With a Little Help from My Friends: Nearest-Neighbor Contrastive Learning of Visual Representations
Contents
- Abstract
- Related Work
- Approach
- Contrastive Instance Discrimination
- Nearest-Neighbor CLR (NNCLR)
- Implementation Details
0. Abstract
Use positive samples from OTHER instances in the dataset
propose NNCLR
- samples the nearest neighbors from the dataset in the latent space & treat them as positives
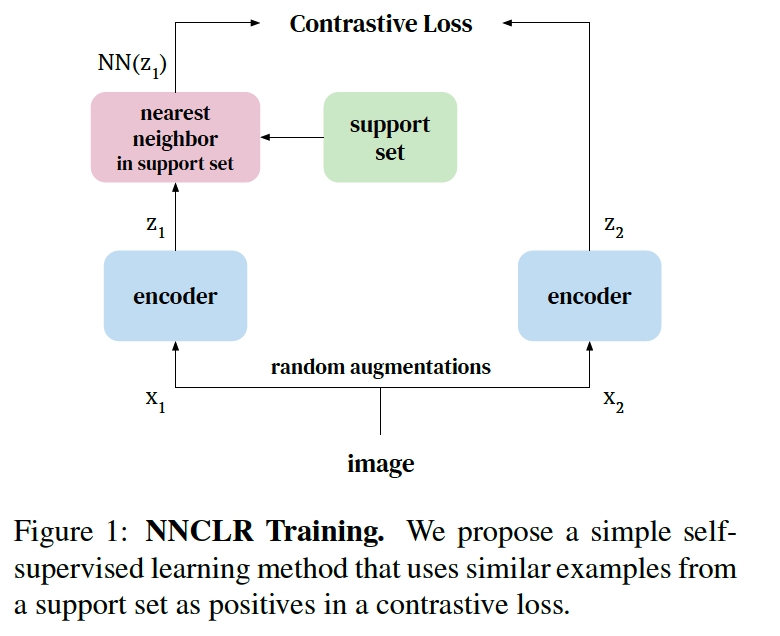
1. Related Work
Queues and Memory Banks
use a SUPPORT set as memory during training
( similar to MoCO )
MoCo vs NNCLR
- [MoCo] uses elements of the queue as NEGATIVES
- [NNCLR] ~ POSITIVES
2. Approach
describe contrastive learning in the context of
- (1) instance discrimination
- (2) SimCLR
(1) Contrastive Instance Discrimination
InfoNCE
\(\mathcal{L}_{i}^{\text {InfoNCE }}=-\log \frac{\exp \left(z_{i} \cdot z_{i}^{+} / \tau\right)}{\exp \left(z_{i} \cdot z_{i}^{+} / \tau\right)+\sum_{z^{-} \in \mathcal{N}_{i}} \exp \left(z_{i} \cdot z^{-} / \tau\right)}\).
SimCLR
uses 2 views of same image as positive pair
Given mini-batch of images \(\left\{x_{1}, x_{2} \ldots, x_{n}\right\}\),
\(\rightarrow\) 2 different augmentations (views) are generated
- (1) \(z_{i}=\phi\left(\operatorname{aug}\left(x_{i}\right)\right)\)
- (2) \(z_{i}^{+}=\phi\left(\operatorname{aug}\left(x_{i}\right)\right)\)
InfoNCE loss used in SimCLR : \(\mathcal{L}_{i}^{\text {SimCLR }}=-\log \frac{\exp \left(z_{i} \cdot z_{i}^{+} / \tau\right)}{\sum_{k=1}^{n} \exp \left(z_{i} \cdot z_{k}^{+} / \tau\right)}\)
- each embedding is \(l_{2}\) normalized before the dot product is computed in the loss
(2) Nearest-Neighbor CLR (NNCLR)
propose using \(z_{i}\) ‘s NN in the support set \(Q\) to form the positive pair
- \(\mathcal{L}_{i}^{\mathrm{NNCLR}}=-\log \frac{\exp \left(\mathrm{NN}\left(z_{i}, Q\right) \cdot z_{i}^{+} / \tau\right)}{\sum_{k=1}^{n} \exp \left(\mathrm{NN}\left(z_{i}, Q\right) \cdot z_{k}^{+} / \tau\right)}\).
- where \(\mathbf{N N}(z, Q)=\underset{q \in Q}{\arg \min } \mid \mid z-q \mid \mid _{2}\)
(3) Implementation Details
(1) symmetric loss
- add \(-\log \left(\exp \left(\mathrm{NN}\left(z_{i}, Q\right) \cdot z_{i}^{+} / \tau\right) / \sum_{k=1}^{n} \exp \left(\mathrm{NN}\left(z_{k}, Q\right) \cdot z_{i}^{+} / \tau\right)\right.\)
(2) insipred by BYOL …
- pass \(z_{i}^{+}\)through a prediction head \(g\) to produce embeddings \(p_{i}^{+}=g\left(z_{i}^{+}\right)\).
- then use \(p_{i}^{+}\)instead of \(z_{i}^{+}\)in \(\mathcal{L}_{i}^{\mathrm{NNCLR}}=-\log \frac{\exp \left(\mathrm{NN}\left(z_{i}, Q\right) \cdot z_{i}^{+} / \tau\right)}{\sum_{k=1}^{n} \exp \left(\mathrm{NN}\left(z_{i}, Q\right) \cdot z_{k}^{+} / \tau\right)}\).
Support Set
implement support set as queue
- dimension : \([m, d]\)
- \(m\) : size of queue
- \(d\) : size of embeddingsRandAugment
