( 참고 : 패스트 캠퍼스 , 한번에 끝내는 컴퓨터비전 초격차 패키지 )
EfficientNet & SqueezeNet & Shift
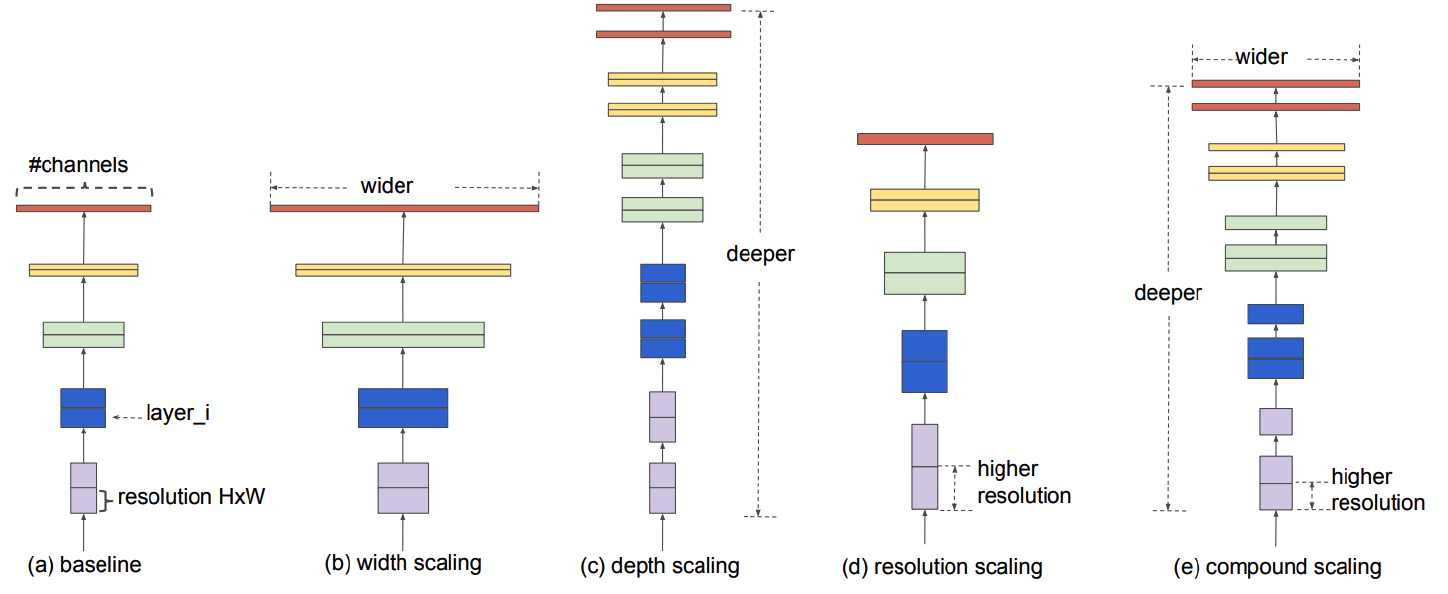
[1] EfficientNet
- scaling up baseline
- model search with compount scaling
- notation
- \(\text { depth: } d=\alpha^{\phi}\).
- \(\text { width: } w=\beta^{\phi}\).
- \(\text { resolution: } r=\gamma^{\phi}\).
- \(\begin{aligned} \text { s.t. } & \alpha \cdot \beta^{2} \cdot \gamma^{2} \approx 2 \\ & \alpha \geq 1, \beta \geq 1, \gamma \geq 1 \end{aligned}\).
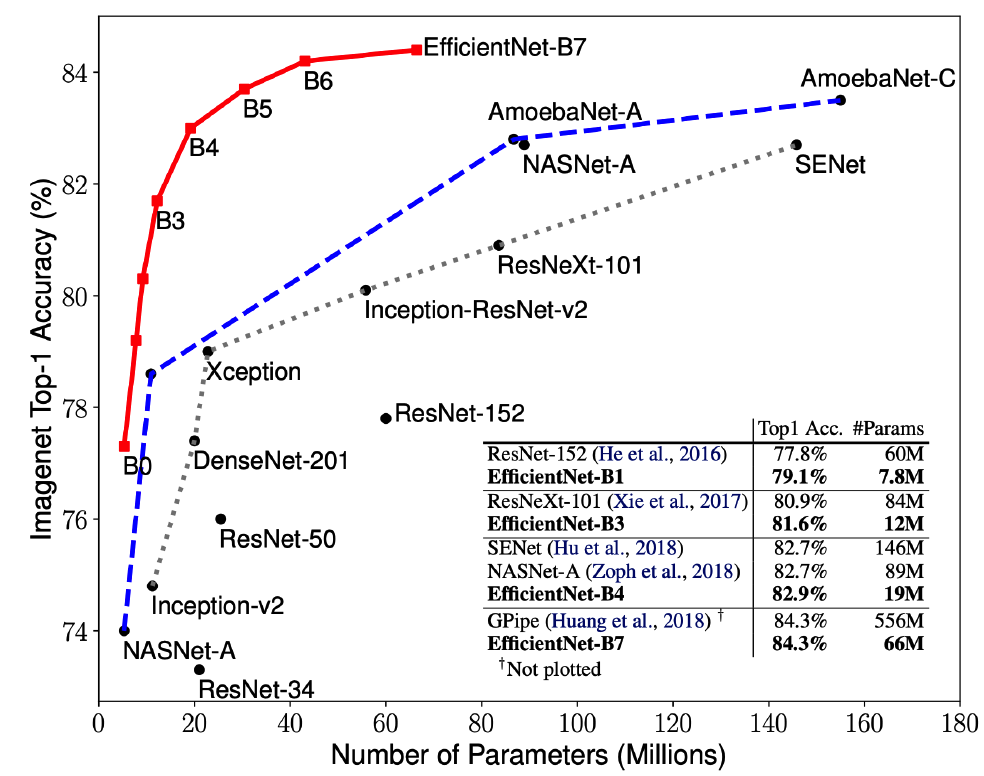
Number of parameters
Code
Import models
efficientnet_b0 = models.efficientnet_b0(pretrained=True)
efficientnet_b1 = models.efficientnet_b1(pretrained=True)
efficientnet_b2 = models.efficientnet_b2(pretrained=True)
efficientnet_b3 = models.efficientnet_b3(pretrained=True)
efficientnet_b4 = models.efficientnet_b4(pretrained=True)
efficientnet_b5 = models.efficientnet_b5(pretrained=True)
efficientnet_b6 = models.efficientnet_b6(pretrained=True)
efficientnet_b7 = models.efficientnet_b7(pretrained=True)
Count the number of parameters
from prettytable import PrettyTable
def count_parameters(model):
table = PrettyTable(["Modules", "Parameters"])
n_params = 0
for name, parameter in model.named_parameters():
if not parameter.requires_grad:
continue
n_param = parameter.numel()
table.add_row([name, n_param])
n_params+=n_param
print(table)
print(f"Total Trainable Params: {total_params}")
return total_params
count_parameters(efficientnet_b0)
+---------------------------------+------------+
| Modules | Parameters |
+---------------------------------+------------+
| features.0.0.weight | 864 |
| features.0.1.weight | 32 |
| features.0.1.bias | 32 |
| features.1.0.block.0.0.weight | 288 |
| features.1.0.block.0.1.weight | 32 |
| features.1.0.block.0.1.bias | 32 |
| features.1.0.block.1.fc1.weight | 256 |
| features.1.0.block.1.fc1.bias | 8 |
| features.1.0.block.1.fc2.weight | 256 |
| features.1.0.block.1.fc2.bias | 32 |
| features.1.0.block.2.0.weight | 512 |
| features.1.0.block.2.1.weight | 16 |
| features.1.0.block.2.1.bias | 16 |
| features.2.0.block.0.0.weight | 1536 |
| features.2.0.block.0.1.weight | 96 |
| features.2.0.block.0.1.bias | 96 |
| features.2.0.block.1.0.weight | 864 |
| features.2.0.block.1.1.weight | 96 |
| features.2.0.block.1.1.bias | 96 |
| features.2.0.block.2.fc1.weight | 384 |
| features.2.0.block.2.fc1.bias | 4 |
| features.2.0.block.2.fc2.weight | 384 |
...
| classifier.1.weight | 1280000 |
| classifier.1.bias | 1000 |
+---------------------------------+------------+
Total Trainable Params: 5288548
5288548
[2] SqueezeNet
Three strategies
-
3x3 filters \(\rightarrow\) 1x1 filters
( number of params = reduced to 1/9 )
-
decrease # of input channels of 3x3 filters
-
downsample “late”, to have large receptive field
Fire Module
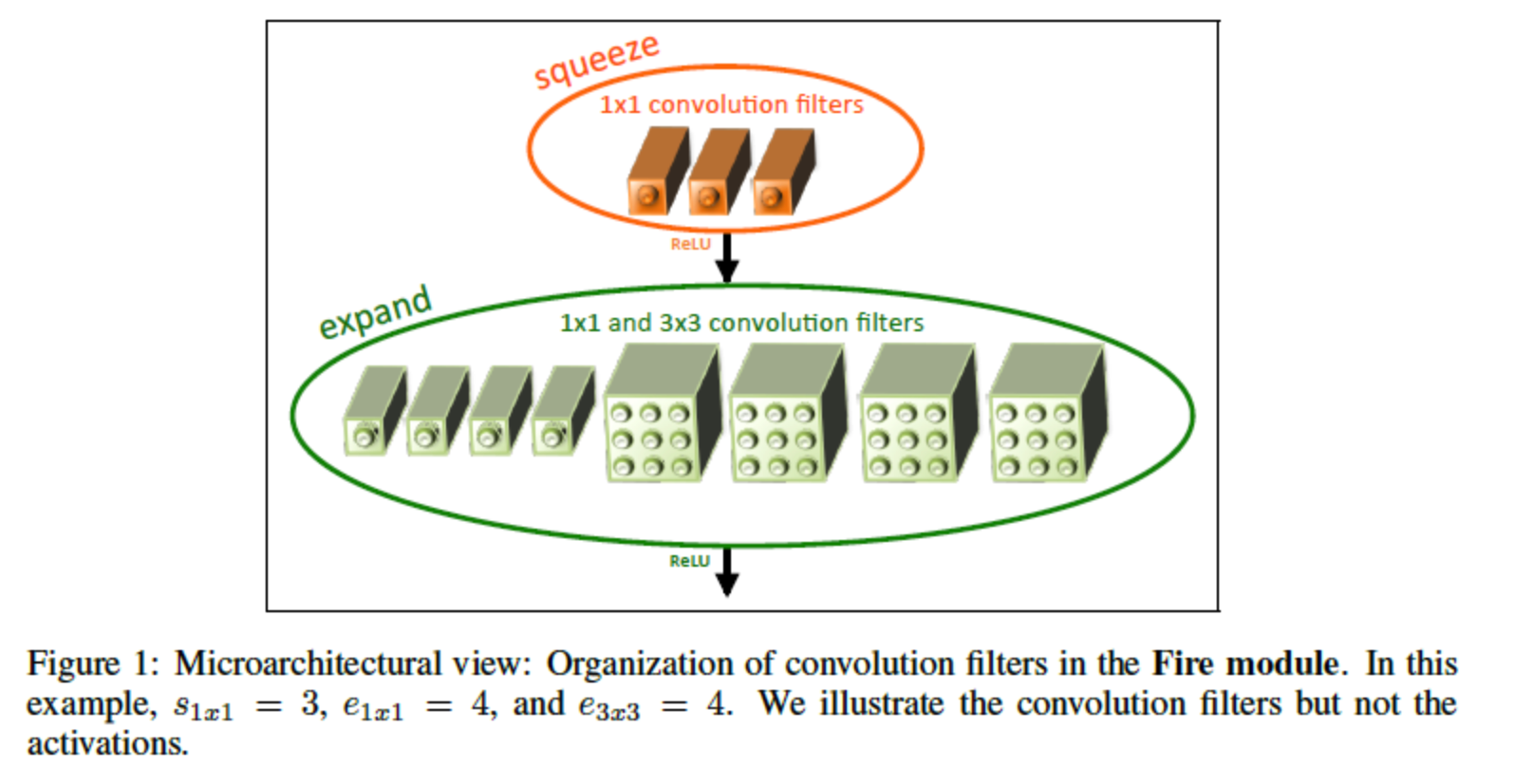
- SQUEEZE convolution layer ( only 1x1 filter )
- EXPAND convolution layer ( 1x1 filter & 3x3 filter )
class Fire(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplanes: int, squeeze_planes: int, expand1x1_planes: int, expand3x3_planes: int) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.inplanes = inplanes
#----------------------------------------------------------------#
# [1] Squeeze convolution layer
self.squeeze = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, squeeze_planes, kernel_size=1)
self.squeeze_activation = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
#----------------------------------------------------------------#
# [2] Expand convolution layer
self.expand1x1 = nn.Conv2d(squeeze_planes, expand1x1_planes, kernel_size=1)
self.expand1x1_activation = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.expand3x3 = nn.Conv2d(squeeze_planes, expand3x3_planes, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.expand3x3_activation = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
#----------------------------------------------------------------#
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x = self.squeeze_activation(self.squeeze(x))
return torch.cat(
[self.expand1x1_activation(self.expand1x1(x)),
self.expand3x3_activation(self.expand3x3(x))], 1)
Overall Architecture
class SqueezeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, version: str = "1_0", num_classes: int = 1000, dropout: float = 0.5) -> None:
super().__init__()
_log_api_usage_once(self)
self.num_classes = num_classes
if version == "1_0":
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 96, kernel_size=7, stride=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True),
Fire(96, 16, 64, 64),
Fire(128, 16, 64, 64),
Fire(128, 32, 128, 128),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True),
Fire(256, 32, 128, 128),
Fire(256, 48, 192, 192),
Fire(384, 48, 192, 192),
Fire(384, 64, 256, 256),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True),
Fire(512, 64, 256, 256),
)
elif version == "1_1":
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True),
Fire(64, 16, 64, 64),
Fire(128, 16, 64, 64),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True),
Fire(128, 32, 128, 128),
Fire(256, 32, 128, 128),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True),
Fire(256, 48, 192, 192),
Fire(384, 48, 192, 192),
Fire(384, 64, 256, 256),
Fire(512, 64, 256, 256),
)
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported SqueezeNet version {version}: 1_0 or 1_1 expected")
final_conv = nn.Conv2d(512, self.num_classes, kernel_size=1)
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=dropout), final_conv, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
if m is final_conv:
init.normal_(m.weight, mean=0.0, std=0.01)
else:
init.kaiming_uniform_(m.weight)
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x = self.features(x)
x = self.classifier(x)
return torch.flatten(x, 1)
Code
models.SqueezeNet()
models.squeezenet1_0()
models.squeezenet1_1()
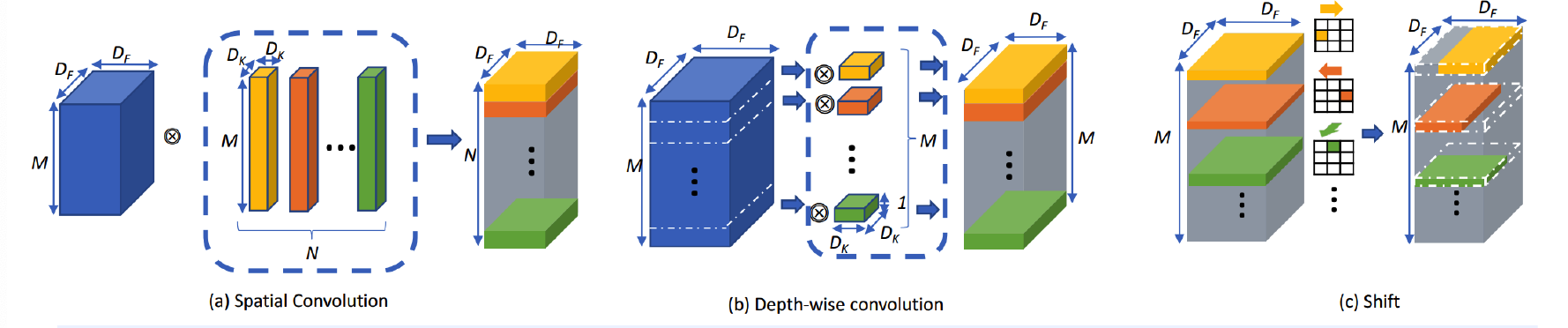
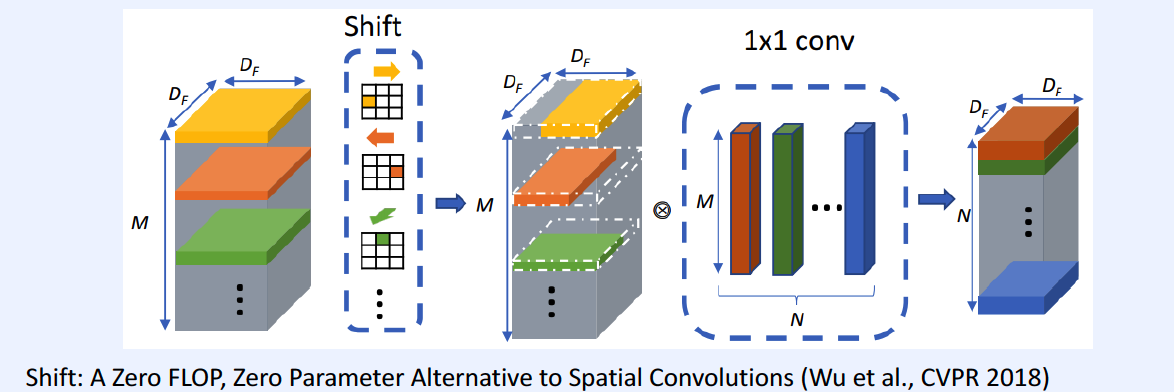
[3] Shift
Spatial Convolution may not be necessary!
\(\rightarrow\) instead of spatial convolution … just use shift operation
( & just use 1x1 conv for feature extraction )