Large Scale Adversarial Representation Learning
Contents
- Abstract
- BigBiGAN
- Encoder \(\mathcal{E}\)
- Joint Discriminator \(\mathcal{D}\)
0. Abstract
BigBiGAN
- builds upon BiGAN model
- extend it to representation learning, by…
- (1) adding an encoder
- (2) modifying the discriminator
1. BigBiGAN
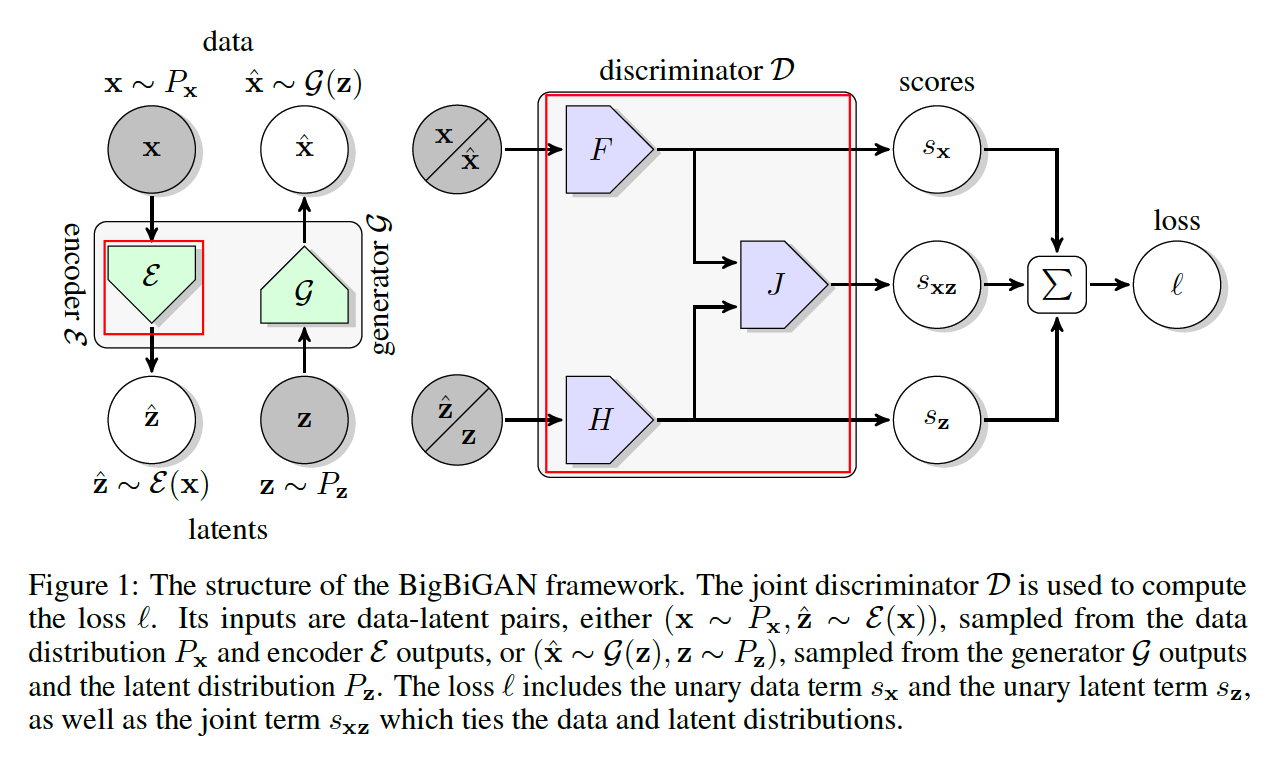
(1) Encoder \(\mathcal{E}\)
models the inverse conditional distn \(P(\mathbf{z} \mid \mathbf{x})\)
( = predicting latents \(\mathbf{z}\) given \(\mathbf{x}\) )
(2) Joint Discriminator \(\mathcal{D}\)
-
takes as input data-latent pairs \((\mathbf{x}, \mathbf{z})\)
-
learns to discriminate between pairs from (1) vs (2)
- (1) data distribution and encoder \(\left(\mathbf{x} \sim P_{\mathbf{x}}, \hat{\mathbf{z}} \sim \mathcal{E}(\mathbf{x})\right)\)
- (2) generator and latent distribution \(\left(\hat{\mathbf{x}} \sim \mathcal{G}(\mathbf{z}), \mathbf{z} \sim P_{\mathbf{z}}\right)\)
Loss function :
\(\min _{\mathcal{G} \mathcal{E}} \max _{\mathcal{D}}\left\{\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x} \sim P_{\mathbf{x}}, \mathbf{z} \sim \mathcal{E}_{\Phi}(\mathbf{x})}[\log (\sigma(\mathcal{D}(\mathbf{x}, \mathbf{z})))]+\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{z} \sim P_{\mathbf{z}}, \mathbf{x} \sim \mathcal{G}_{\Phi}(\mathbf{z})}[\log (1-\sigma(\mathcal{D}(\mathbf{x}, \mathbf{z})))]\right\}\).
