Chapter 9. Recurrent GNN
( 참고 : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JtDgmmQ60x8&list=PLGMXrbDNfqTzqxB1IGgimuhtfAhGd8lHF )
1) Recurrent vs Convolution
지금까지는, graph NN로써 “recurrent”한 방식이 아닌 “convolution” 방식을 사용했었다.
이 둘에는 어떠한 차이가 있는지, 아래 그림을 통해 살펴보자
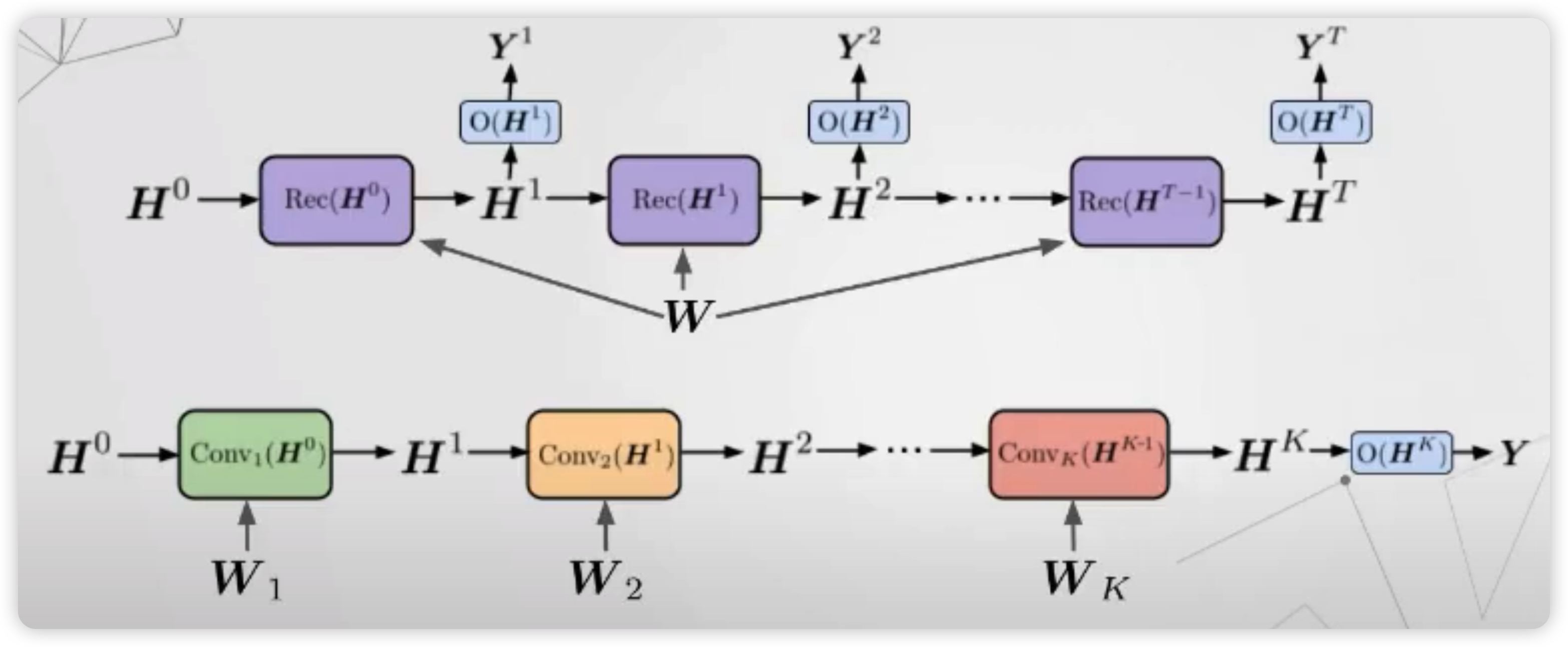
(아래 그림) Convolution
- layer마다 서로 다른 파라미터를 가진다 ( 다른 색 )
- \(K\) 개의 layer를 쌓는 다는건, 그 만큼 넓은 범위의 이웃을 보고싶음을 의미한다
(위 그림) Recurrent
-
layer마다 서로 동일한 파라미터를 가진다
-
매 timestep마다,
- (1) hidden state
- (2) output
을 동시에 내뱉는다. 이 output은, 추가적인 layer를 거쳐서 최종적인 output으로 나오게 된다.
2) GNNM (Graph Neural Network Model)
- GNN의 선구자적인 역할을 하는 모델
- diffusion mechanism 사용
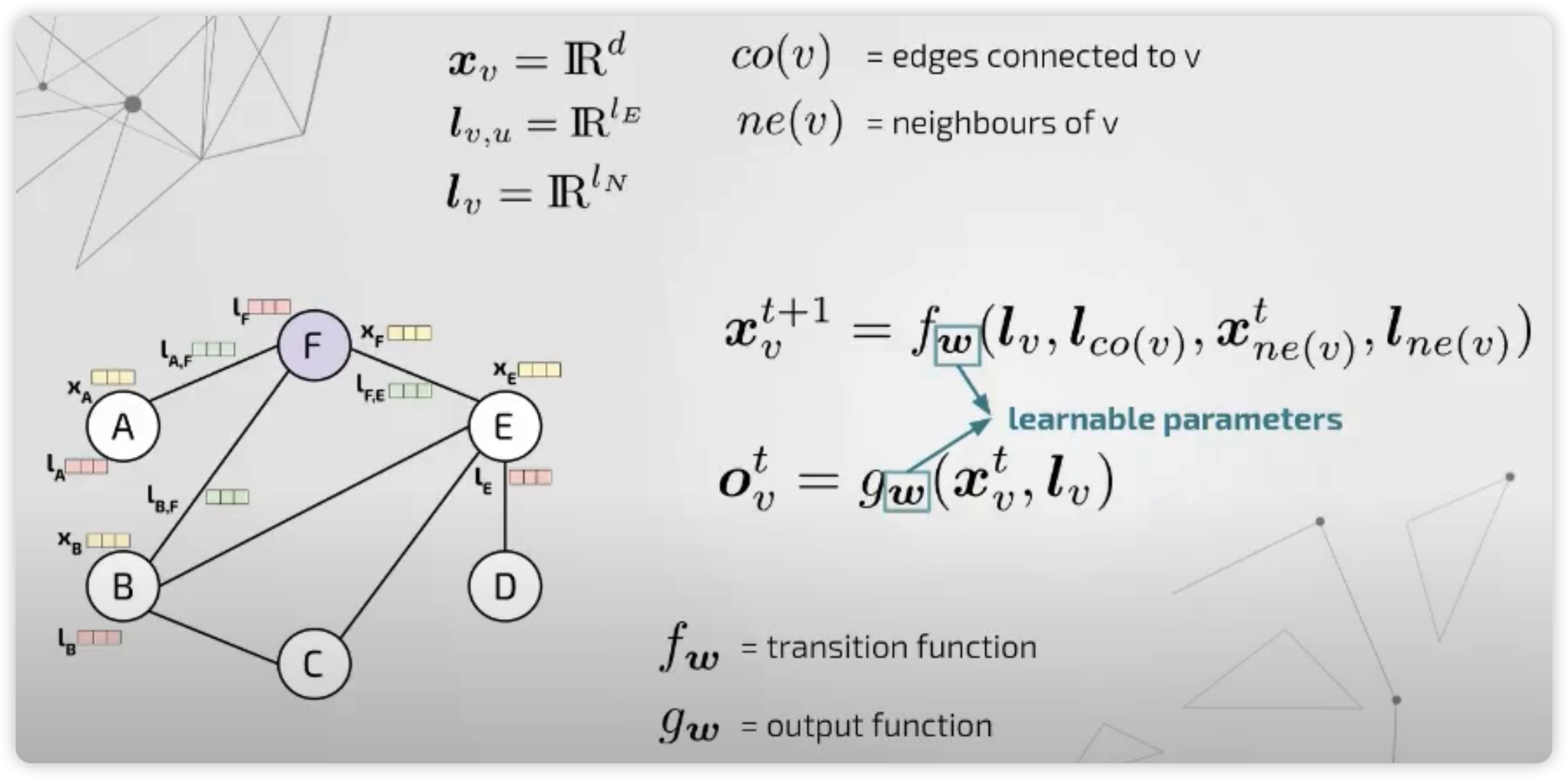
가장 general한 framework을 제시하였다.
이 모델은, 크게 2개의 함수로 구성이 된다.
- (1) transition function : 다음 step의 hidden representation을 생성하는 함수
- (2) output function : hidden representation을 인풋으로 받아, output을 생성하는 함수
이때, notation을 보면 알 수 있지만, 매 step마다 동일한 파라미터가 사용된다. \((f_w, g_w)\)
이러한 transition function을 여러 step에 걸쳐서 전달시키게 되면, 이는 일종의 “encoding network”로 볼 수 있다.
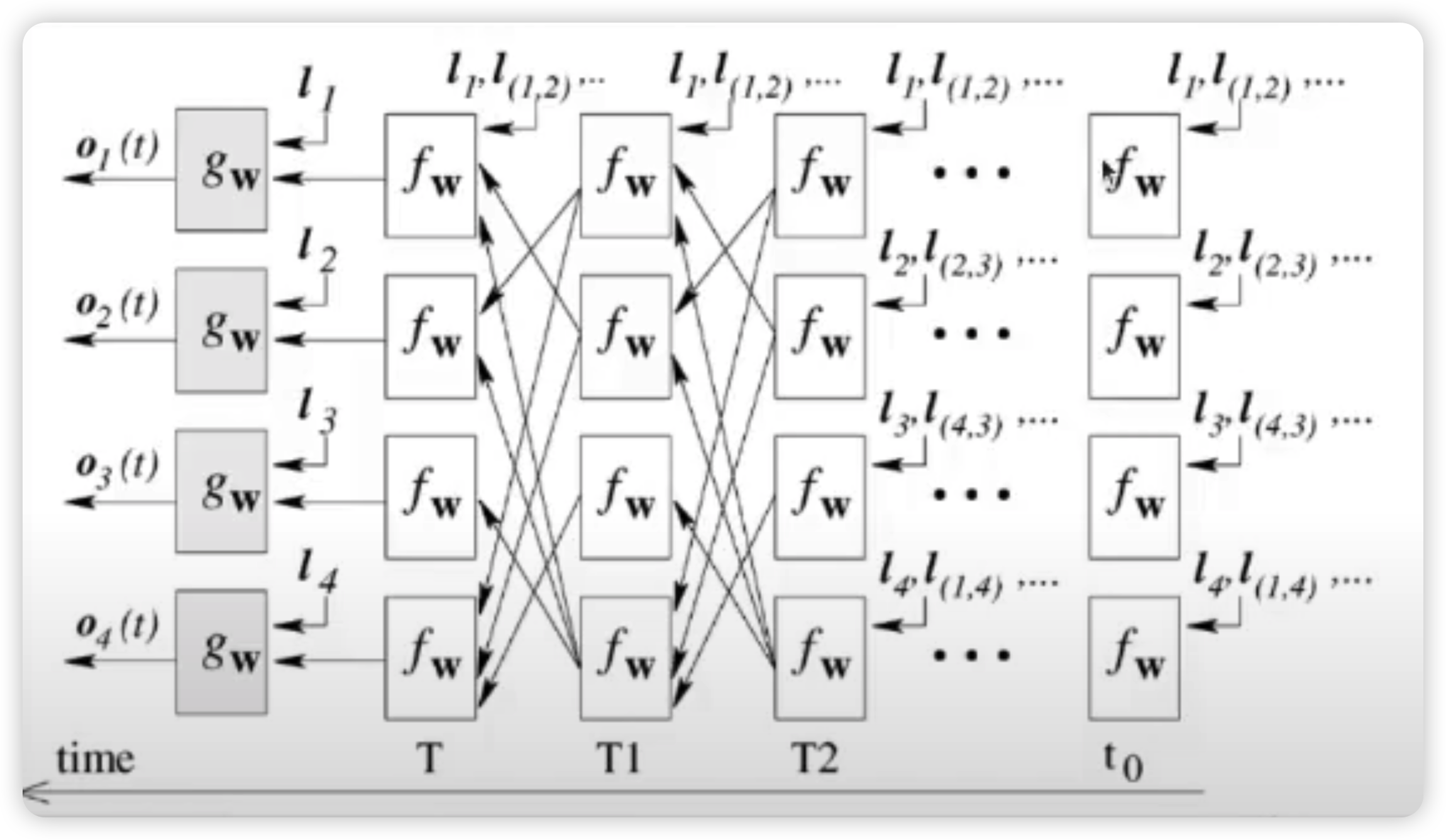
Goal : converge to a UNIQUE solution for \(\mathbf{x_v}\) & \(\mathbf{o_v}\)
이를 달성하기 위해, 아래와 같은 조건을 걸어서, 해당 조건이 만족될때까지 step을 계속 진행하게 된다.
- \(\mid \mid \boldsymbol{x}_{v}^{t+1}-\boldsymbol{x}_{v}^{t} \mid \mid <\epsilon\).
3) Gated GNN
Gated GNN은, 위의 GNNM을 적용한 알고리즘이라고 보면 된다.
핵심은, transition function으로 GRU를 사용했다는 점이다.
또한, 수렴 조건을 만족할 때까지 iterate하는 것이 아니라, 지정한 \(T\) timestep만큼 진행하게 된다.
GRU ( propagation model )
-
input : \(\mathbf{h}_{v}^{(1)}=\left[\boldsymbol{x}_{v}^{\top}, \mathbf{0}\right]^{\top}\)
( xxx과정을 거쳐서 )
-
output : \(\mathbf{h}_{v}^{(t)}=\left(1-\mathbf{z}_{v}^{t}\right) \odot \mathbf{h}_{v}^{(t-1)}+\mathbf{z}_{v}^{t} \odot \widetilde{\mathbf{h}_{v}^{(t)}}\)
위 notation에서, \(\mathbf{h}_{v}\) 는 node state를 의미하고, \(\boldsymbol{x}_{v}\) 는 (사전에 알고있는 노드에 대한 정보) node annotation을 의미한다.
가장 마지막으로, 최종 output은 위의 GRU transition function를 다 거친 뒤 나온 결과와, 노드에 대한 정보를 결합하여 산출되게 된다.
- \(\mathrm{o}_{\mathrm{v}}=\mathrm{g}\left(\mathbf{h}_{\mathrm{v}}{ }^{(\mathrm{T})}, \mathrm{x}_{\mathrm{v}}\right)\).
4) Gated Graph Sequence Network ( GGSNN )
위의 Gated GNN을 여러개 stack하여, 하나의 output이 아니라 여러 개의 sequential output을 낸 알고리즘이다.
Notation
- \(\mathcal{F}_{x}^{(k)}\) : computes \(\mathbf{X}^{(k+1)}\) from \(\mathbf{X}^{(k)}\)
- \(\mathcal{\mathcal { F }}{ }_{o}^{(k)}\) : computes \({o}^{(k)}\) from \(\mathbf{X}^{(k)}\)
( 여기서, \(\mathcal{F}(k)\)는 transition & output function 역할을 동시에 한다 )
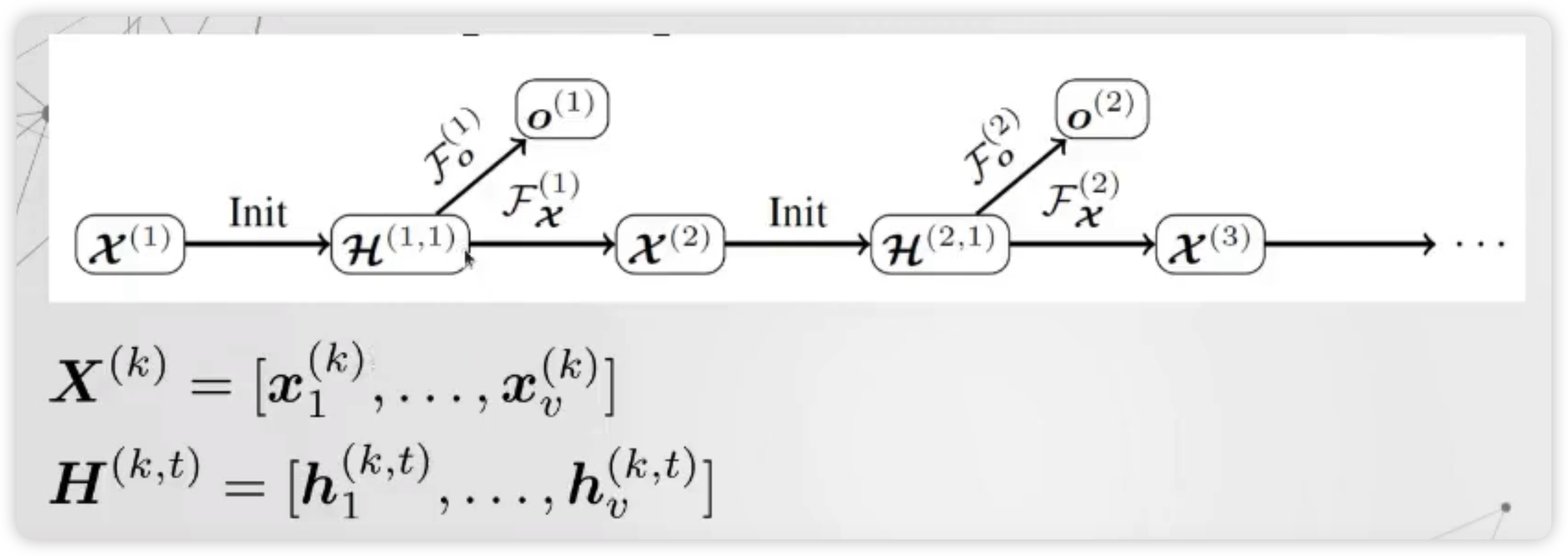
- \(k\) : length of sequence
- \(t\) : timesteps
5) 패키지 & 데이터셋 준비
import os.path as osp
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch_geometric.transforms as T
import torch_geometric
from torch_geometric.datasets import Planetoid, TUDataset
from torch_geometric.data import DataLoader
from torch_geometric.nn.inits import uniform
from torch.nn import Parameter as Param
from torch import Tensor
torch.manual_seed(42)
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
from torch_geometric.nn.conv import MessagePassing
dataset = 'Cora'
transform = T.Compose([
T.RandomNodeSplit('train_rest', num_val=500, num_test=500),
T.TargetIndegree(),
])
path = osp.join('data', dataset)
dataset = Planetoid(path, dataset, transform=transform)
data = dataset[0]
6) GNNM 코드
class GNNM(MessagePassing):
def __init__(self, n_nodes, out_channels, features_dim,
hid_dims, num_layers = 50, eps=1e-3, aggr = 'add',
bias = True, **kwargs):
super(GNNM, self).__init__(aggr=aggr, **kwargs)
self.node_states = Param(torch.zeros((n_nodes, features_dim)),
requires_grad=False)
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.eps = eps
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.transition = MLP(features_dim, hid_dims, features_dim)
self.readout = MLP(features_dim, hid_dims, out_channels)
self.reset_parameters()
print(self.transition)
print(self.readout)
def reset_parameters(self):
self.transition.reset_parameters()
self.readout.reset_parameters()
def forward(self):
edge_index = data.edge_index
edge_weight = data.edge_attr
node_states = self.node_states
for i in range(self.num_layers):
m = self.propagate(edge_index, x=node_states,
edge_weight=edge_weight,
size=None)
new_states = self.transition(m)
with torch.no_grad():
distance = torch.norm(new_states - node_states, dim=1)
convergence = distance < self.eps
node_states = new_states
if convergence.all():
break
out = self.readout(node_states)
return F.log_softmax(out, dim=-1)
def message(self, x_j, edge_weight):
return x_j if edge_weight is None else edge_weight.view(-1, 1) * x_j
def message_and_aggregate(self, adj_t, x) :
return matmul(adj_t, x, reduce=self.aggr)
def __repr__(self):
return '{}({}, num_layers={})'.format(self.__class__.__name__,
self.out_channels,
self.num_layers)
model = GNNM(data.num_nodes, dataset.num_classes, 32, [64,64,64,64,64],
eps=0.01).to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
7) Gated GNN 코드
class GatedGraphConv(MessagePassing):
def __init__(self, out_channels, num_layers,
aggr = 'add',
bias = True, **kwargs):
super(GatedGraphConv, self).__init__(aggr=aggr, **kwargs)
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.weight = Param(Tensor(num_layers, out_channels, out_channels))
self.rnn = torch.nn.GRUCell(out_channels, out_channels, bias=bias)
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
uniform(self.out_channels, self.weight)
self.rnn.reset_parameters()
def forward(self, data):
""""""
x = data.x
edge_index = data.edge_index
edge_weight = data.edge_attr
if x.size(-1) > self.out_channels:
raise ValueError('The number of input channels is not allowed to '
'be larger than the number of output channels')
if x.size(-1) < self.out_channels:
zero = x.new_zeros(x.size(0), self.out_channels - x.size(-1))
x = torch.cat([x, zero], dim=1)
for i in range(self.num_layers):
m = torch.matmul(x, self.weight[i])
m = self.propagate(edge_index, x = m,
edge_weight = edge_weight,
size=None)
x = self.rnn(m, x)
return x
def message(self, x_j, edge_weight):
return x_j if edge_weight is None else edge_weight.view(-1, 1) * x_j
def message_and_aggregate(self, adj_t, x):
return matmul(adj_t, x, reduce=self.aggr)
def __repr__(self):
return '{}({}, num_layers={})'.format(self.__class__.__name__,
self.out_channels,
self.num_layers)
class GGNN(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(GGNN, self).__init__()
self.conv = GatedGraphConv(1433, 3)
self.mlp = MLP(1433, [32,32,32], dataset.num_classes)
def forward(self):
x = self.conv(data)
x = self.mlp(x)
return F.log_softmax(x, dim=-1)
model = GGNN().to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
8) train & test 코드
def train():
model.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss_fn(model()[data.train_mask], data.y[data.train_mask]).backward()
optimizer.step()
def test():
model.eval()
logits, accs = model(), []
for _, mask in data('train_mask', 'val_mask', 'test_mask'):
pred = logits[mask].max(1)[1]
acc = pred.eq(data.y[mask]).sum().item() / mask.sum().item()
accs.append(acc)
return accs
