Overcoming catastrophic forgetting in neural networks
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Elastic Weight Consolidation
0. Abstract
task를 sequential하게 배우는 능력은 중요하다!
( task A 배우고, 이를 활용하여 task B를 배우고 ,…. task Z를 배우고 … )
Catastrophic Forgetting
-
NN에서 사실상 불가피한 문제
-
How to 해결?
\(\rightarrow\) SLOW DOWN learning on the weights IMPORTANT for those task!
1. Introduction
실제 문제 상황
- task들에 label이 잘 없는 경우
- task가 계속해서 바뀌는 경우
- 한번 학습했던 task가 더 이상(혹은 긴 시간 동안) 다시 나오지 않는 경우
\(\rightarrow\) 따라서, continual learning이 중요하다!
( ability to learn consecutive tasks without forgetting how to perform previously trained tasks )
기존 task를 풀기 위해 사용했던 데이터들을, 새로운 task를 풀 때도 계속해서 사용한다면 풀 수야 있겠지만… task가 너무 많아질 경우? IMPRACTICAL!
사람/동물을 생각해보자! 이들은 매우 continual fashion으로 새로운 것들을 학습한다!
( 기존꺼 잊지 않고도 새로운거 잘 학습함 )
이를 컨셉으로 한 NN을 만들자!
EWC (Elastic Weight Consolidation)
- analgous to synaptic consolidation (인간의 뇌 처럼)
- 과거 task를 푸는데에 있어서, weight들이 얼마나 중요한 역할을 차지했는지에 따라 learning 속도 조절!
2. Elastic Weight Consolidation
NN도 Brain처럼 만들자!
-
idea : 과거의 task 풀 때 중요했던 parameter들은, update를 적게(느리게) 시키자!
-
task B를 새로 배울 때, task A를 여전히 잘 풀기 위해,
constrain the parameters to stay in a region of low error for task A, centered around \(\theta_A^{*}\)
( quadratic penalty를 부여함으로써 )
-
식) \(\mathcal{L}(\theta)=\mathcal{L}_{B}(\theta)+\sum_{i} \frac{\lambda}{2} F_{i}\left(\theta_{i}-\theta_{A, i}^{*}\right)^{2}\).
(뒤에서 자세히 설명)
-
그림 )
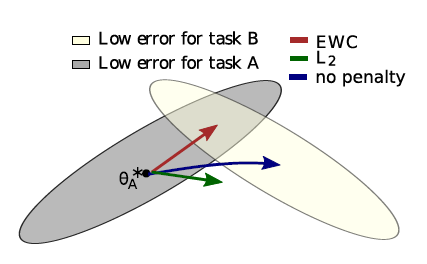 .
.
이 문제를 probabilistic view로 보면 이해가 잘 될 것이다!
[ Bayes Rule ]
\(\log p(\theta \mid \mathcal{D})=\log p(\mathcal{D} \mid \theta)+\log p(\theta)-\log p(\mathcal{D})\).
\(\log p(\theta \mid \mathcal{D})=\log p\left(\mathcal{D}_{B} \mid \theta\right)+\log p\left(\theta \mid \mathcal{D}_{A}\right)-\log p\left(\mathcal{D}_{B}\right)\).
- task \(A\)에 대한 정보가, posterior에 이미 반영된 것을 알 수 있다!
EWC의 loss function
\(\mathcal{L}(\theta)=\mathcal{L}_{B}(\theta)+\sum_{i} \frac{\lambda}{2} F_{i}\left(\theta_{i}-\theta_{A, i}^{*}\right)^{2}\).
-
Laplace Approximation
-
mean : \(\theta_A^{*}\)
-
diagonal precision : Fisher information matrix의 diagonal!
( 핵심 정보들이 담아있는 것을 반영 )
-
-
\(\mathcal{L}_{B}(\theta)\) : task B를 위한 loss
-
\(\lambda\) : 기존 task가 (신규 task에 비해) 얼마나 중요한지를 조절
Supervised Learning & Reinforcement Learning에서 그 성능을 입증함!
