[Paper Review] 28. StarGAN : Unified GAN for Multi-Domain Image-to-Image translation
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- StarGAN
- Multi-domain Image-to-Image Translation
- Training with Multiple Datasets
0. Abstract
limited scalability and robustness in handling more than 2 domains
$\rightarrow$ propose “StarGAN”
- novel & scalable approach, that can perform image-to-image translations for multiple domains using only a SINGLE model
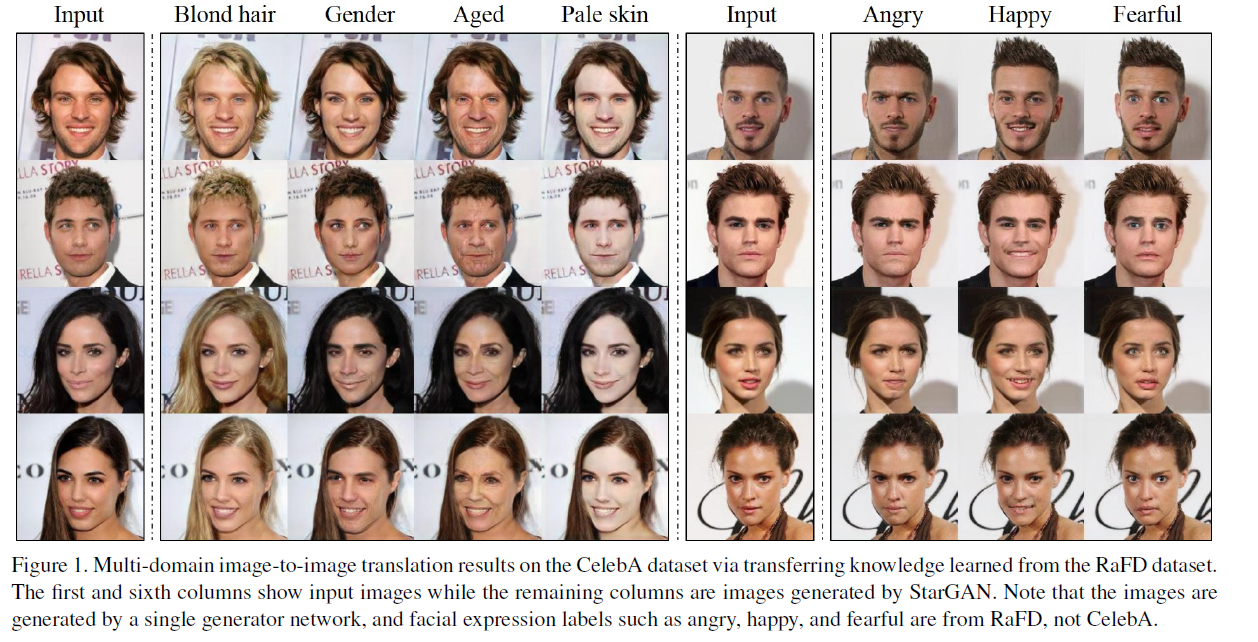
1. Introduction
Definition
- 1) attribute :
- ex) hair color, gender, age
- 2) attribute value :
- ex) black/bond/brown for hair color, male/female for gender
- 3) domain :
- set of images sharing the same attribute values
- ex) images of women
Previous methods :
- Mapping among $k$ domains, $k(k-1)$ generators have to be trained
Propose “StarGAN”
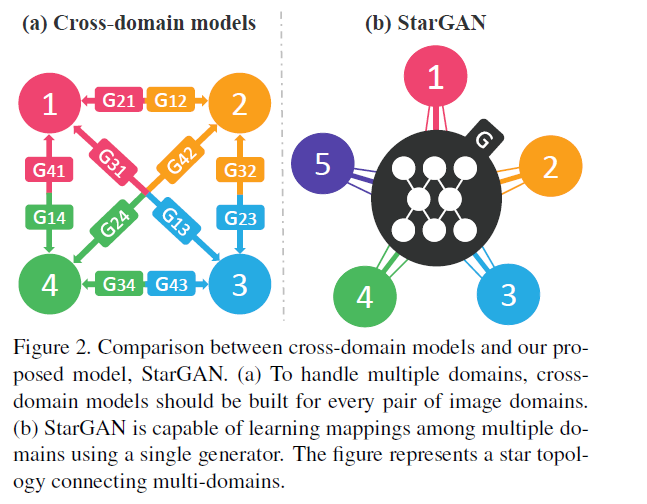
-
instead of learning fixed translation,
takes in as inputs “both image & domain information”
and learns to “flexibly translate the image into the corresponding domain”
-
use label ( binary / one hot vector ) to represent domain information
-
introduce simple & effective approach,
that enables joint training between domains of “different datasets”
by adding a “mask vector” to the domain label
$\rightarrow$ ignore unknown labels, and focus on the label provided by particular dataset
2. StarGAN
-
address multi-domain image-to-image translation
-
discuss how StarGAN incorporates multiple datasets, containing different label sets
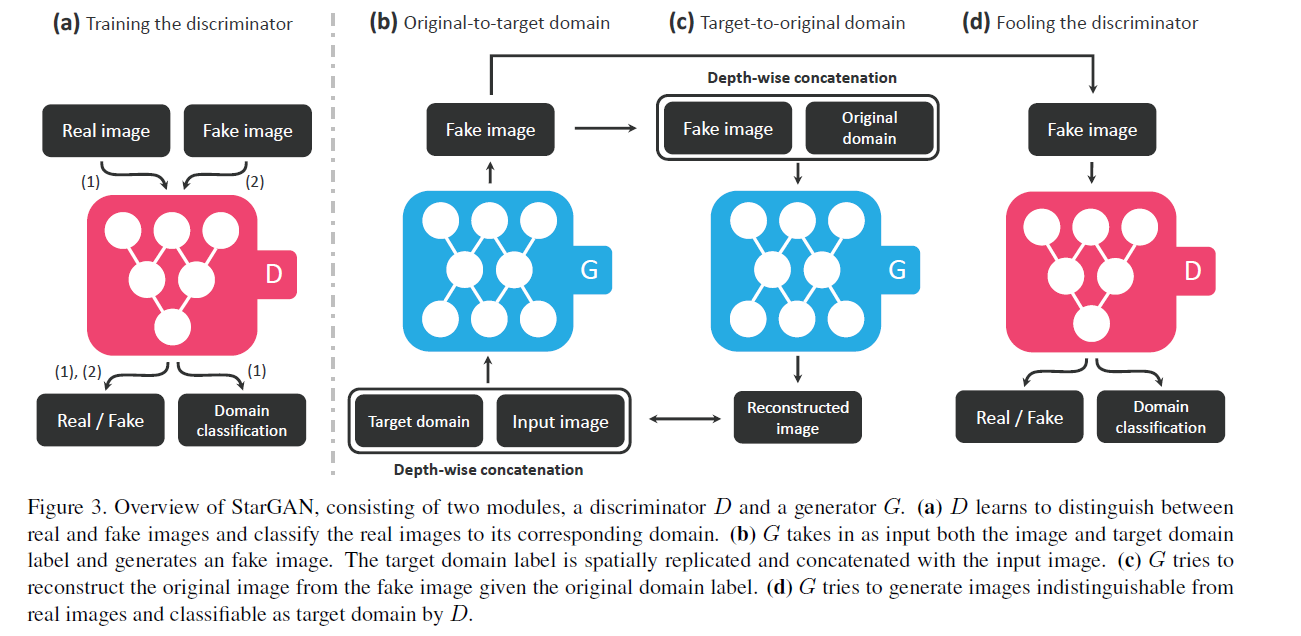
1) Multi-domain Image-to-Image Translation
Notation
- target domain label : $c$
- original domain : $c’$
training $G$ …. ( $G(x,c) \rightarrow y$ )
- translate input image $xx$
- into output image $y$
- conditioned on $c$
training $D$ …. ( $D: x \rightarrow\left{D_{s r c}(x), D_{c l s}(x)\right}$ )
- probability distn over sources
- probability distn over domain labels
[ Adversarial Loss ]
- generated images vs real images
- $\mathcal{L}{a d v}= \mathbb{E}{x}\left[\log D_{s r c}(x)\right]+ \mathbb{E}{x, c}\left[\log \left(1-D{s r c}(G(x, c))\right)\right]$.
[ Domain Classification Loss ]
-
given input image $x$ & target domain label $c$…
-
goal : translate $x$ to $y$
which is properly classified to class $c$
-
decompose objective into 2 terms
- 1) domain classification loss of “real images” used to optimize $D$
- $\mathcal{L}{c l s}^{r}=\mathbb{E}{x, c^{\prime}}\left[-\log D_{c l s}\left(c^{\prime} \mid x\right)\right]$.
- 2) domain classification loss of “fake images” used to optimize $G$
- $\mathcal{L}{c l s}^{f}=\mathbb{E}{x, c}\left[-\log D_{c l s}(c \mid G(x, c))\right]$.
- 1) domain classification loss of “real images” used to optimize $D$
[ Reconstruction Loss ]
- apply a cycle consistency loss to generator
- $\mathcal{L}{r e c}=\mathbb{E}{x, c, c^{\prime}}\left[\left|x-G\left(G(x, c), c^{\prime}\right)\right|_{1}\right]$.
[ Full Objective ]
Objective functions to optimize $G$ and $D$
- $\mathcal{L}{D}=-\mathcal{L}{a d v}+\lambda_{c l s} \mathcal{L}_{c l s}^{r}$.
- $\mathcal{L}{G}=\mathcal{L}{a d v}+\lambda_{c l s} \mathcal{L}{c l s}^{f}+\lambda{r e c} \mathcal{L}_{r e c}$.
2) Training with Multiple Datasets
simultaneously incorporates “multiple datasets, containing different types of labels”
so that StarGAN can control all the labels at the test phase!
[ Mask Vector ]
introduce mask vector $m$
- allows StarGAN to ignore unspecified labels
- define a unified version of label as a vector
- $\tilde{c}=\left[c_{1}, \ldots, c_{n}, m\right]$.
- if use two datasets ( CelebA & RaFD datasets ) : $n=2$
vector of the known label $c_i$ : can be either
- 1) Binary Vector ( for binary attributes )
- 2) Categorical Attributes ( for categorical attributes )
