Deep Walk with Softmax
# Skip-Gram # SGD # Embedding Vector
- 목표 : Karate Graph를 Input으로, 2차원의 Embedding Vector로 표현하라
1. Import Dataset
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import random
import pandas as pd
from random import shuffle
from copy import copy
%matplotlib inline
edge = pd.read_csv('karate_club.edgelist', sep=' ', names=['x','y','w'])
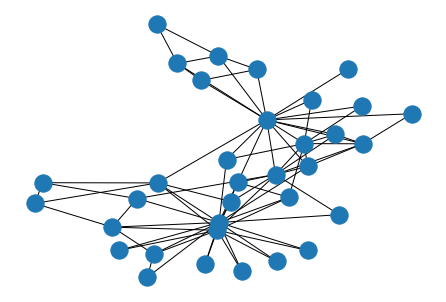
networx를 이용해서 graph를 그려보면, 다음과 같은 모양을 가진다.
graph = nx.Graph()
for i in range(edge.shape[0]):
graph.add_node(node_for_adding = edge['x'][i])
graph.add_node(node_for_adding = edge['y'][i])
graph.add_edge(edge['x'][i], edge['y'][i])
nx.draw(graph,with_label=True)
1) Adjacency Matrix
인접행렬 ( 1 : 연결, 0 : 연결X)
A = nx.to_numpy_matrix(graph, nodelist=sorted(graph.nodes()))
A
matrix([[0., 1., 1., ..., 1., 0., 0.],
[1., 0., 1., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[1., 1., 0., ..., 0., 1., 0.],
...,
[1., 0., 0., ..., 0., 1., 1.],
[0., 0., 1., ..., 1., 0., 1.],
[0., 0., 0., ..., 1., 1., 0.]])
2) Input Node Vector ( One-Hot encoded )
Input으로 들어갈 vector들 ( One-hot Encoded된 34차원의 Identity Matrix )
OH = np.identity(34)
OH
array([[1., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
...,
[0., 0., 0., ..., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 1.]])
2. Define Functions
- 1) random step
- 2) softmax
- 3) feed forward
- 4) back propagation
1). Random Walk
- take steps randomly, with length ‘w’
def random_step(i,w):
walk_list = []
walk_list.append(i)
for k in range(w):
ad = np.nonzero(A[i])[1] # i와 인접한 vertex들의 list
rand = random.choice(ad) # 그 list중 랜덤하게 하나 고르기
walk_list.append(rand)
i = rand
return walk_list
- ex) take 10 steps, starting from node index ‘3’
random_step(3,10)
[3, 12, 3, 0, 31, 33, 19, 1, 21, 0, 19]
2) Softmax
def softmax(x):
c = np.max(x)
b = x-c
exp_x = np.exp(b)
sum_exp_x = np.sum(exp_x)
y = exp_x / sum_exp_x
return y
3) Feed Forward
def feedforward(input_word,index,w1,w2):
h=np.matmul(w1.T,input_word[index])
u=np.matmul(w2.T,h)
y = softmax(u)
return h,u,y
4) Back Propagation
- update weights using backpropagation
def backprop(input_word,w1,w2,lr,h,y_pred,index,window_size):
front = input_word[index-window_size : index]
back = input_word[index+1 : index+window_size+1]
window_OH = np.concatenate([front,back])
# output -> hidden
for j in range(w2.shape[1]):
adjust = (y_pred-window_OH)[:,j].sum()*h
w2[:,j] -= -lr*adjust
# hidden -> input
adjust2 = ((y_pred-window_OH).sum(axis=0)*w2).T
w1-= lr*adjust2
return w1,w2
3. Deep Walk
- 위에서 만든 함수들을 바탕으로 Deep Walk를 구현한다.
def Deepwalk(input_word, reduced_dim, lr, walk_size, window_size,epoch):
W1 = np.random.random((input_word.shape[0],reduced_dim))
W2 = np.random.random((reduced_dim, input_word.shape[0]))
for _ in range(epoch):
input_word = copy(input_word)
shuffle(input_word)
for index in range(input_word.shape[0]):
RW = input_word[random_step(index,walk_size)]
for i in range(len(RW)):
h,u,y = feedforward(RW,i,W1,W2)
W1,W2 = backprop(RW,W1,W2,lr,h,y,i,window_size)
return W1,W2
4. Result
- reduced_dim (줄이고자 하는 목표 차원) : 2
- lr (학습률) : 0.001
- walk_size (random walk을 할때의 walk length) : 15
- window_size (참고할 양 옆의 window size) : 5
- epoch(에폭) : 5
w1,w2 = Deepwalk(OH,reduced_dim=2, lr=0.001,
walk_size=15,window_size=5,epoch=5)
