Multimodal Learning (3) Alignment, (4) Fusion
참고 논문 :
Baltrušaitis, Tadas, Chaitanya Ahuja, and Louis-Philippe Morency. “Multimodal machine learning: A survey and taxonomy.” IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 41.2 (2018): 423-443.
Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Multimodal Representations
- Unimodal Representation
- Multimodal Representation의 2 종류
- Joint representation 모델
- Coordinated representation 모델
- 요약
- Translation
- Example-based
- Generative approaches
- Alignment
- Explicit alignment
- Implicit alignment
- 요약
- Fusion
- Model-agnostic approaches
- Model-based approaches
- 요약
- Co-learning
- Parallel data
- Non-parallel data
- Hybrid data
- 요약
- Conclusion
4. Alignment
여러 modality 사이의 relation 파악
- ex) 이미지 & 주석이 주어졌을 때, 주석에서 말하는 대상/장소를 해당 이미지 내에서 찾기위해
두 종류의 alignments
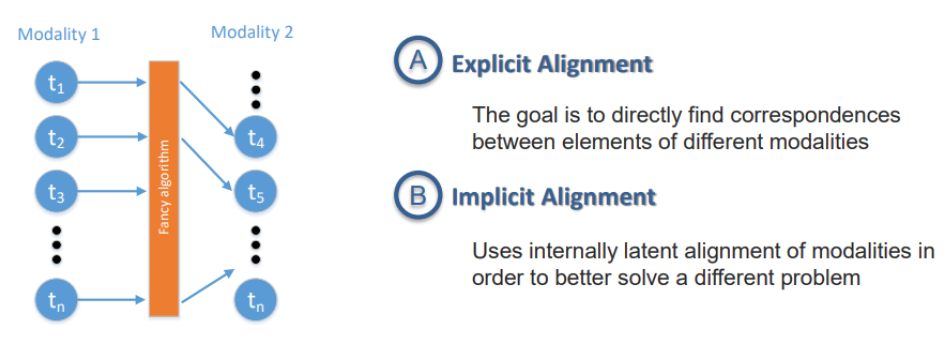
- 1) Explicit alignment
- 2) Implicit alignment
(1) Explicit alignment
목표 : aligning sub-components between modalities
- similarity metric를 잘 설정하는 것이 매우 중요!
- 2단계로 구분
- unsupervised
- (weakly) supervised
Unsupervised
-
(등장 배경) alignment for SMT(statistical machine translation), genome sequences
-
1) DTW (Dynamic Time Warpling)
-
multi-view time series에서 자주 사용
-
두 sequence 사이의 similarity를 측정 & time warping을 통해 최적의 match를 찾음
-
CCA based DTW (linear)
DCCA based DTW (non-linear)
-
-
2) graphical models
- generative graphical models
- factored HMM
- dynamic Bayesian Network
- hierarchical HMM
-
DTW & graphical model 모두 restriction 부여 가능
( ex. temporal consistency, no large jumps in time, monotonicity )
Supervised
- Unsupervised에서 영감을 많이 받음
- Deep Learning based approach
(2) Implicit alignment
목표 : 다른 task를 위한 intermediate (latent) step으로써 사용
- 다른 task : speech recognition, machine translation, …
learn how to “latently align” the data during model training
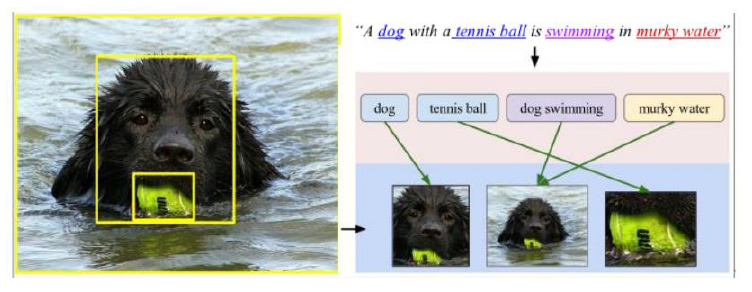
Graphical Models
- align words between languages
-
alignment of speech phonemes
- 단점 ) modalities 사이의 mapping이 manual함
Neural Networks
-
intermediate step에서 alignment이 잘 수행되면, “Translation”이 improve될 수 있음
( 만약 implicit alignment 없이 translation이 수행되었다면, encoder에 너무 큰 weight 부여해서, 단지 하나의 single vector로 제대로 summarize 못할 수도! )
-
이를 다룰 수 있는 방법이 “Attention”
- translate되어야하는 source의 부분에 보다 집중
(3) 요약
Multimodal alignment는 여러가지 어려움을 겪는다.
- 1) few datasets with explicitly annotated alignments
- 2) similarity metric design해야
- 3) multiple possible alignments & 그에 해당하는 다른 modality가 없을 수도
Earlier works : unsupervised 사용
- 1) graphical models
- 2) dynamic programming
- hand-defined measures of similarity 사용
Recent works : supervised 사용
- label training data가 많아짐에 따라!
5. Fusion
다양한 modality의 데이터를 integrate!
Then, 최종 prediction 수행!
3 main benefits
- 1) robust predictions
- 2) capture complementary information
- 3) can still operate when one of the modalities is missing
Applications
- AVSR ( audio-visual speech recognition )
-
multimodal emotion recognition
- medical image analysis…
최근 들어, multimodal representation & fusion 사이의 경계가 모호해짐!
Multimodal fusion은 크게 2가지 category로 나뉨
- 1) model-agnostic
- 2) model-based
- kernel-based
- graphical models
- neural networks
(1) Model-agnostic
세 종류로 나뉨
- 1) Early Fusion
- 2) Late Fusion
- 3) Hybrid Fusion
Early Fusion
-
feature extraction이후 바로 integrate!
- low level feature들 간의 correlation/interaction을 장바냄
- 미리 앞단계에서 integration한 뒤 진행하기 때문에, single model! 더 simple한 pipeline
Late Fusion
- 각 modality에서 decision을 다 내린 뒤 integrate!
- ex) averaging, voting schemes, weighting based on channel noise, signal variance
- 특정 modality가 missing 해도 OK
- 다만, low level interaction을 못잡아낸다는 단점도!
Hybrid Fusion
- early fusion과 각각 unimodal predictors의 output을 combine!
(2) Model-based approaches
앞서 다룬 model-agnostic approach는 unimodal 방법을 사용하여 쉽게 구현할 수 있으나, 이들은 본질적으로 “multimodal data를 다루기 위한 방법”은 아니다.
Multimodal fusion을 목적으로 제안된 방법들은, 아래와 같이 나뉠 수 있다!
- 1) Multiple kernel learning (MKL)
- 2) Graphical models
- 3) Neural networks
Multiple kernel learning (MKL)
SVM 사용 ( 다른 modality에 다른 kernel 사용 )
장점
- kernel selection에 flexiblity O
- loss function은 convex
- regression/classification에 모두 사용 가능
단점
- slow inference & large memory footprint
Graphical models
크게 두 종류로 나뉨
- 1) generative model : modeling “joint probability” ( \(P(X)\) or \(P(X,Y)\))
- 2) discriminative : modeling “conditional probability” ( \(P(Y \mid X)\) )
장점
- spatial & temporal structure 잘 잡아냄
- human expert knowledge 사용 가능
Neural networks
다양한 분야에서 사용
- visual & media question answering
- gesture recognition
- affet analysis
- video description generation
Temporal data도 다룸 ( by RNNs, LSTMs )
장점
- 방대한 양의 데이터로부터 학습 가능
- end-to-end training
- 좋은 성능
단점
- 해석력 (interpretability) 떨어짐
- 방대한 양의 데이터가 필요
(3) 요약
최근들어 NN이 multimodal fusion에 자주 사용된다.
( 하지만 kernel learning & graphical model들도 사용되고 있긴 함…..데이터가 부족한 상황에서 )
Multimodal fusion의 challenges
-
1) signals might not be tempraolly aligned
( dense continuous signal & sparse event )
-
2) supplementary & complementary information을 모두 뽑아내기 쉽지 않아
-
3) 각각의 modality가 서로 다른 시점/level에서 다른 형태의 noise를 가질 수 있음