[Paper Review] 29. StarGAN v2 : Diverse Image Synthesis for Multiple Domains
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- StarGAN v2
- Proposed Framework
- Training Objectives
0. Abstract
good image-to-image translation model :
- property 1) diversity of generated images
- property 2) scalability over multiple domains
1. Introduction
to address scalability, StarGAN has been rpoposed
-
learns the mappings between all available domains, using only SINGLE generator
- takes “domain label” as an additional input
- then, learns to transform an image into the corresponding domain
-
problem
-
deterministic mapping
( does not capture multi-modal nature of data distn )
-
StarGAN v2
- a scalable approach, that can generate DIVERSE images across MULTIPLE domains
- can represent “diverse styles of a specific domains”
2. StarGAN v2
describe
- 1) proposed framework
- 2) training objective functions
1) Proposed Framework
Goal : train a SINGLE \(G\) that can generate diverse images of each domain \(y\) that corresponds to the image \(x\)
- generate domain-specific style vectors
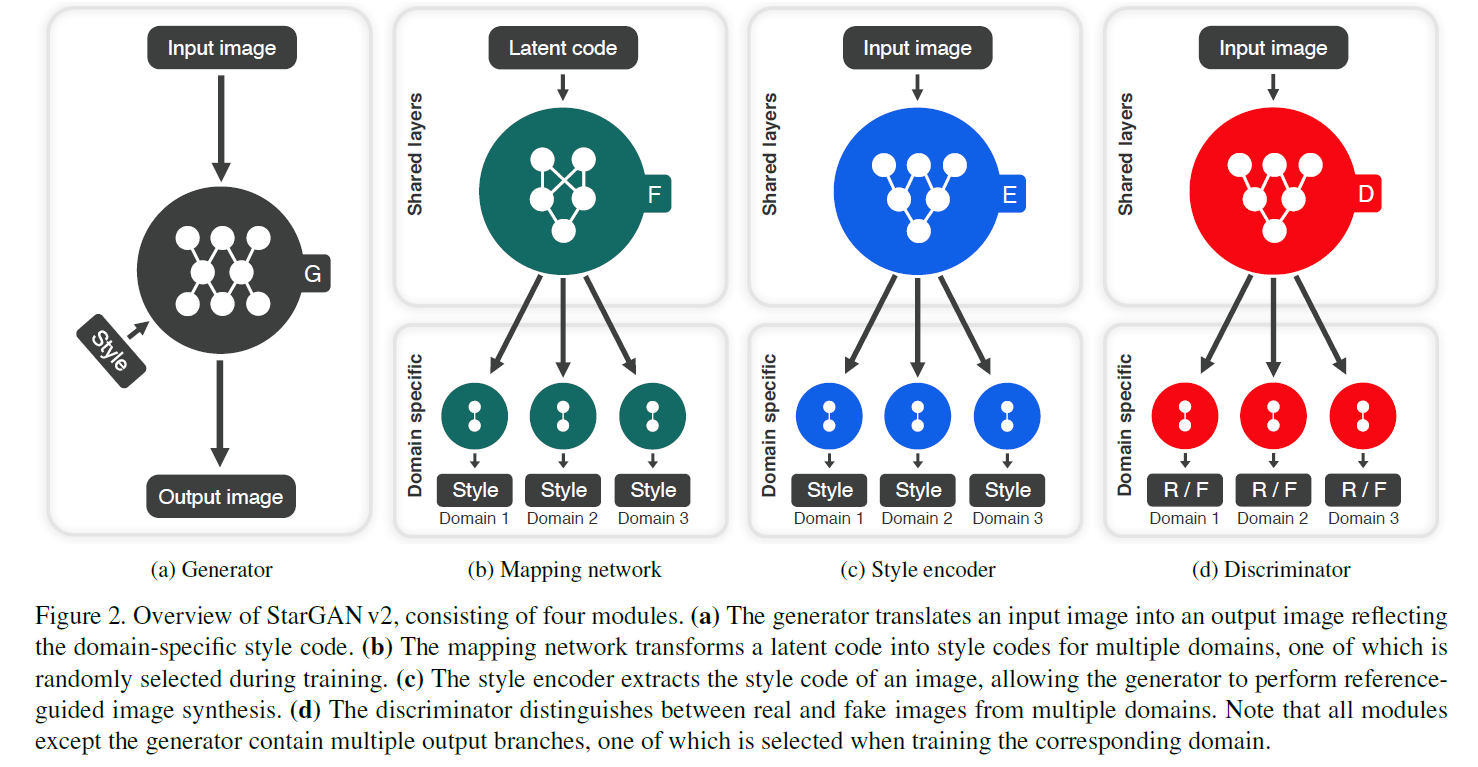
[ a. Generator, \(G\) ]
-
input : \(x\)
-
output : \(G(x,s)\)
( reflecting specific style code \(s\) , provided by…. mapping network \(F\) or style encoder \(E\) )
[ b. Mapping Network, \(F\) ]
-
input : latent code \(\mathbf{z}\) & domain \(y\)
-
output : \(s=F_y(\mathbf{z})\)
-
consists of MLP, with multiple output branches,
to provide style codes for all available domains
[ c. Style Encoder, \(E\) ]
- input : \(x\) & corresponding domain \(y\)
- output : \(s= E_y(x)\)
- goal : extract the style code of \(x\)
[ d. Discriminator, \(D\) ]
- learns a binary classification
- determine whether \(x\) is …
- real image of its domain \(y\)
- fake image \(G(x,s)\)
2) Training Objectives
[ a. Adversarial objective ]
- generate a target style code \(\widetilde{\mathbf{s}}=F_{\widetilde{y}}(\mathbf{z})\)
- \(\mathcal{L}_{a d v}= \mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x}, y}\left[\log D_{y}(\mathbf{x})\right]+ \mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x}, \widetilde{y}, \mathbf{z}}\left[\log \left(1-D_{\widetilde{y}}(G(\mathbf{x}, \widetilde{\mathbf{s}}))\right)\right]\).
[ b. Style Reconstruction ]
- \(\mathcal{L}_{s t y}=\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x}, \widetilde{y}, \mathbf{z}}\left[\left \mid \mid \widetilde{\mathbf{s}}-E_{\widetilde{y}}(G(\mathbf{x}, \widetilde{\mathbf{s}}))\right \mid \mid _{1}\right]\).
[ c. Style Diversification ]
-
enable \(G\) to produce diverse images!
-
regularize \(G\) with “diversity sensitive loss”
-
\(\mathcal{L}_{d s}=\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x}, \widetilde{y}, \mathbf{z}_{1}, \mathbf{z}_{2}}\left[\left \mid \mid G\left(\mathbf{x}, \widetilde{\mathbf{s}}_{1}\right)-G\left(\mathbf{x}, \widetilde{\mathbf{s}}_{2}\right)\right \mid \mid _{1}\right]\).
-
where target style codes \(\widetilde{\mathbf{s}}_{1}\) and \(\widetilde{\mathbf{s}}_{2}\) :
produced by \(F\) conditioned on two random latent codes \(\mathbf{z}_{1}\) and \(\mathbf{z}_{2}\)
-
[ d. Cycle consistency loss ]
- preserve source characteristics
-
guarantee that the genrated image \(G(x,\tilde{s})\) preserves domain invariant characteristics of its input images \(x\)
- \(\mathcal{L}_{c y c}=\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x}, y, \widetilde{y}, \mathbf{z}}\left[ \mid \mid \mathbf{x}-G(G(\mathbf{x}, \widetilde{\mathbf{s}}), \hat{\mathbf{s}}) \mid \mid _{1}\right]\).
[ e. Full Objective ]
- \(\min _{G, F, E} \max _{D} \mathcal{L}_{a d v}+\lambda_{s t y} \mathcal{L}_{s t y} -\lambda_{d s} \mathcal{L}_{d s}+\lambda_{c y c} \mathcal{L}_{c y c}\).
