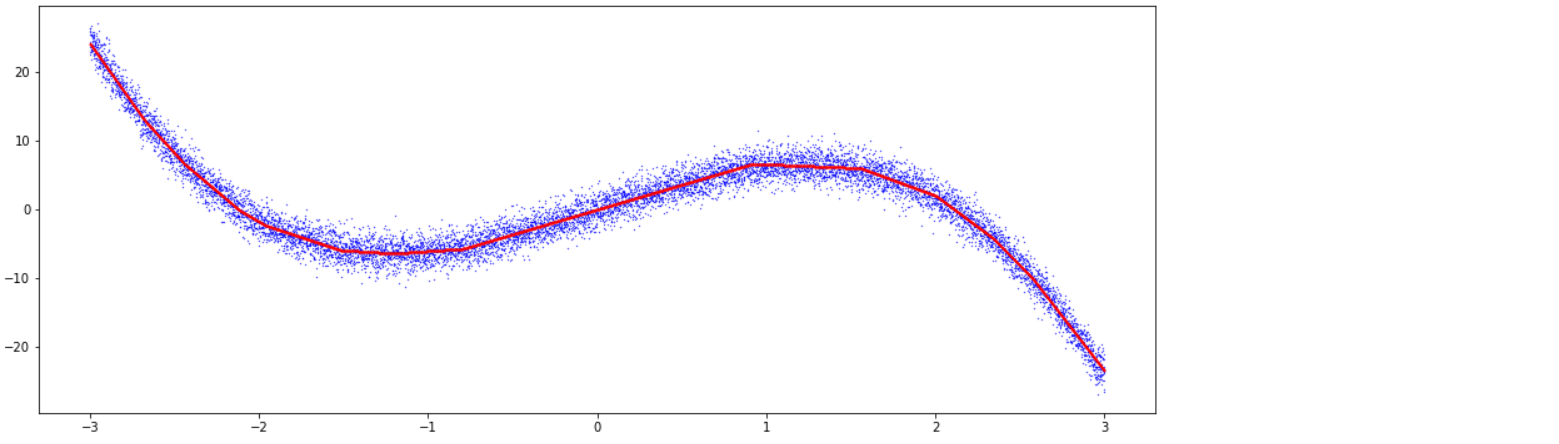
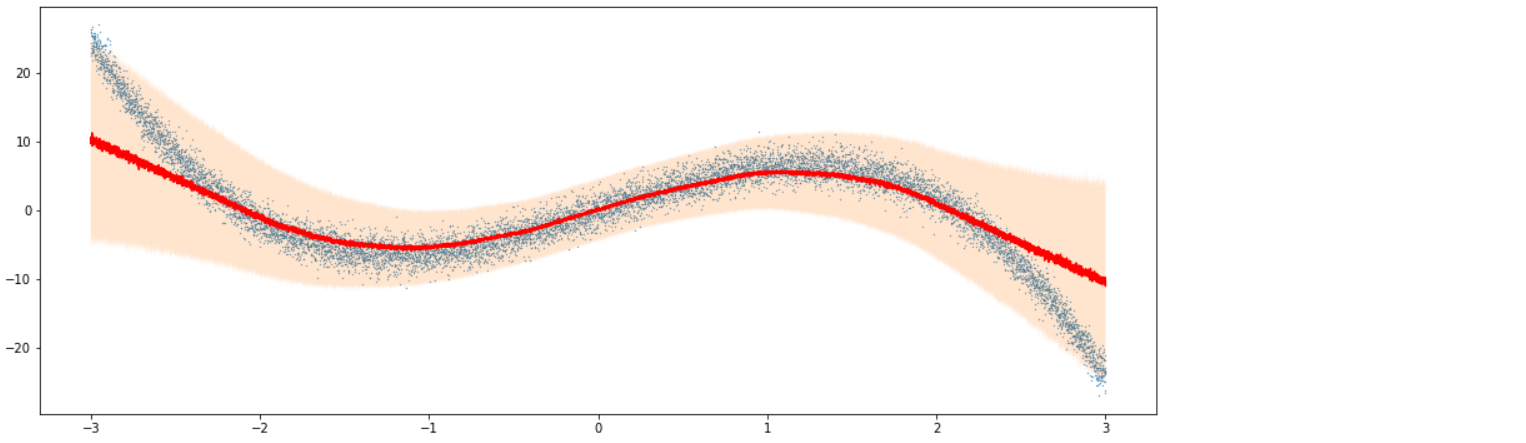
6-2. Variational Regression 모델
q1, mu, q2 = np.quantile(Y_vi_pred.detach().cpu(), [0.05, 0.5, 0.95], axis=1)
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 6))
plt.scatter(X.detach().cpu(), Y_noise.detach().cpu(),s=0.1)
plt.plot(X.detach().cpu(), mu,color='red')
plt.fill_between(X.detach().cpu().flatten(), q1, q2, alpha=0.2)