Deep Walk with Hierarchical Softmax
이전 포스트에서는 그냥 “Softmax”를 사용했었다. 하지만 이것은 output의 개수가 매우 많을 경우 비효율적일 수 있다. (자세한 내용은 xxx 참고)
따라서 이번엔 보다 효율적인 “Hierarchical Softmax”를 사용하여 Deep Walk를 구현하였다.
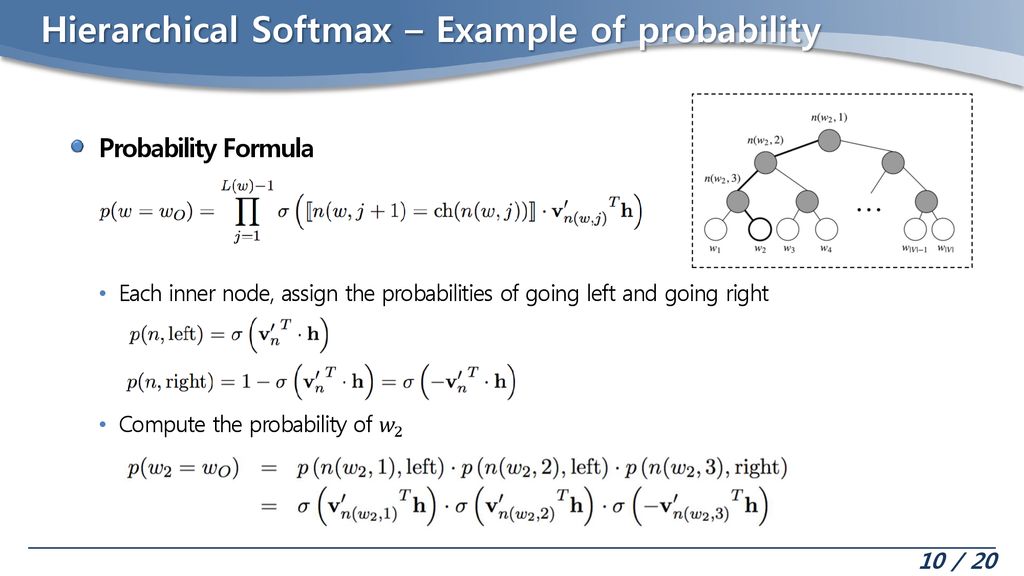
( 동일한 부분에 대한 설명은 생략한다 . xxx 참고 )
1. Import Dataset
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import random
import pandas as pd
from random import shuffle
from copy import copy
%matplotlib inline
edge = pd.read_csv('karate_club.edgelist', sep=' ', names=['x','y','w'])
graph = nx.Graph()
for i in range(edge.shape[0]):
graph.add_node(node_for_adding = edge['x'][i])
graph.add_node(node_for_adding = edge['y'][i])
graph.add_edge(edge['x'][i], edge['y'][i])
1) Adjacency Matrix
A = nx.to_numpy_matrix(graph, nodelist=sorted(graph.nodes()))
A
matrix([[0., 1., 1., ..., 1., 0., 0.],
[1., 0., 1., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[1., 1., 0., ..., 0., 1., 0.],
...,
[1., 0., 0., ..., 0., 1., 1.],
[0., 0., 1., ..., 1., 0., 1.],
[0., 0., 0., ..., 1., 1., 0.]])
2). Input Node Vector ( One-Hot encoded )
OH = np.identity(34)
OH
array([[1., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
...,
[0., 0., 0., ..., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 1.]])
2. Random Walk
def random_step(i,w):
walk_list = []
walk_list.append(i)
for k in range(w-1):
ad = np.nonzero(A[i])[1] # i와 인접한 vertex들의 list
rand = random.choice(ad) # 그 list중 랜덤하게 하나 고르기
walk_list.append(rand)
i = rand
return walk_list
random_step(3,10)
[3, 7, 0, 12, 3, 1, 21, 1, 17, 1]
3. Binary Tree for Hierarchical Softmax
- 탐색을 위한 Binary Tree(이진 분류 트리)
- 이에 대해 좀 더 자세히 알고 싶으면 https://github.com/seunghan96/datascience/tree/master/Data_Structure/2.Algorithm 를 참고 ( 자료구조 (Data Structure) )
class Node:
def __init__(self,value):
self.value = value
self.left = None
self.right = None
class BinaryTree:
def __init__(self,head):
self.head = head
self.left= None
self.right= None
def insert(self,key_val):
key = key_val[0]
self.current_node = self.head
while True:
if key < self.current_node.value[0]:
if self.current_node.left != None:
self.current_node = self.current_node.left
else :
self.current_node.left = Node(key_val)
break
else :
if self.current_node.right !=None:
self.current_node = self.current_node.right
else :
self.current_node.right = Node(key_val)
break
def path(self,key):
self.current_node = self.head
path_list = []
way_list = []
while key>1:
if key%2 ==0:
path_list.append(int(key/2))
way_list.append(1)
else :
path_list.append(int((key-1)/2))
way_list.append(-1)
key = int(key/2)
return np.flip(path_list), np.flip(way_list)
Make Nodes for 34 Words ( Total : 67 )
- 단어 개수가 N개이면, 필요한 총 node의 개수 : 2N-1개다
- 각 Node에 초기에 random하게 vector를 부여한다.
node_dicts = {}
node_k = range(1,68)
node_v = np.random.normal(0.5,0.1,(67,2))
for i in node_k:
for x in node_v:
node_dicts[i] = x
node_dicts
{1: array([0.59719917, 0.38779335]),
2: array([0.59719917, 0.38779335]),
3: array([0.59719917, 0.38779335]),
4: array([0.59719917, 0.38779335]),
5: array([0.59719917, 0.38779335]),
6: array([0.59719917, 0.38779335]),
7: array([0.59719917, 0.38779335]),
...
- 위에서 만든 node들을 바탕으로 Tree를 만든다.
head = Node(list(node_dicts.items())[0])
H_Softmax = BinaryTree(head)
V = 34
for num in range(1,2*V-1):
k_v = list(node_dicts.items())[num]
H_Softmax.insert(k_v)
4. Hierarchical Softmax
Define Functions
def sigmoid(x):
return 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
def index2key(num):
return num+34
def key2index(num):
return num-34
def ReLU(x):
return np.maximum(x,0)
DeepWalk with Hierarchical Softmax
def Deepwalk_HS(input_word,reduced_dim,window_size,walk_length,lr,epoch):
W1 = np.random.normal(0.5,0.1,(input_word.shape[0],reduced_dim))
for _ in range(epoch):
for index in range(input_word.shape[0]):
RW_ = random_step(index,walk_length)
for w in range(len(RW_)):
RW = RW_[w : w+2*window_size+1]
for i in range(len(RW)):
h = np.matmul(W1.T, input_word[RW[i]])
RW_except_i = RW[:i] + RW[i+1:]
for j in RW_except_i :
total_list = []
j = index2key(j)
for k in range(len(H_Softmax.path(j)[0])):
vector_value = node_dicts[H_Softmax.path(j)[0][k]]
vector_way = H_Softmax.path(j)[1][k]
result = np.matmul(vector_value*vector_way, h)
result2 = sigmoid(result)
total_list.append(result2)
# Output - Hidden
for k in range(len(H_Softmax.path(j)[0])-1, -1, -1):
error = (total_list[k] - ReLU(H_Softmax.path(j)[1][k]))
node_dicts[H_Softmax.path(j)[0][k]] -= lr*error*h
# Hidden - Input
total_sum = 0
for m in range(len(H_Softmax.path(j)[0])):
error = (total_list[m] - ReLU(H_Softmax.path(j)[1][m]))
v_ = node_dicts[H_Softmax.path(j)[0][m]]
total_sum += error * v_
W1[key2index(j)] -= lr*total_sum
return W1
- reduced_dim (줄이고자 하는 목표 차원) : 2
- window_size(양 옆으로 참고하고자 하는 window의 크기) : 3
- walk_length(random walk을 할 때의 walk length) : 18
- lr(학습률) : 0.01
- epoch(에폭) : 3
Deepwalk_HS(OH,2,3,18,0.01,3).round(3)
-
weight들을 보면 다음과 같다
array([[0.483, 0.6 ], [0.379, 0.49 ], [0.44 , 0.586], [0.431, 0.407], [0.516, 0.452], [0.638, 0.5 ], [0.58 , 0.475],
…
4. Result
최종적으로 embedding된 벡터
w1 = Deepwalk_HS(OH,2,3,18,0.01,3)
Emb = np.matmul(OH,w1)
