6. Graph Attention Networks (GATs)
GCN : treates all neighbors EQUALLY
GAT : assing DIFFERENT ATTENTION SCORE
2 varinants
- (1) GAT
- (2) GAAN
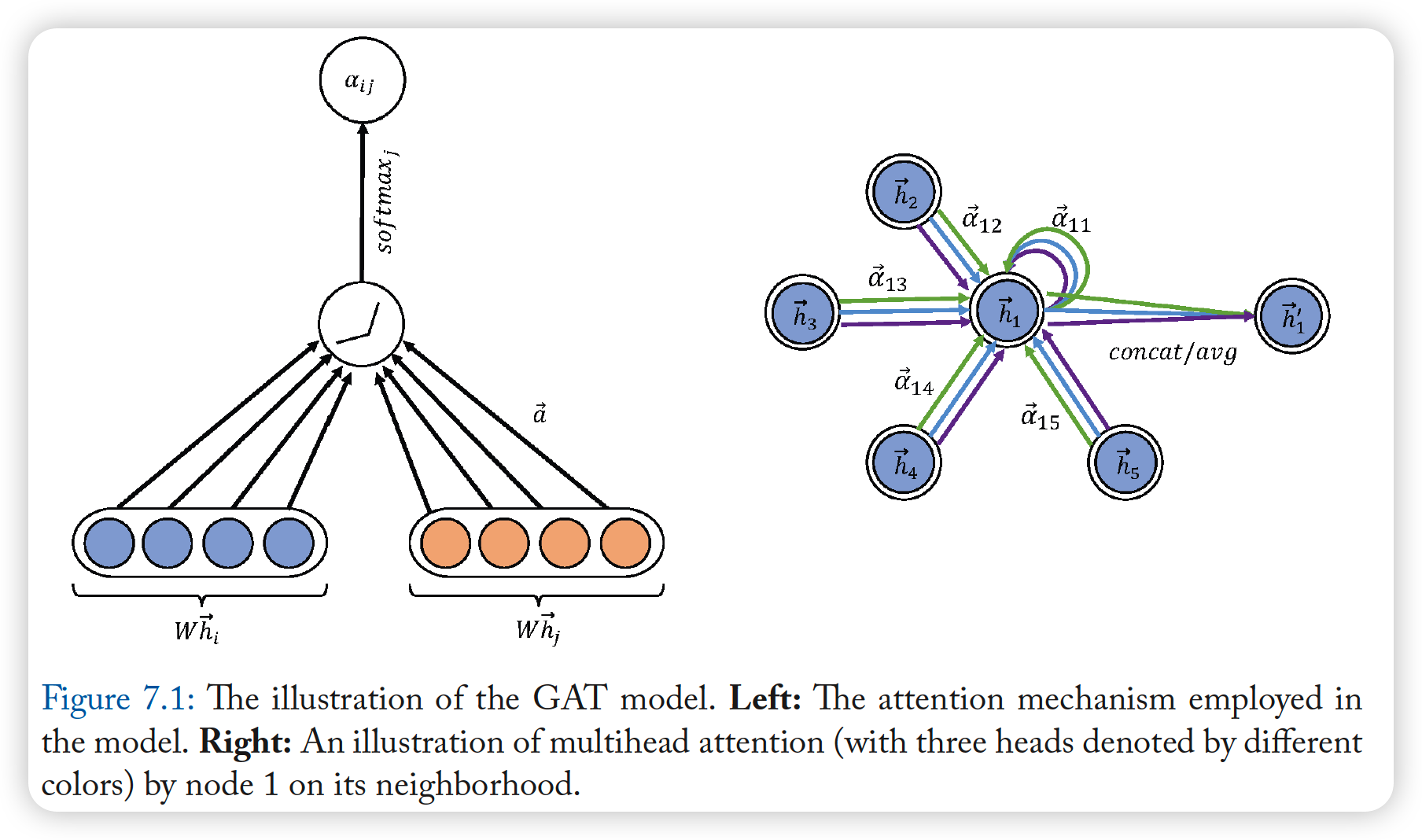
6-1. GAT
attention mechanism of node pair \((i,j)\)
- \(\alpha_{i j}=\frac{\exp \left(\operatorname{LeakyReLU}\left(\mathbf{a}^{T}\left[\mathbf{W h}_{i} \mid \mid \mathbf{W h}_{j}\right]\right)\right)}{\sum_{k \in N_{i}} \exp \left(\operatorname{LeakyReLU}\left(\mathbf{a}^{T}\left[\mathbf{W h}_{i} \mid \mid \mathbf{W h}_{k}\right]\right)\right)}\).
final output features of each node :
- \(\mathbf{h}_{i}^{\prime}=\sigma\left(\sum_{j \in N_{i}} \alpha_{i j} \mathbf{W h}_{j}\right)\).
Multi-head Attention
- apply \(K\) independent attention mechanism
Concatenate ( or Average features )
- ( concatenate )
- \(\mathbf{h}_{i}^{\prime} = \mid \mid _{k=1}^{K} \sigma\left(\sum_{j \in N_{i}} \alpha_{i j}^{k} \mathbf{W}^{k} \mathbf{h}_{j}\right)\).
- ( average )
- \(\mathbf{h}_{i}^{\prime} =\sigma\left(\frac{1}{K} \sum_{k=1}^{K} \sum_{j \in N_{i}} \alpha_{i j}^{k} \mathbf{W}^{k} \mathbf{h}_{j}\right)\).
Properties of GAT
-
(1) parallizeable ( efficient )
-
(2) can deal with nodes with different degrees
& assign correspoding weights to their neighbors
-
(3) can be applied to inductive learning problems
\(\rightarrow\) outperforms GCN!
6-2. GAAN
also uses multi-head attention
GAT vs GaAN : for computing attention coefficients…
- (1) GAT : use FC layer
- (2) GaAN : uses key-value attention & dot product attention
Assigns different weights for different heads,
by computing additional soft gate ( = gated attention aggregator )
