Variational Continual Learning
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
0. Abstract
Variational Continual Learning
-
VCL = (1) continual learning + (2) online VI + (3) Monte Carlo VI
-
두 가지에 적용 가능
- 1) deep discriminative models
- 2) deep generative models
1. Introduction
Bayesian Inference 요약
-
distribution over model parameters
-
new data arrive시, 기존의 data와 combine
( multiplying & renormalizing 함으로써 new posterior 계산)
-
하지만, exact Bayesian Inference는 불가능
( intractable…따라서 approximation이 필요함 )
따라서, 이 논문은 Continual learning에, Bayesian Inference를 적용하는데,
이를 위한 approximation으로 online VI & Monte Carlo VI 사용
2. Continual Learning by Approximated Bayesian Inference
Discriminative model : \(p(y \mid \boldsymbol{\theta}, \boldsymbol{x})\)
-
prior : \(p(\boldsymbol{\theta})\)
-
posterior = prior x likelihood :
\(p\left(\boldsymbol{\theta} \mid \mathcal{D}_{1: T}\right) \propto p(\boldsymbol{\theta}) \prod_{t=1}^{T} \prod_{n_{t}=1}^{N_{t}} p\left(y_{t}^{\left(n_{t}\right)} \mid \boldsymbol{\theta}, \boldsymbol{x}_{t}^{\left(n_{t}\right)}\right)=p(\boldsymbol{\theta}) \prod_{t=1}^{T} p\left(\mathcal{D}_{t} \mid \boldsymbol{\theta}\right) \propto p\left(\boldsymbol{\theta} \mid \mathcal{D}_{1: T-1}\right) p\left(\mathcal{D}_{T} \mid \boldsymbol{\theta}\right)\).
-
위 식에서 Recursive 구조 가 발견됨!
( 즉, Bayes Rule 사용하여 online updating을 할 수 있음 )
하지만, posterior는 intractable!
\(\rightarrow\) 따라서 approximate inference 필요
\(p\left(\boldsymbol{\theta} \mid \mathcal{D}_{1: T}\right) \approx q_{T}(\boldsymbol{\theta})=\operatorname{proj}\left(q_{T-1}(\boldsymbol{\theta}) p\left(\mathcal{D}_{T} \mid \boldsymbol{\theta}\right)\right)\).
- (1) Laplace’s Approximation
- (2) Variational KL minimization
- (3) Moment Matching
- (4) Importance Sampling
위의 (1)~(4)에 해당하는 projection operators :
- (1) Laplace Propagation
- (2) online VI
- (3) assumed density filtering (ADF)
- (4) sequential Monte Carlo (SMC)
2-1. VCL & Episodic Memory Enhancement
minimize해야하는 대상 :
- \(q_{t}(\boldsymbol{\theta})=\arg \min _{q \in \mathcal{Q}} \mathrm{KL}\left(q(\boldsymbol{\theta}) \| \frac{1}{Z_{t}} q_{t-1}(\boldsymbol{\theta}) p\left(\mathcal{D}_{t} \mid \boldsymbol{\theta}\right)\right), \text { for } t=1,2, \ldots, T\).
하지만, 위 방법론들은 어디까지나 “근사(approximation)”이므로…
additional information이 손실 될 수 있다.
따라서, 이를 보완하기 위해 coreset 도입
( = key information을 담고 있는 episodic memory와 유사한 개념이라고 생각하면 됨. 원할 때 언제든지 참조할 수 있음 )
[ Algorithm ]
coreset \(C_t\) : (1) 현재의 data \(D_t\)와, (2) 이전의 coreset \(C_{t-1}\)의 조합으로 생성
- ex) \(K\)개의 data가 \(D_t\)에서 샘플된 뒤, \(C_{t-1}\)와 합쳐져서 \(C_t\) 생성
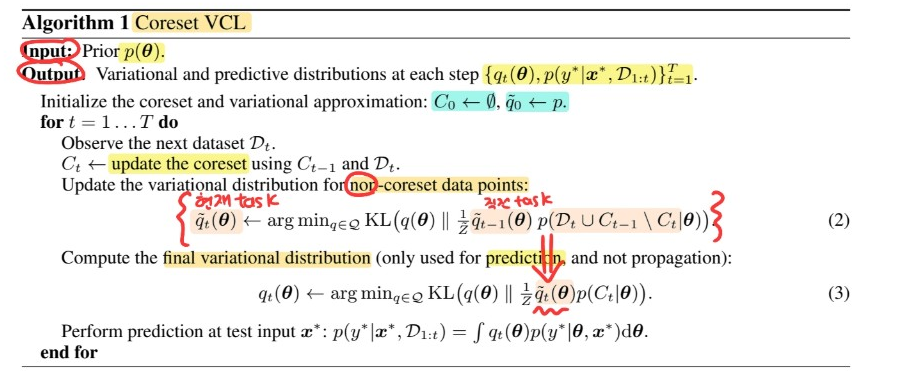
3. VCL in Deep DISCRIMINATIVE models
general solution to CL : automatic continual model building
( = 새로운 task 들어오면, add “NEW STRUCTURE” to 기존 모델 )
Variational Continual Learning
-
\(q(\theta)\)에 대한 specification이 필요
-
“Gaussian” MVFI 가정 ( \(q_{t}(\boldsymbol{\theta})=\prod_{d=1}^{D} \mathcal{N}\left(\theta_{t, d} ; \mu_{t, d}, \sigma_{t, d}^{2}\right)\) )
-
task 데이터 \(D_t\)들어올 때마다…
- TASK SPECIFIC parameter는, “해당 task 때만” update
- COMMON parameter는 “항상” update
Variational Parameters : \(\left\{\mu_{t, d}, \sigma_{t, d}\right\}_{d=1}^{D}\)
Goal : 아래의 ELBO를 maximize
- \(\mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{VCL}}^{t}\left(q_{t}(\boldsymbol{\theta})\right)=\sum_{n=1}^{N_{t}} \mathbb{E}_{\boldsymbol{\theta} \sim q_{t}(\boldsymbol{\theta})}\left[\log p\left(y_{t}^{(n)} \mid \boldsymbol{\theta}, \mathbf{x}_{t}^{(n)}\right)\right]-\mathrm{KL}\left(q_{t}(\boldsymbol{\theta}) \| q_{t-1}(\boldsymbol{\theta})\right)\).
4. VCL in Deep GENERATIVE models
Introduction
- pass simple noise ( \(z\) )!
- generate image/sound/video…
Goal
- VCL framework를 “VAE로 확장”한다
- ( 나중에 GAN으로 확장도 가능 )
Model 소개 : \(p(\mathbf{x} \mid \mathbf{z}, \boldsymbol{\theta}) p(\mathbf{z})\)
- prior \(p(\mathbf{z})\) : Gaussian
- likelihood \(p(\mathbf{x} \mid \mathbf{z}, \boldsymbol{\theta})\)
- parameters는 DNN의 output으로 나옴
- ex) Bernoulli likelihood : \(p(\mathbf{x} \mid \mathbf{z}, \boldsymbol{\theta})=\operatorname{Bern}\left(\mathbf{x} ; \boldsymbol{f}_{\boldsymbol{\theta}}(\mathbf{z})\right)\)
Parameter
- \(\phi\) : encoder parameter
- \(\theta\) : decoder parameter
Goal ( VAE & VCL )
-
VAE의 목표 : 아래의 ELBO를 maximize ( with respect to \(\theta\) and \(\phi\) )
- \(\mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{VAE}}(\boldsymbol{\theta}, \boldsymbol{\phi})=\sum_{n=1}^{N} \mathbb{E}_{q_{\phi}\left(\mathbf{z}^{(n)} \mid \mathbf{x}^{(n)}\right)}\left[\log \frac{p\left(\mathbf{x}^{(n)} \mid \mathbf{z}^{(n)}, \boldsymbol{\theta}\right) p\left(\mathbf{z}^{(n)}\right)}{q_{\boldsymbol{\phi}}\left(\mathbf{z}^{(n)} \mid \mathbf{x}^{(n)}\right)}\right]\).
-
VCL의 목표 : ( \(q_{t}(\boldsymbol{\theta}) \approx p\left(\boldsymbol{\theta} \mid \mathcal{D}_{1: t}\right)\) )
아래의 ELBO를 maximize ( with respect to \(\theta\) and \(\phi\) )
- \(\mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{VCL}}^{t}\left(q_{t}(\boldsymbol{\theta}), \boldsymbol{\phi}\right)=\mathbb{E}_{q_{t}(\boldsymbol{\theta})}\left\{\sum_{n=1}^{N_{t}} \mathbb{E}_{q_{\phi}\left(\mathbf{z}_{t}^{(n)} \mid \mathbf{x}_{t}^{(n)}\right)}\left[\log \frac{p\left(\mathbf{x}_{t}^{(n)} \mid \mathbf{z}_{t}^{(n)}, \boldsymbol{\theta}\right) p\left(\mathbf{z}_{t}^{(n)}\right)}{q_{\phi}\left(\mathbf{z}_{t}^{(n)} \mid \mathbf{x}_{t}^{(n)}\right)}\right]\right\}-\mathrm{KL}\left(q_{t}(\boldsymbol{\theta}) \| q_{t-1}(\boldsymbol{\theta})\right)\).
