( 참고 : 패스트 캠퍼스 , 한번에 끝내는 컴퓨터비전 초격차 패키지 )
Data Augmentation (3)
Categories of Data Augmentation
- (1) Rule-based
- (2) GAN-based
- (3) AutoML-based
(3) AutoML-based
- AutoAugment
- Population Based AutoAugment
- Fast AutoAugment
- Faster AutoAugment
- RandAugment
- UniformAugment
- TrivialAugment
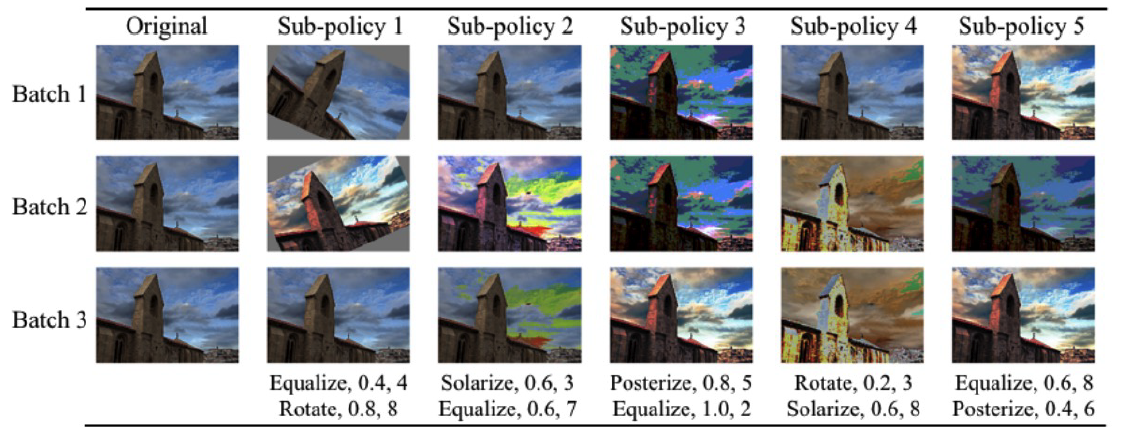
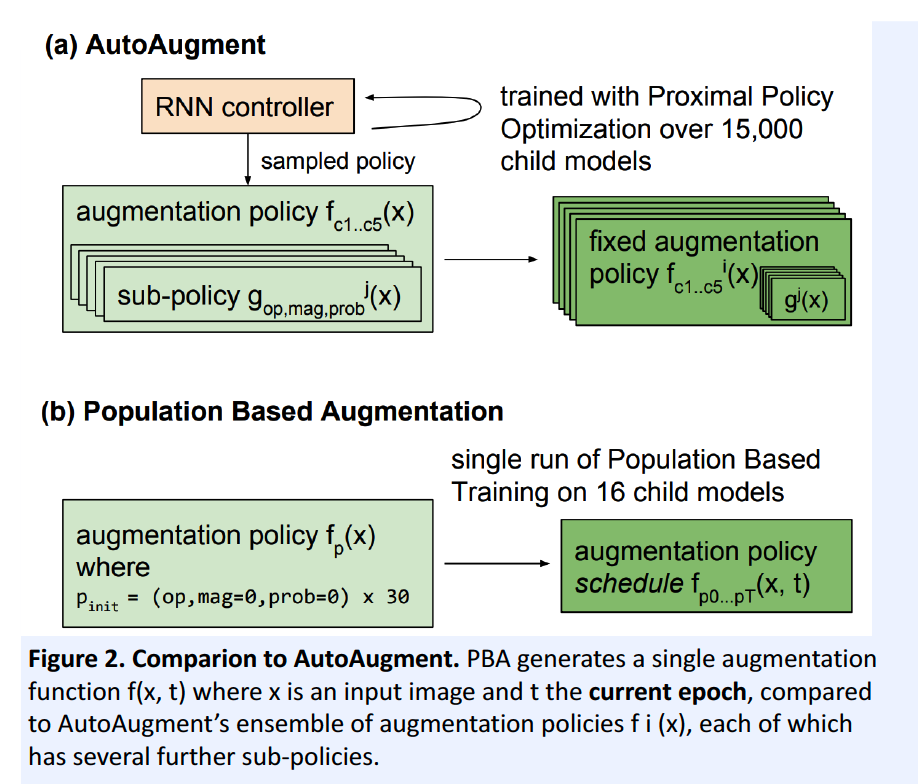
1) AutoAugment
( AutoAugment : Learning Augmentation Policies from Data, Cubuk et al., CVPR 2019 )
- like NAS (Neural Architecture Search), sample Augmentation Policy from RNN controller
- Reinforcment Learning / Policy gradient
- reward : validation accuracy
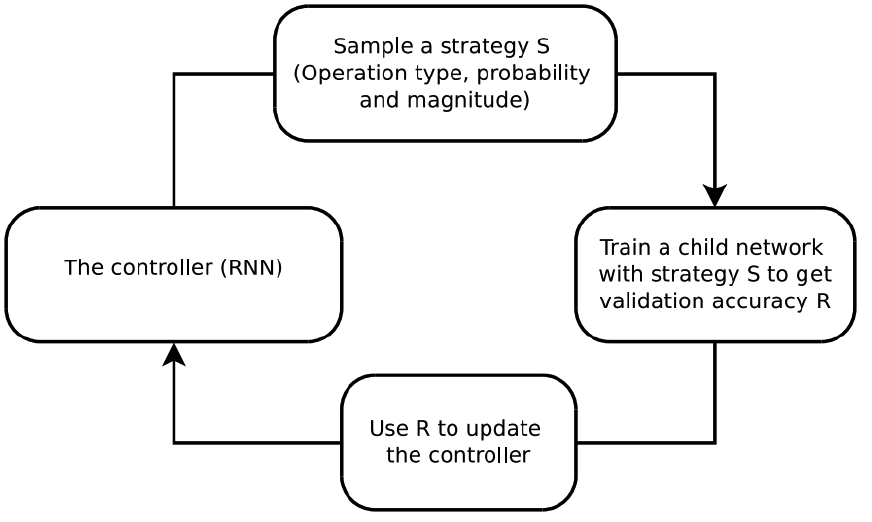

Cons : TOO MUCH COMPUTATION TIME
( \(\because\) policy gradient based on validation error )
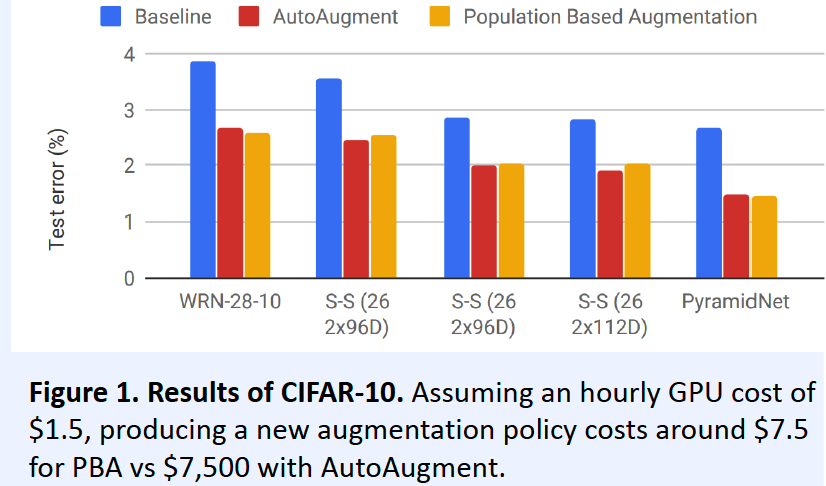
2) Population Based AutoAugment
( Population Based Augmentation : Efficient Learning of Augmentation Policy Schedules, Ho et al., ICML 2019 )
Problem of AutoAugment : computationally infeasible
\(\rightarrow\) solution : Population Based AutoAugment
Characteristics
-
non-stationary augmentation policy schedules
( instead of fixed augmentaiton policy )
-
Exploration & exploitation
\(\rightarrow\) outputs an augmentation policy!

3) Fast AutoAugment
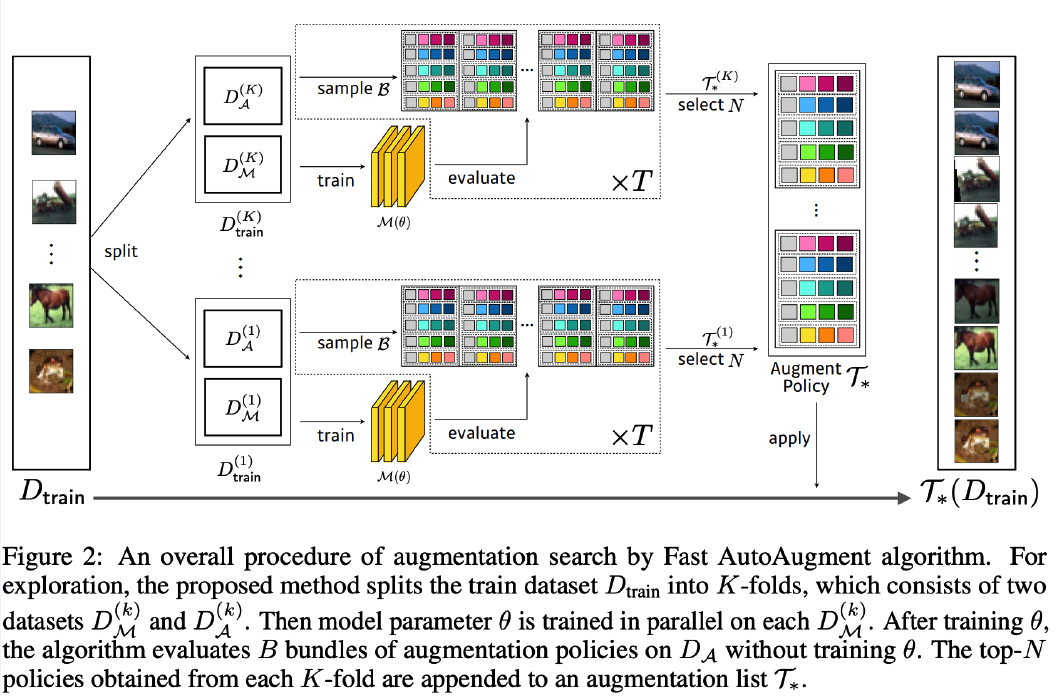
( Fast AutoAugment, Lim et al., NeurIPS 2019 )
Problem of AutoAugment : computationally infeasible
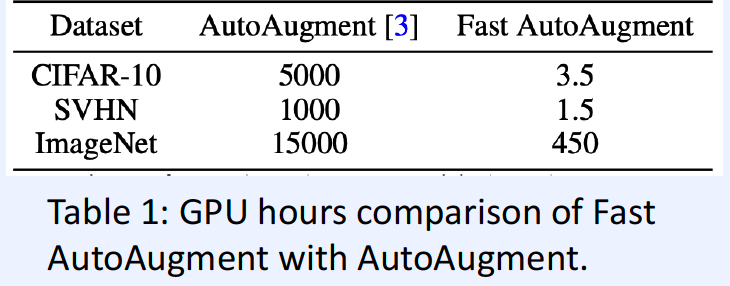
Solution : efficient search strategy, using density matching
- concept of Bayesian Optimization ( Tree-structued Parzen Estimator (TPE) )
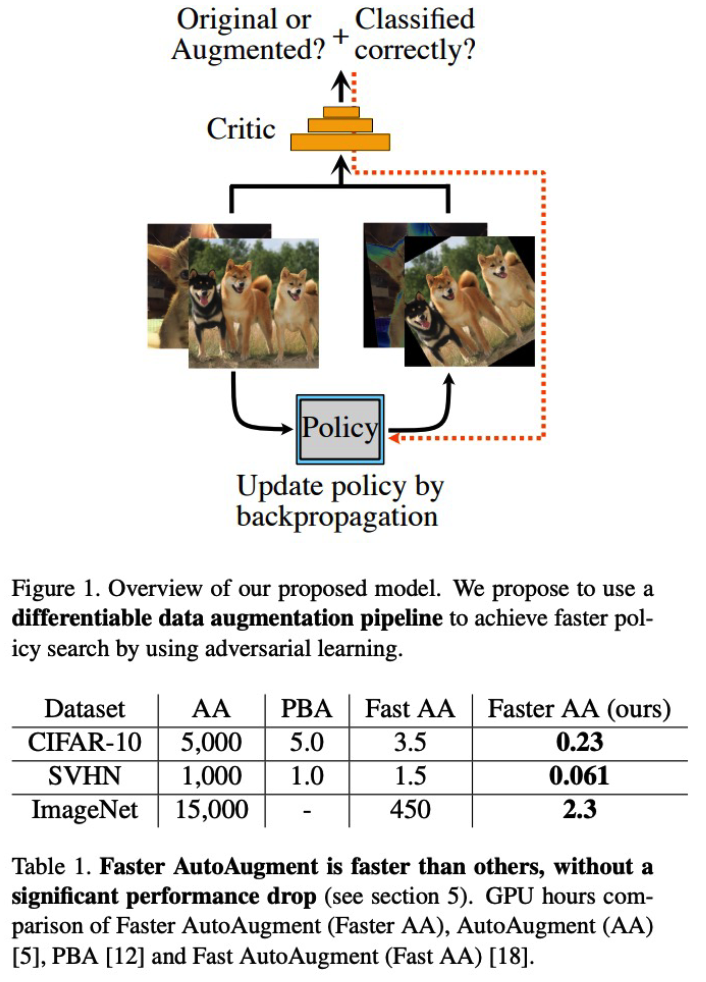
4) Faster AutoAugment
( Faster AutoAugment : Learning Augmentation Strategies using Backpropagation, Hataya et al., ECCV 2020 )
Motivation
- make it differentiable ! DIFFERENTIABLE AutoAugment
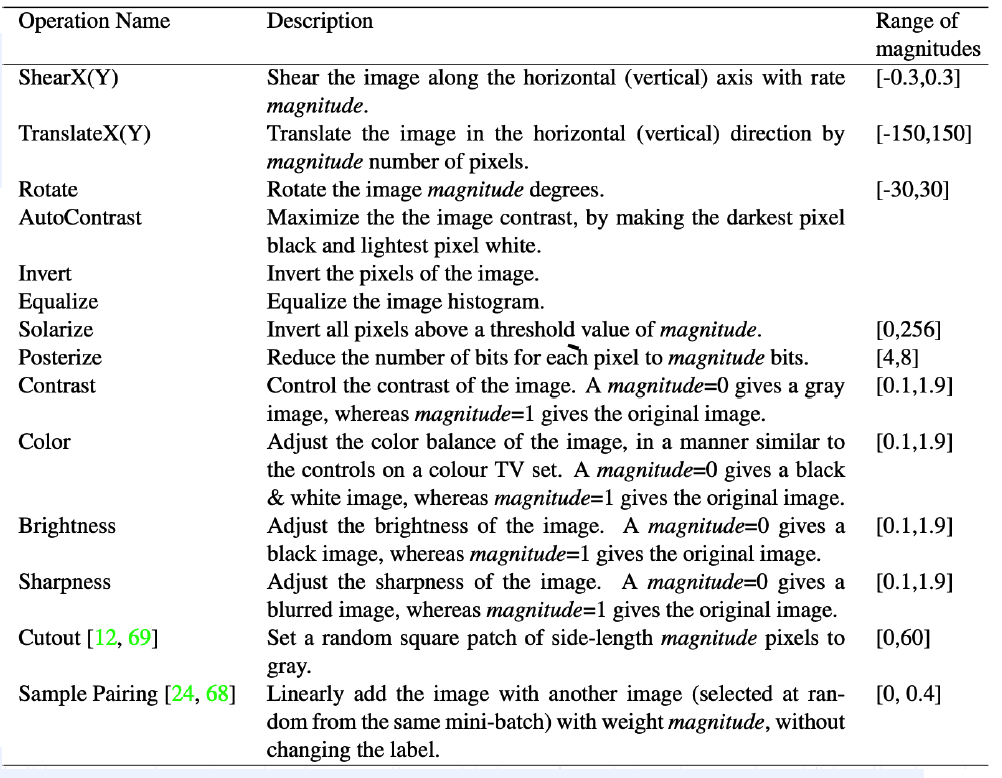
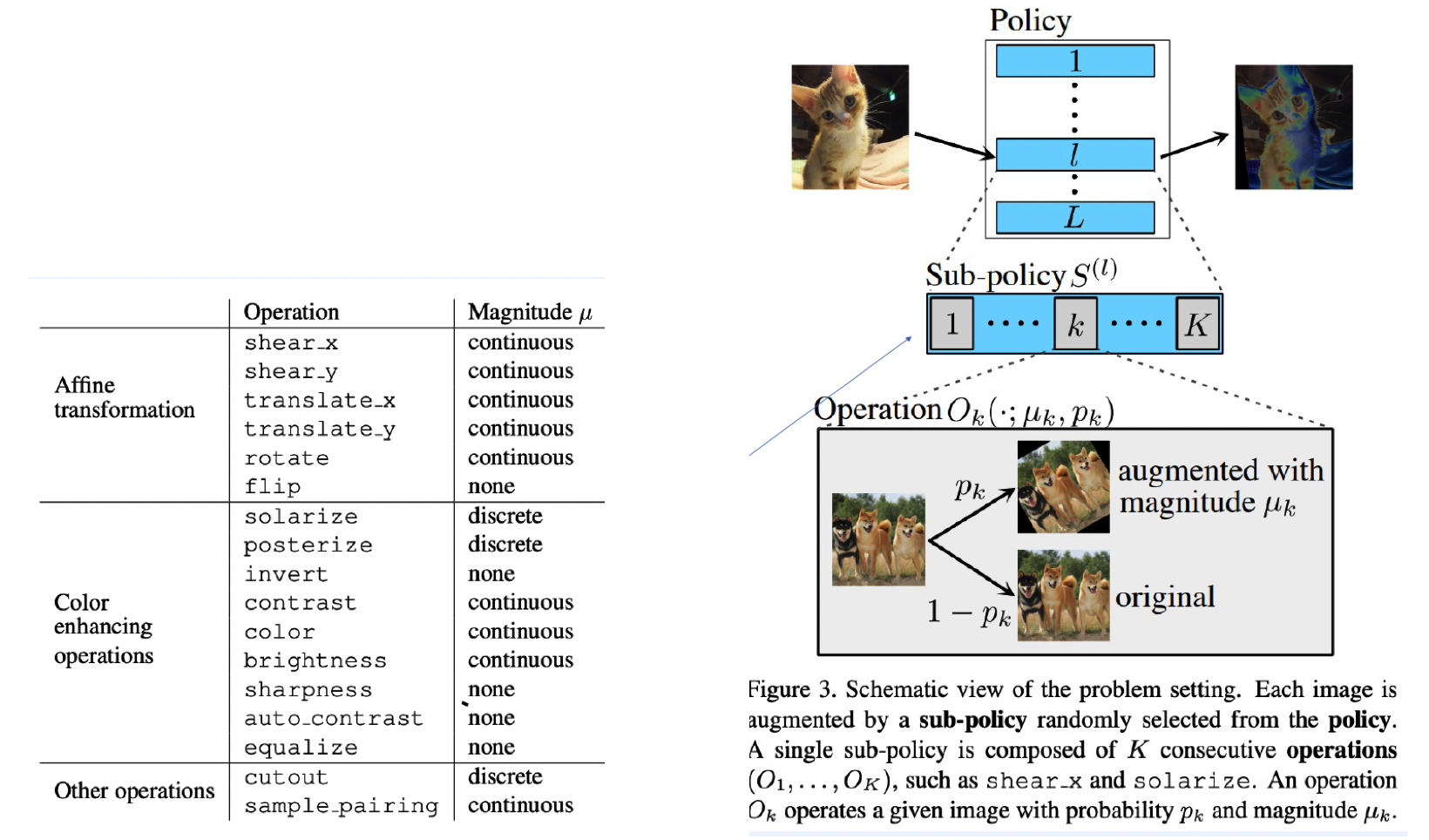
Candidates of operations :
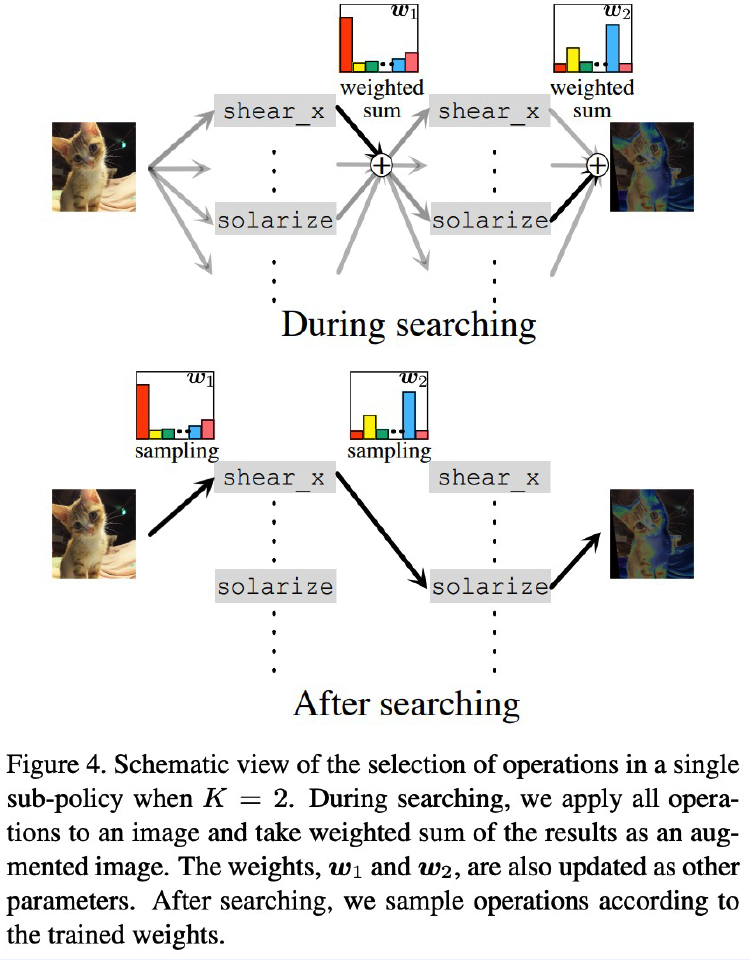
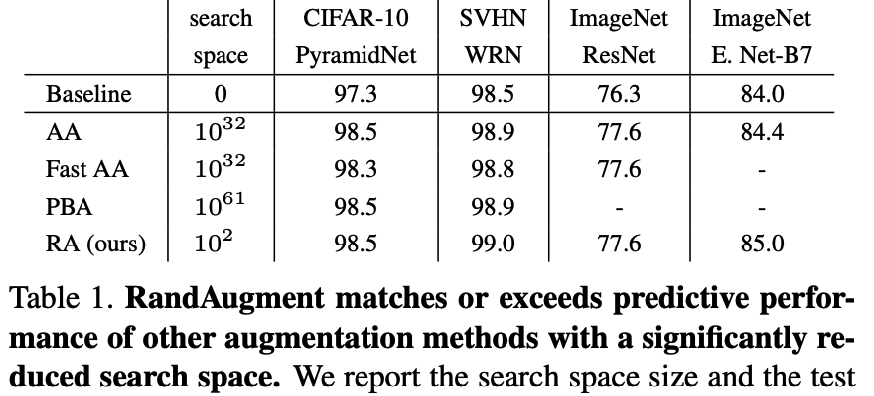
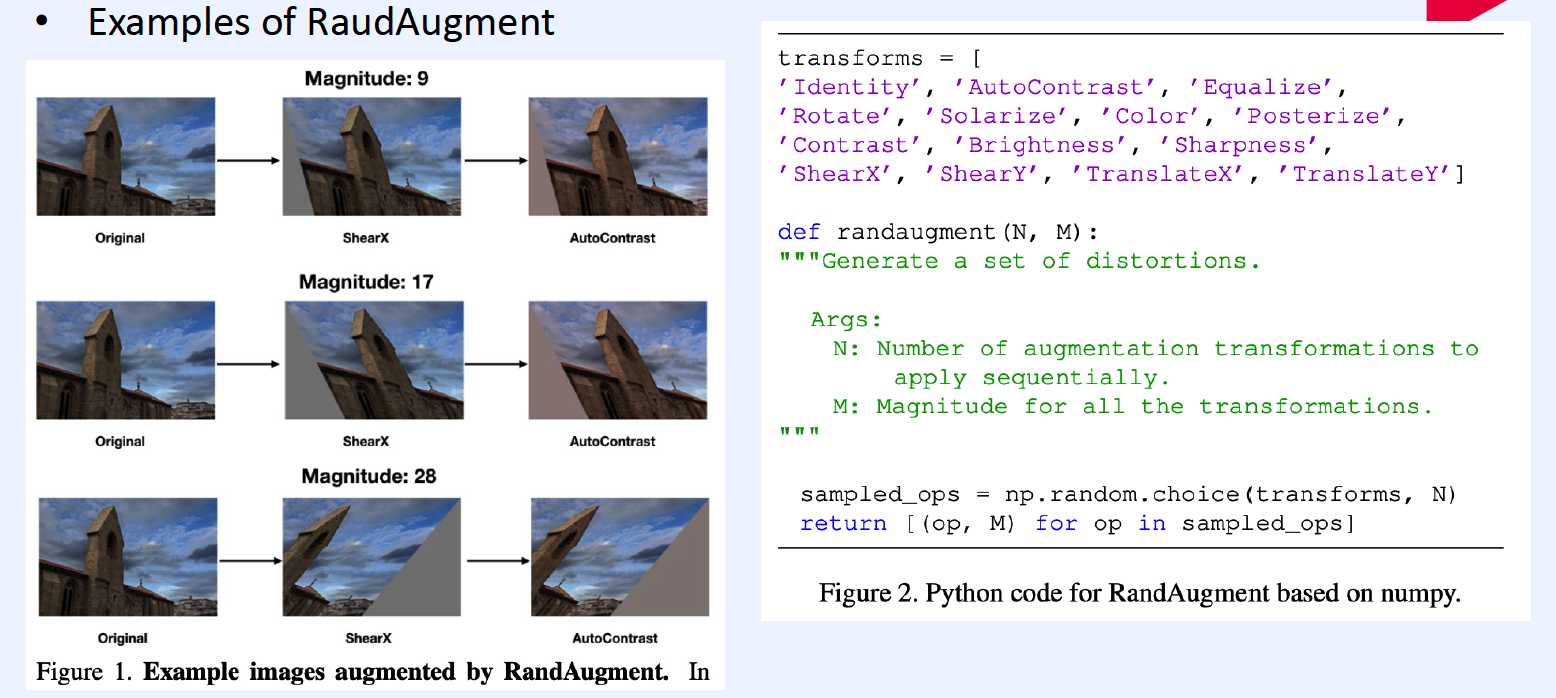
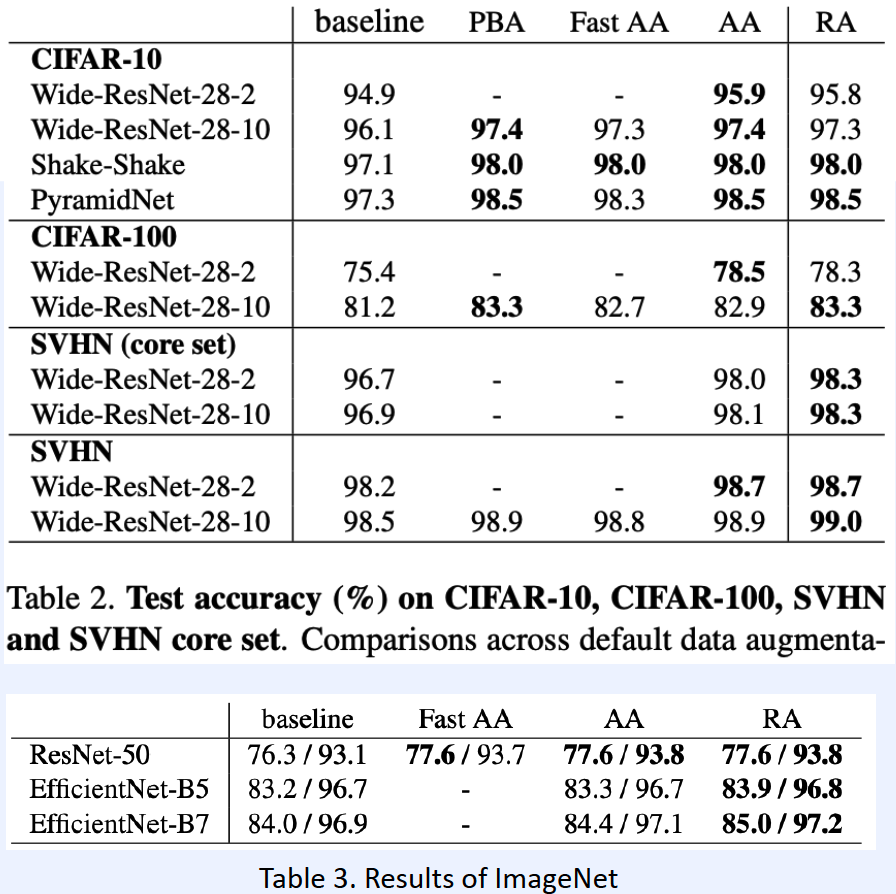
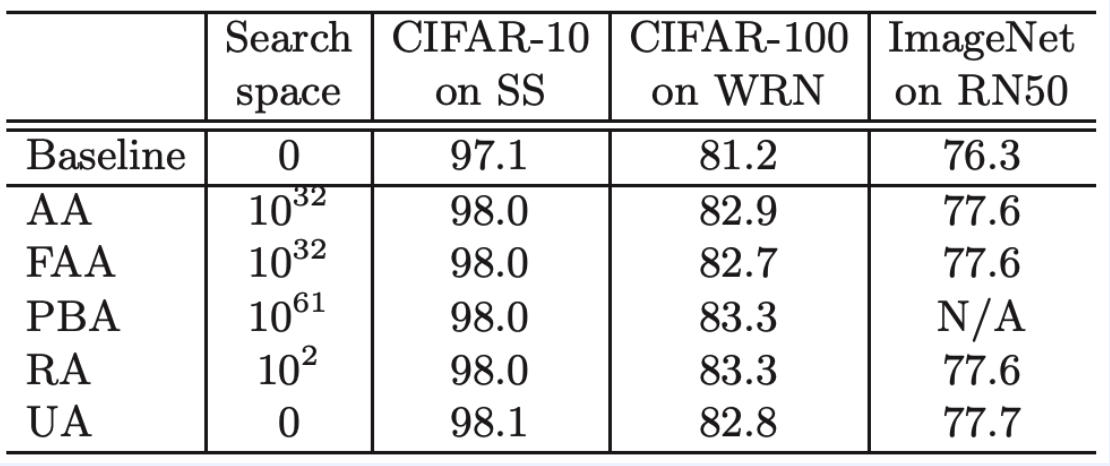
5) RandAugment
( RandAugment : Practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space, Cebuk et al., NeurIPS 2020 )
Why need AutoML? Too LARGE search space!
\(\rightarrow\) Instead of searching, random sample
hyperparameter :
- \(N\) : number of operations
- \(M\) : range of operations
6) UniformAugment
( UniformAugment : A Search-free Probabilistic Data Augmentation Approach, LingChen et al. )
- mix 2 images pixel wise ( NO SEARCH )
- train : N-class multi-label prediction
- Prob 0~1 of,,,
- using certain augmentation (O,X)
- Magnitude of augmentation
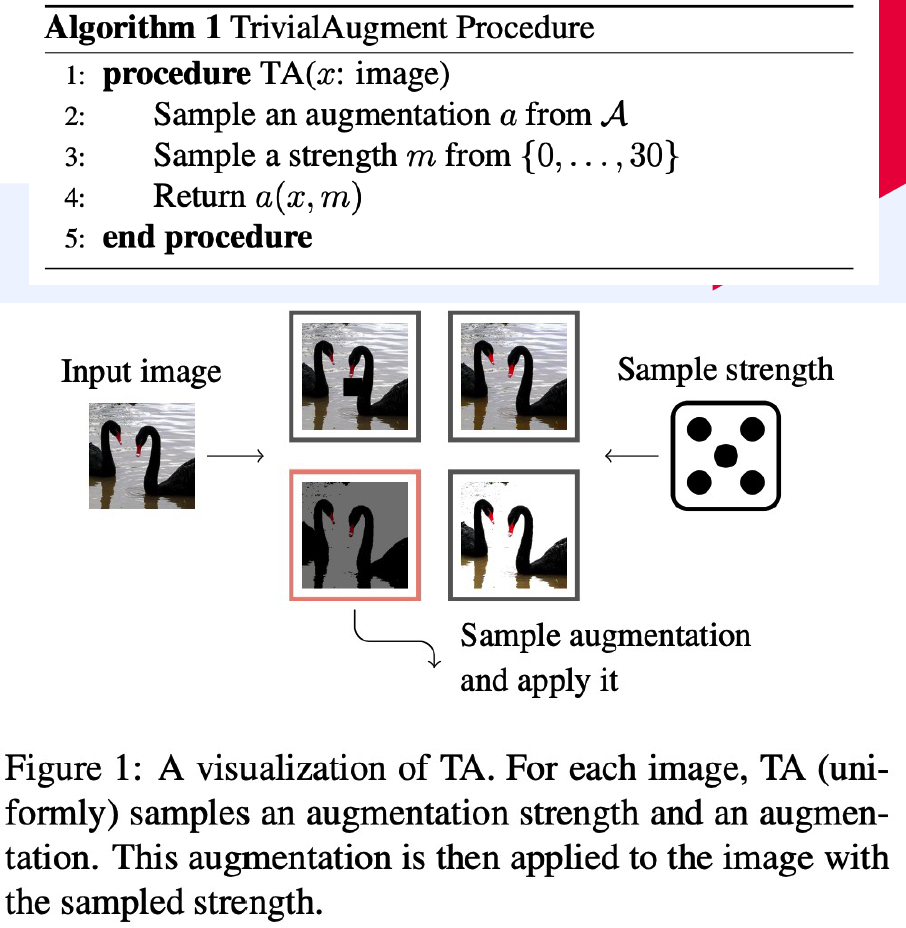
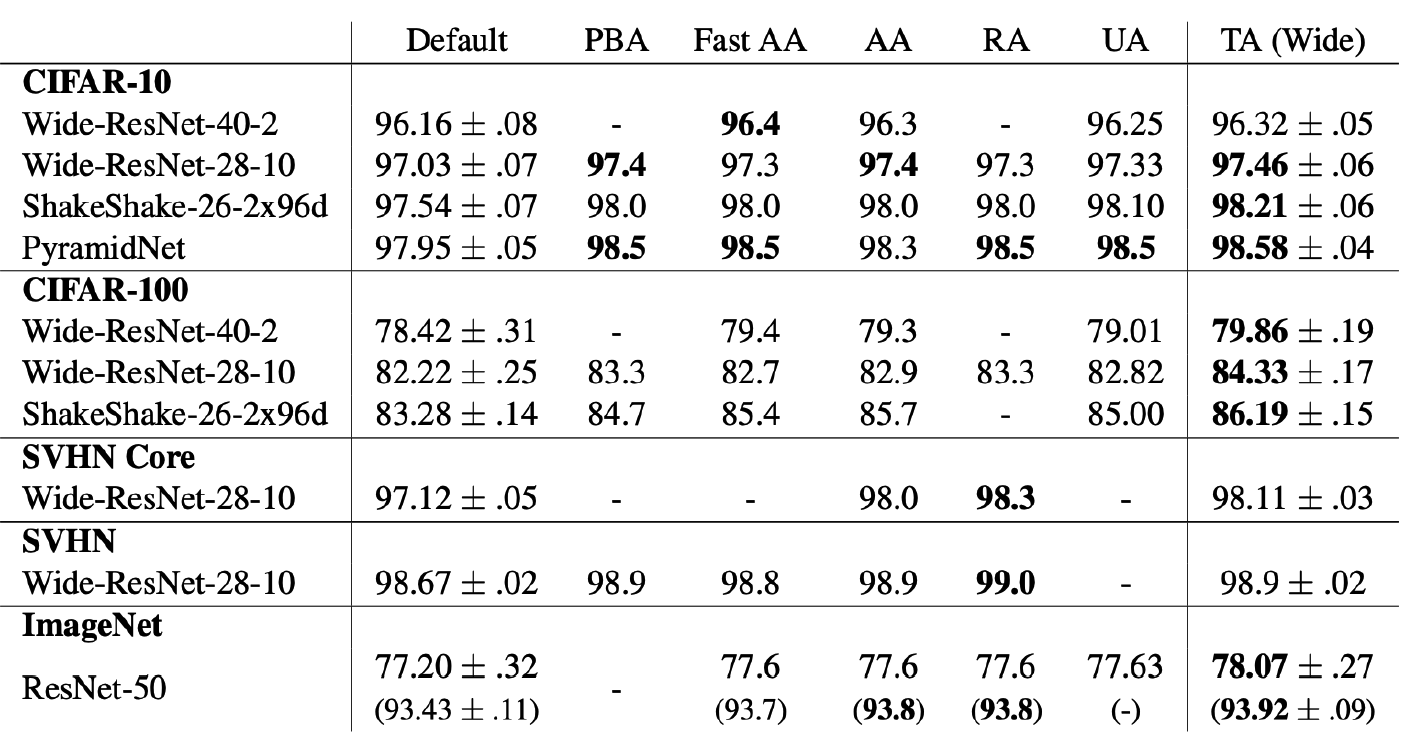
7) TrivialAugment
( Trivial Augment : Tuning-free Yet State-of-the-Art Data Augmentation, mUiller et al., ICCV 2021 )
previous methods
- consider trade-off between efficiency & effectiveness
Proposes…
- instead of parameter-free, just search important factors
- (1) Augmentation Type
- (2) Magnitude